Ownership Structure
The following diagram illustrates the ownership structure of ROCH, ParentCo, Merger Sub LLC, Merger Sub Corp and PCT prior to the Business Combination and then after the Business Combination.
Prior to the Business Combination
As filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission on November 30, 2020
Registration No. 333-
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM S-1
REGISTRATION STATEMENT UNDER THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
ROTH CH ACQUISITION I CO. PARENT CORP.*
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in its Charter)
| Delaware | 5093 | 83-3584792 | ||
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(Primary Standard Industrial Classification Code Number) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
888 San Clemente Drive, Suite 400
Newport Beach, CA 92660
(949) 720-5700
(Address, Including Zip Code, and Telephone Number, Including Area Code, of Registrant’s Principal Executive Offices)
Gordon Roth
Roth CH Acquisition I Co.
888 San Clemente Drive, Suite 400
Newport Beach, CA 92660
(949) 720-5700
(Name, Address, Including Zip Code, and Telephone Number, Including Area Code, of Agent for Service)
Copies to:
|
Mitchell Nussbaum, Esq. Norwood P. Beveridge, Esq. Loeb & Loeb LLP 345 Park Avenue New York, NY 10154 Phone: (212) 407-4000 |
Joel T. May, Esq. Patrick S. Baldwin, Esq. Jones Day 1420 Peachtree Street, N.E., Suite 800 Atlanta, Georgia 30309 Tel: (404) 581-8967 |
Approximate date of commencement of proposed
sale to public:
From time to time after the effective date hereof.
If any of the securities being registered on this Form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, check the following box. ☒
If this Form is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer ☐ | Accelerated filer ☐ | |||||
| Non-accelerated filer ☒ | Smaller reporting company ☒ | |||||
| Emerging growth company ☒ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act. ☐
CALCULATION OF REGISTRATION FEE
| Title of Each Class of Security Being Registered(1) | Amount Being Registered(2) |
Proposed Maximum Offering Price Per Security |
Proposed Maximum Aggregate Offering Price |
Amount of Registration Fee |
||||||||||
| Shares of Common Stock, $.001 par value (“Common Stock”) | 25,000,000 | $ | 10.45(3) | $ | 261,250,000(2) | $ | 28,502.38 | |||||||
| (1) | All securities being registered will be issued by Roth CH Acquisition I Co. Parent Corp. (“ParentCo”), a Delaware corporation and wholly-owned subsidiary of Roth CH Acquisition I Co., a Delaware corporation (“ROCH”), in connection with ROCH’s previously announced initial business combination (the “Business Combination”) with ParentCo, Roth CH Merger Sub LLC (“Merger Sub LLC”), Roth CH Merger Sub Corp. (“Merger Sub Corp”) and PureCycle Technologies LLC (“PCT”), pursuant to which ParentCo will issue the shares of ParentCo Common Stock registered hereunder to certain institutions and accredited investors of ROCH in exchange for shares of ROCH common stock purchased by such investors in a transaction exempt from the registration requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”). |
| (2) | Pursuant to Rule 416 under the Securities Act, the registrant is also registering an indeterminate number of additional shares of common stock that may become issuable as a result of any stock dividend, stock split, recapitalization or other similar transaction. |
| (3) | Pursuant to Rule 457(c) under the Securities Act, and solely for the purpose of calculating the registration fee, the proposed maximum offering price is $10.45, which is the average of the high and low prices of shares of ROCH common stock on the Nasdaq Capital Market on November 23, 2020 (such date being within five business days of the date that this registration statement was filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”)). |
* Upon the closing of the Business Combination, the name of ParentCo is expected to change to PureCycle Technologies, Inc.
The registrant hereby amends this registration statement on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its effective date until the registrant shall file a further amendment which specifically states that this registration statement shall thereafter become effective in accordance with Section 8(a) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or until the registration statement shall become effective on such date as the Commission, acting pursuant to Section 8(a), may determine.
EXPLANATORY NOTE
This registration statement registers the resale of securities to be issued in a private placement in connection with the consummation of the proposed business combination (the “Business Combination”) by and among Roth CH Acquisition I Co. (“ROCH”), Roth CH Acquisition I Co. Parent Corp. (“we,” “us,” “our” or “ParentCo”), a wholly owned subsidiary of ROCH, Roth CH Merger Sub LLC (“Merger Sub LLC”), Roth CH Merger Sub Corp. (“Merger Sub Corp”) and PureCycle Technologies LLC (“PCT”). The shares of ParentCo common stock covered by this registration statement will not be entitled to vote at the special meeting of ROCH’s stockholders to be held to approve the Business Combination, and will not receive any proceeds from the trust account established in connection with ROCH’s initial public offering in the event ROCH does not consummate an initial business combination by the deadline in its amended and restated certificate of incorporation.
The information contained in this preliminary prospectus is not complete and may be changed. These securities may not be sold until the registration statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission is effective. This preliminary prospectus is not an offer to sell these securities and it is not soliciting an offer to buy these securities in any state where the offer or sale is not permitted.
| PRELIMINARY PROSPECTUS | SUBJECT TO COMPLETION | DATED NOVEMBER 30, 2020 |
ROTH CH ACQUISITION I CO. PARENT CORP.
25,000,000 Shares
Common Stock
This prospectus relates to the resale from time to time of certain shares of common stock to be issued pursuant to the terms of those certain subscription agreements entered into (the “PIPE Investment”) in connection with the proposed business combination (the “Business Combination”) by and among Roth CH Acquisition I Co. (“ROCH”), Roth CH Acquisition I Co. Parent Corp. (“we,” “us,” “our,” or “ParentCo”), a wholly owned subsidiary of ROCH, Roth CH Merger Sub LLC (“Merger Sub LLC”), Roth CH Merger Sub Corp. (“Merger Sub Corp”) and PureCycle Technologies LLC (“PCT”) pursuant to the Agreement and Plan of Merger dated as of November 16, 2020, as amended from time to time (the “Merger Agreement”).
In connection with the Business Combination, Merger Sub Corp will merge with and into ROCH (the “RH Merger”), with ROCH surviving the RH Merger as a wholly-owned subsidiary of ParentCo (the “ROCH Surviving Company”); simultaneously with the RH Merger, Merger Sub LLC will merge with and into PCT (the “PCT Merger”), with PCT surviving the PCT Merger as a wholly-owned subsidiary of ParentCo (the “Surviving Company”); following the PCT Merger, ParentCo will contribute to the Surviving Company the proceeds of the PIPE Investment, other than the par value of the ROCH common stock which will have been disbursed to ROCH, and, within two days following the closing of the Business Combination, ROCH Surviving Company will acquire, and ParentCo will contribute to ROCH Surviving Company all of the common units of the Surviving Company directly held by ParentCo after the PCT Merger (the “ParentCo Contribution”), such that, following the ParentCo Contribution, Surviving Company shall be a wholly-owned subsidiary of the ROCH Surviving Company.
Upon closing of the Business Combination, the name of ParentCo is expected to change to PureCycle Technologies, Inc. In connection with the closing of the Business Combination, the currently issued and outstanding shares of ROCH’s common stock, par value $0.0001 per share (“Common Stock”), will be exchanged, on a one-for-one basis, for shares of ParentCo common stock, par value $0.001 per share (“ParentCo Common Stock”). Accordingly, all references in this prospectus to “ParentCo Common Stock” refer to shares of ParentCo Common Stock, which will be issued at the closing of the Business Combination in exchange for all issued and outstanding shares of Common Stock of ROCH.
As described herein, the selling securityholders named in this prospectus or their permitted transferees (collectively, the “Selling Stockholders”), may sell from time to time up to 25,000,000 shares of ParentCo Common Stock that will be issued to certain institutions and accredited investors in connection with the closing of the PIPE Investment and Business Combination.
We will bear all costs, expenses and fees in connection with the registration of the ParentCo Common Stock and will not receive any proceeds from the sale of the ParentCo Common Stock. The Selling Stockholders will bear all commissions and discounts, if any, attributable to their respective sales of the ParentCo Common Stock.
Upon the consummation of the Business Combination, ParentCo’s Common Stock, warrants and units are expected to trade on the Nasdaq Capital Market (“Nasdaq”) under the proposed symbols “PCT,” “PCTTW” and “PCTTU,” respectively.
We are an “emerging growth company” as defined under the U.S. federal securities laws and, as such, have elected to comply with certain reduced public company reporting requirements.
Investing in our common stock is highly speculative and involves a high degree of risk. See “Risk Factors” beginning on page 23.
Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved of these securities or determined if this prospectus is truthful or complete. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
The date of this prospectus is , 2021
Table of Contents
You should rely only on the information contained in this prospectus. We have not authorized any other person to provide you with information different from or in addition to that contained in this prospectus. If anyone provides you with different or inconsistent information, you should not rely on it. We are not making an offer to sell these securities in any jurisdiction where an offer or sale is not permitted. You should assume that the information appearing in this prospectus is accurate only as of the date on the front cover of this prospectus. Our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects may have changed since that date.
In this prospectus, we rely on and refer to information and statistics regarding our industry. We obtained this statistical, market and other industry data and forecasts from publicly available information. While we believe that the statistical data, market data and other industry data and forecasts are reliable, we have not independently verified the data.
Unless otherwise stated in this prospectus, the terms, “we,” “us” or “our” refer to Roth CH Acquisition I Co., a Delaware corporation, prior to the consummation of the Business Combination and Roth CH Acquisition I Co. Parent Corp., a Delaware corporation to be renamed PureCycle Technologies, Inc., from and after the consummation of the Business Combination. Further, in this document:
• “Authority” means the Southern Ohio Port Authority, the issuer of the Revenue Bonds.
• “Board” means the board of directors of ROCH.
• “Business Combination” means the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement.
• “Certificate of Incorporation” means ROCH’s Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation.
• “Closing Date” means date of the consummation of the Business Combination.
• “Code” means the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended.
• “Combined Company” means ParentCo and its consolidated subsidiaries after the Business Combination.
• “Common Stock” means the shares of common stock, par value $0.0001 per share, of ROCH.
• “Continental” means Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company, ROCH’s transfer agent.
• “Convertible Notes” means the up to $60.0 million in aggregate principal amount of PCT’s 5.875% Convertible Senior Secured Notes due 2022.
• “Effective Time” means the time at which the Business Combination becomes effective.
• “Equity Plan” means the PureCycle Technologies, Inc. 2021 Equity and Incentive Compensation Plan.
• “Exchange Act” means the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
• “First Tranche Notes” means the $48.0 million in aggregate principal amount of Convertible Notes issued on October 7, 2020.
• “GAAP” means accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
• “Guarantor Liquidity Account” means the liquidity reserve held by U.S. Bank, as Escrow Agent, under an Escrow Agreement dated October 7, 2020 in connection with the Guaranty.
• “Guarantor Liquidity Reserve Amount” means the $50 million to be fully funded by PCT into the Guarantor Liquidity Account by January 31, 2021.
• “Guaranty” means that certain Guaranty of Completion, dated as of October 7, 2020, by and between PCT and UMB Bank, N.A., entered into in connection with the Revenue Bonds.
• “Initial Stockholders” means the officers and directors of ROCH and certain other stockholders who acquired shares of ROCH prior to the IPO.
2
• “IPO” refers to the initial public offering of 7,500,000 ROCH Units consummated on May 7, 2020 and includes the partial exercise of the underwriters’ over- allotment option in connection therewith.
• “Loan Agreement” means that certain Loan Agreement, dated as of October 1, 2020, by and between the Authority and Purecycle Ohio, entered into in connection with the Revenue Bonds.
• “Magnetar Guarantors” means the Combined Company and each subsidiary of the Combined Company that is a direct or indirect parent of PCT.
• “Magnetar Indenture” means that certain indenture, dated as of October 7, 2020, by and between PCT and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee and collateral agent pursuant to which the Convertible Notes were issued.
• “Magnetar Investors” means certain funds managed by Magnetar Capital LLC or its affiliates that purchased the Convertible Notes.
• “Magnetar Registration Rights Agreement” means that certain Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of October 28, 2020, by and between PCT and the Magnetar Investors entered into in connection with the Convertible Notes.
• “Merger Agreement” means that certain Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of November 16, 2020, by and among ParentCo, ROCH, Merger Sub LLC, Merger Sub Corp and PCT, as may be amended.
• “Merger Sub Corp” means Roth CH Merger Sub Corp., a Delaware corporation and wholly-owned subsidiary of ParentCo.
• “Merger Sub LLC” means Roth CH Merger Sub LLC, a Delaware limited liability company of which ParentCo is the sole member.
• “Note Purchase Agreement” means that certain Note Purchase Agreement, dated as of October 6, 2020, by and among PCT and the Magnetar Investors, entered into in connection with the Convertible Notes.
• “Organizational Documents” means certificate of incorporation and bylaws.
• “ParentCo” means Roth CH Acquisition I Co. Parent Corp., a Delaware corporation and wholly-owned subsidiary of ROCH, prior to the consummation of the Business Combination.
• “PCT” means PureCycle Technologies LLC, a Delaware limited liability company.
• “PCT Units” means, collectively, the Class A Units, Class B preferred Units, Class B-1 preferred Units and Class C Units of PCT.
• “PCT Unitholders” means the current holders of PCT Units.
• “Phase I Facility,” “Feedstock Evaluation Unit,” and “FEU” each refer to the pilot line which PCT uses to screen potential feedstock sources.
• “Phase II Facility” and “Plant 1” each refer to PCT’s first commercial-scale plant in Ironton, Ohio.
• “PIPE Investment” means the purchase by certain institutions and accredited investors of 25,000,000 shares of Common Stock, which will be exchanged for shares of ParentCo Common Stock in the Business Combination, for an aggregate of $250,000,000 in a private placement intended to close immediately prior to the closing of the Business Combination.
• “Private Shares” means the shares of Common Stock underlying the ROCH Units issued in a private placement.
3
• “Private Units” means the 265,500 units of ROCH sold to the Initial Stockholders upon consummation of the IPO, consisting of one Private Share and three quarters of one Private Warrant to purchase a share of Common Stock at an exercise price of $11.50.
• “Private Warrant” means a warrant underlying the Private Units to purchase one Private Share at an exercise price of $11.50 in a private placement transaction.
• “Project” refers to the Phase I Facility and Phase II Facility together.
• “Project site” refers to the location of the Project.
• “Proxy Statement/Prospectus” refers to the proxy statement/prospectus sent to holders of Common Stock in connection with the Special Meeting.
• “Public Shares” means the registered shares of Common Stock underlying the ROCH Units sold in the IPO.
• “Public Stockholders” means holders of Public Shares.
• “Public Warrant” means a registered warrant to purchase a share of Common Stock at an exercise price of $11.50.
• “Purecycle Ohio” means Purecycle: Ohio LLC, a Delaware limited liability company and an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of PCT.
• “Revenue Bonds” means, collectively, the Series 2020A Bonds, Series 2020B Bonds, and Series 2020C Bonds.
• “Revenue Bonds Trustee” means UMB Bank, N.A., as trustee under the indenture relating to the Revenue Bonds.
• “ROCH Units” means the 7,650,000 registered units sold by ROCH in connection with its IPO and the partial exercise of the underwriters’ over-allotment option, consisting of one Public Share and three quarters of one Public Warrant to purchase a share of Common Stock at an exercise price of $11.50.
• “SEC” means the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission.
• “Second Tranche Notes” means the additional $12.0 million of aggregate principal amount of Convertible Notes to be issued to the Magnetar Investors within 45 days after the entry into the Merger Agreement, subject to the satisfaction of customary closing conditions.
• “Securities Act” means the Securities Act of 1933, as amended.
• “Series 2020A Bonds” or “the Senior Bonds” means the tax-exempt senior secured bonds in the aggregate principal amount of $219.6 million.
• “Series 2020B Bonds” or “the Tax-Exempt Subordinate Bonds” means the tax-exempt subordinate secured bonds in the aggregate principal amount of $20.0 million.
• “Series 2020C Bonds” or “the Taxable Subordinate Bonds” means the taxable subordinate secured bonds in the aggregate principal amount of $10.0 million.
• “sinking fund redemption amounts” means periodic payments reflecting the Authority’s obligation to mandatorily redeem a portion of the Revenue Bonds from time to time.
• “Special Meeting” means the special meeting of the stockholders of ROCH held on , 2021, at which the stockholders of ROCH, among other things, voted to approve the Business Combination.
• “Trust Account” means the trust account of ROCH that holds the proceeds of the IPO in accordance with that certain Investment Management Trust Agreement between Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company and ROCH.
4
cautionary statement on forward-looking statements
This prospectus contains forward-looking statements, including statements about the parties’ ability to close the Business Combination, the anticipated benefits of the Business Combination, and the financial condition, results of operations, earnings outlook and prospects of ROCH, ParentCo and/or PCT and may include statements for the period following the consummation of the Business Combination. Forward- looking statements appear in a number of places in this prospectus, including, without limitation, in the sections entitled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and “Description of PCT Business.” In addition, any statements that refer to projections, forecasts or other characterizations of future events or circumstances, including any underlying assumptions, are forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements are typically identified by words such as “plan,” “believe,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “outlook,” “estimate,” “forecast,” “project,” “continue,” “could,” “may,” “might,” “possible,” “potential,” “predict,” “should,” “would” and other similar words and expressions, but the absence of these words does not mean that a statement is not forward-looking.
The forward-looking statements are based on the current expectations of the management of ROCH, ParentCo and PCT as applicable and are inherently subject to uncertainties and changes in circumstances and their potential effects and speak only as of the date of such statement. There can be no assurance that future developments will be those that have been anticipated. These forward-looking statements involve a number of risks, uncertainties or other assumptions that may cause actual results or performance to be materially different from those expressed or implied by these forward-looking statements. These risks and uncertainties include, but are not limited to, those factors described in “Risk Factors,” those discussed and identified in public filings made with the SEC by ROCH and ParentCo and the following:
| • | PCT's ability to meet, and to continue to meet, applicable regulatory requirements for the use of PCT’s UPRP in food grade applications; |
| • | PCT's ability to comply on an ongoing basis with the numerous regulatory requirements applicable to the UPRP and PCT’s facilities; |
| • | expectations regarding PCT’s strategies and future financial performance, including its future business plans, expansion plans or objectives, prospective performance and opportunities and competitors, revenues, products and services, pricing, operating expenses, market trends, liquidity, cash flows and uses of cash, capital expenditures, and PCT’s ability to invest in growth initiatives; |
| • | PCT’s ability to scale and build Plant 1 in a timely and cost-effective manner; |
| • | the implementation, market acceptance and success of PCT’s business model and growth strategy; |
| • | the success or profitability of PCT’s offtake arrangements; |
| • | PCT’s future capital requirements and sources and uses of cash; |
| • | PCT’s ability to obtain funding for its operations and future growth; |
| • | developments and projections relating to PCT’s competitors and industry; |
| • | the occurrence of any event, change or other circumstances that could give rise to the termination of the Merger Agreement; |
| • | the outcome of any legal proceedings that may be instituted against ROCH or PCT following announcement of the Merger Agreement and the transactions contemplated therein; |
| • | the inability to complete the Business Combination; |
5
| • | the risk that the announcement and consummation of the proposed Business Combination disrupts PCT’s current plans; |
| • | the ability to recognize the anticipated benefits of the Business Combination; |
| • | unexpected costs related to the proposed Business Combination; |
| • | limited liquidity and trading of ROCH’s securities; |
| • | geopolitical risk and changes in applicable laws or regulations; |
| • | the possibility that ROCH and/or PCT may be adversely affected by other economic, business, and/or competitive factors; |
| • | operational risk; |
| • | risk that the COVID-19 pandemic, and local, state, and federal responses to addressing the pandemic may have an adverse effect on ROCH’s or PCT’s business operations, as well as ROCH’s or PCT’s financial condition and results of operations; and |
| • | the risks that the consummation of the Business Combination is substantially delayed or does not occur. |
Should one or more of these risks or uncertainties materialize or should any of the assumptions made by the management of ROCH and PCT prove incorrect, actual results may vary in material respects from those projected in these forward-looking statements.
All subsequent written and oral forward-looking statements concerning the Business Combination or other matters addressed in this prospectus and attributable to ROCH, PCT or any person acting on their behalf are expressly qualified in their entirety by the cautionary statements contained or referred to in this proxy statement. Except to the extent required by applicable law or regulation, ROCH and PCT undertake no obligation to update these forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances after the date of this prospectus or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events.
6
This summary highlights information related to the Business Combination and the business of PCT appearing elsewhere in this prospectus. Because it is only a summary, it does not contain all of the information that you should consider before investing in shares of ParentCo Common Stock and it is qualified in its entirety by, and should be read in conjunction with, the more detailed information appearing elsewhere in this prospectus. Before you decide to invest in ParentCo Common Stock, you should read the entire prospectus carefully, including “Risk Factors” beginning on page 23 and the financial statements and related notes included in this prospectus.
This prospectus includes trademarks, service marks and trade names owned by us or other companies. All trademarks, service marks and trade names included in this prospectus are the property of their respective owners.
The Parties to the Business Combination
Roth CH Acquisition I Co.
Roth CH Acquisition I Co., or ROCH, is a blank check company incorporated in Delaware and formed for the purpose of entering into a merger, share exchange, asset acquisition, stock purchase, recapitalization, reorganization or other similar business combination with one or more businesses or entities. Although ROCH is not limited to a particular industry or geographic region for purposes of consummating an initial business combination, ROCH focused its search on businesses that have their primary operations in the business services, consumer, healthcare, technology or wellness sectors.
ROCH’s units, common stock, and warrants trade on NASDAQ under the symbols “ROCH.U,” “ROCH” and “ROCH.W,” respectively. At the Closing, the outstanding shares of ROCH Common Stock will be exchanged for shares of ParentCo Common Stock.
The mailing address of ROCH’s principal executive office is 888 San Clemente Drive, Suite 400, Newport Beach, CA 92660, and its telephone number is 949-720-5700.
PureCycle Technologies LLC
PureCycle Technologies LLC, or PCT, is commercializing a patented purification recycling technology (the “Technology”), originally developed by The Procter & Gamble Company (“P&G”), for restoring waste polypropylene into resin with near-virgin characteristics. PCT refers to this resin as ultra-pure recycled polypropylene (“UPRP”), which has nearly identical properties and applicability for reuse as virgin polypropylene. PCT has a global license for the technology from P&G. PCT intends to build its first commercial-scale plant in Ironton, Ohio (referred to herein as “Plant 1” or the “Phase II Facility”), which is expected to have nameplate capacity of approximately 107 million pounds/year when fully operational. Production is expected to commence in late 2022 and the plant is expected to be fully operational in 2023. PCT has secured and contracted all of the feedstock and product offtake for this initial plant. PCT’s goal is to create an important new segment of the global polypropylene market that will assist multinational entities in meeting their sustainability goals, provide consumers with polypropylene-based products that are sustainable, and reduce overall polypropylene waste in the world’s landfills and oceans.
The mailing address of PCT’s principal executive office is 5950 Hazeltine National Drive, Suite 650, Orlando, Florida 32822, and its telephone number is 877-648-3565.
Roth CH Acquisition I Co. Parent Corp.
Roth CH Acquisition I Co. Parent Corp., or ParentCo, is a Delaware corporation that was incorporated on October 16, 2020 to facilitate the Business Combination. To date, ParentCo has not conducted any material activities other than those incident to its formation. Other than 100 shares of common stock held by ROCH, there are no shares of ParentCo common stock, ParentCo warrants or ParentCo units currently outstanding. ParentCo is applying to have its common stock, warrants and units listed on NASDAQ under the symbols PCT, PCTTW and PCTTU, respectively.
7
The mailing address of ParentCo’s principal executive office is 888 San Clemente Drive, Suite 400, Newport Beach, CA 92660, and its telephone number is (949) 720-5700.
The Special Meeting
A Special Meeting of stockholders of ROCH was held at 10:00 a.m., Eastern standard time, on , 2021 to approve the Business Combination and related matters (collectively, the “Proposals”). At the Special Meeting of stockholders of ROCH, the ROCH stockholders .
Terms of the Business Combination
The Business Combination will be structured as a “double dummy” transaction, pursuant to which:
| (a) | Each of ParentCo, Merger Sub Corp and Merger Sub LLC are newly formed entities that were formed for the sole purpose of entering into and consummating the transactions set forth in the Merger Agreement. ParentCo is a wholly-owned direct subsidiary of ROCH and both Merger Sub LLC and Merger Sub Corp are wholly-owned direct subsidiaries of ParentCo. |
| (b) | At Closing, each of the following transactions will occur in the following order: (i) ParentCo will complete the RH Merger, with ROCH surviving the RH Merger as a wholly-owned subsidiary of ParentCo (the “ROCH Surviving Company”); (ii) simultaneously with the RH Merger, ParentCo will complete the PCT Merger with PCT surviving the PCT Merger as a wholly-owned subsidiary of ParentCo (the “Surviving Company”); and (iii) following the PCT Merger, ParentCo will contribute to the Surviving Company the proceeds of the PIPE Investment, other than the par value of the Common Stock, which will have been disbursed to ROCH, and, within two days following the Closing, ROCH Surviving Company will acquire, and ParentCo will contribute to ROCH Surviving Company (the “ParentCo Contribution”) all common units of the Surviving Company directly held by ParentCo after the PCT Merger, such that, following the ParentCo Contribution, Surviving Company shall be a wholly-owned subsidiary of the ROCH Surviving Company. |
The Aggregate Consideration payable to the members of PCT in connection with the Business Combination consists of the Closing Share Consideration, the Contingency Consideration and the assumption of all indebtedness of PCT as of the Closing Date (the “Assumed Indebtedness”), including indebtedness related to (a) the Revenue Bonds and (b) the Convertible Notes and other indebtedness used to fund the construction of an industrial process facility in Ironton, Ohio (collectively, the “Construction Indebtedness”).
(a) The Closing Share Consideration
The Closing Share Consideration for PCT Unitholders is the number of shares of ParentCo Common Stock, par value $0.001 per share equal to the quotient of: (a) $835,000,000 divided by (b) $10.00, subject to adjustment as set forth in Section 2.3 of the Merger Agreement. Common Stock, Public Warrants and ROCH Units issued and outstanding immediately prior to the consummation of the Business Combination will be exchanged for ParentCo Securities on a one-for-one basis, as will ROCH’s outstanding warrants and units.
(b) Contingency Consideration
PCT Unitholders will be issued up to 4,000,000 additional shares of ParentCo Common Stock if certain conditions are met. Each of the “First Level Contingency Consideration” and “Second Level Contingency Consideration” is equal to 2,000,000 shares of ParentCo Common Stock. The PCT Unitholders will be entitled to the First Level Contingency Consideration, if after six months after the Closing and prior to or as of the third anniversary of the Closing, the closing price of the ParentCo Common Stock is greater than or equal to $18.00 over any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period. The PCT Unitholders will be entitled to the Second Level Contingency Consideration upon the Phase II Facility becoming operational, as certified by an independent engineering firm in accordance with criteria established in connection with the incurrence of the Construction Indebtedness.
Upon the first Change in Control (as defined in the Merger Agreement) to occur during the Earnout Period (as defined in the Merger Agreement), if the price per share paid or payable to the stockholders of ParentCo in connection with such Change in Control is equal to or greater than $18.00, ParentCo will issue 2,000,000 shares of ParentCo Common Stock. Upon the first Change in Control (substituting “80%” for “50%” in the definition thereof) to occur during the Earnout Period, if the price per share paid or payable to the stockholders of ParentCo in connection with such Change in Control is equal to or greater than $10.00 per share, ParentCo will issue 2,000,000 shares of ParentCo Common Stock.
8
Other Agreements Relating to the Business Combination
Investor Rights Agreement
At the Closing of the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement, ParentCo, certain PCT Unitholders representing at least 70% of PCT’s outstanding membership interests and certain stockholders of ROCH (including certain ROCH officers, directors and sponsors) entered into an investor rights agreement (the “Investor Rights Agreement”), which is a closing condition of the parties to consummate the Business Combination. Pursuant to the Investor Rights Agreement, such PCT Unitholders have agreed to vote in favor of two board designees nominated by a majority of such stockholders of ROCH for a period of two years following the Closing Date (the “IRA Designees”), provided that in the event a majority of the holders of the Pre-PIPE Shares (as defined below) choose to select one of the IRA Designees, the majority of such stockholders of ROCH will select one of the IRA Designees and such holders of the Pre-PIPE Shares will select the other. The holders of the Pre-PIPE Shares may continue to select an IRA Designee until they no longer hold 10% or more of the outstanding Combined Company’s Common Stock. Such PCT Unitholders have also agreed, subject to certain limited exceptions, not to transfer ParentCo Common Stock received in the Business Combination except as follows:
| • | From and after the six-month anniversary of the Closing Date, each Founder (as defined in the Investor Rights Agreement) may sell up to 20% of such Founder’s ParentCo Common Stock and each PCT Unitholder that is not a Founder may sell up to 33.34% of such PCT Unitholder’s ParentCo Common Stock. |
| • | From and after the one-year anniversary of the Closing Date, each Founder may sell up to an additional 30% of such Founder’s ParentCo Common Stock and each PCT Unitholder that is not a Founder may sell up to an additional 33.33% of such PCT Unitholder’s ParentCo Common Stock. |
| • | From and after the Phase II Facility becoming operational, as certified by an independent engineering firm, each Founder may sell up to an additional 50% of such Founder’s ParentCo Common Stock and each PCT Unitholder that is not a Founder may sell up to an additional 33.33% of such PCT shares of ParentCo Common Stock; provided that, in the case of Procter & Gamble, such lock-up will terminate in any event no later than April 15, 2023. |
The Investor Rights Agreement also contains registration rights in favor of the PCT Unitholders and such ROCH stockholders which (in the case of the ROCH stockholders) are intended to replace the registration rights granted to them at the time of ROCH’s IPO.
Subscription Agreements and PIPE Registration Rights Agreement
In connection with the Business Combination, certain institutions and accredited investors (each a “Subscriber”) (i) have purchased prior to the date of the Merger Agreement membership units of PCT at an effective price per ParentCo Common Stock of approximately $8.35 per share for an aggregate cash amount of approximately $60 million (the “Pre-PIPE Shares”) in a private placement (the “Pre-PIPE Placement”) and (ii) have committed to purchase, on a transitory basis simultaneously with the consummation of the Business Combination, shares of Common Stock at a purchase price of $10.00 per share for an aggregate cash amount of $250 million (the “PIPE Shares”) in a private placement (for purposes of this section, the “PIPE Placement”), all of which will be exchanged for ParentCo Common Stock in connection with the closing of the Business Combination. Certain offering related expenses are payable by ROCH and PCT, including customary fees payable to the placement agents: Roth Capital Partners, LLC, Craig-Hallum and Oppenheimer & Co. Inc. (“Oppenheimer”). Such commitments have been made by way of certain subscription or unit purchase agreements (collectively, the “Subscription Agreements”), by and among each Subscriber and PCT or ROCH, as the case may be. The purpose of the sale of the Pre-PIPE Shares and the PIPE Shares is to raise additional capital for use in connection with the PCT business and the Business Combination and, in the case of the PIPE Shares, to meet the minimum cash requirements provided in the Merger Agreement. The Subscription Agreements for the PIPE Placement were entered into contemporaneously with the execution of the Merger Agreement and the proceeds will be deposited into escrow by the Subscribers and released to ParentCo (other than the par value of the PIPE Shares, which will be released to ROCH) in connection with the issuance of ParentCo Common Stock as part of the RH Merger concurrent with the closing of the Business Combination.
9
The PIPE Shares are identical to the shares of Common Stock that will be held by ROCH’s public stockholders at the time of the Closing of the Business Combination, other than the PIPE Shares, when initially issued by ROCH in connection with the PIPE Closing, may not be registered with the SEC.
The closing of the sale of PIPE Shares (the “PIPE Closing”) will be contingent upon the substantially concurrent consummation of the Business Combination. The PIPE Closing will occur on the date of and simultaneously with the consummation of the RH Merger. The PIPE Closing will be subject to customary conditions, including:
| • | ParentCo’s initial listing application with NASDAQ in connection with the Business Combination shall have been approved and, immediately following the Closing of the Business Combination, ParentCo shall satisfy any applicable initial and continuing listing requirements of NASDAQ and ParentCo shall not have received any notice of non-compliance therewith, and the ParentCo Common Stock shall have been approved for listing on NASDAQ; |
| • | all representations and warranties of ROCH and the Subscriber contained in the relevant Subscription Agreement shall be true and correct in all material respects (other than representations and warranties that are qualified as to materiality or Material Adverse Effect (as defined in the Subscription Agreements), which representations and warranties shall be true in all respects) at, and as of, the PIPE Closing; |
| • | as of the Closing Date, there has been no material adverse change in the business, properties, financial condition, stockholders’ equity or results of operations of ROCH and its subsidiaries taken as a whole since the date of the Subscription Agreement (other than the election by holders of the ROCH Class A Common Stock to exercise redemption rights in connection with the special meeting of ROCH’s stockholders to approve the Business Combination); and |
| • | all conditions precedent to the closing of the Business Combination, including the approval by ROCH’s stockholders, shall have been satisfied or waived. |
Each applicable Subscription Agreement will terminate upon the earlier to occur of (w) such date and time as the Merger Agreement is terminated in accordance with its terms, (x) upon the mutual written agreement of each of the parties to such Subscription Agreement, (y) any of the conditions to the PIPE Closing are not satisfied or waived on or prior to the PIPE Closing and, as a result thereof, the transactions contemplated by such Subscription Agreement are not consummated at the PIPE Closing or (z) May 31, 2021.
Pursuant to the Subscription Agreements and PIPE Registration Rights Agreement, ROCH agreed to file (at ROCH’s sole cost and expense) a registration statement registering the resale of the ParentCo Common Stock issuable in respect of the Pre-PIPE Shares and the PIPE Shares, of which registration statement this prospectus forms a part (the “PIPE Resale Registration Statement”), with the SEC no later than the 10th calendar day following the date ROCH first files the Proxy Statement/Prospectus with the SEC. ROCH will use its commercially reasonable efforts to have this PIPE Resale Registration Statement declared effective at the same time that ROCH has cleared comments with the SEC on the Proxy Statement/Prospectus, but no later than the 60th calendar day following the Closing Date (or, in the event the SEC notifies ROCH that it will “review” this PIPE Resale Registration Statement, the 90th calendar day following the date thereof) (the “Effectiveness Date”).
Under certain circumstances, additional payments by ROCH or ParentCo (as applicable) may be assessed with respect to the Pre-Pipe Shares and PIPE Shares in the event that (i) this PIPE Resale Registration Statement has not been filed with the SEC by the closing date; (ii) this PIPE Resale Registration Statement has not been declared effective by the SEC by the Effectiveness Date; (iii) this PIPE Resale Registration Statement is declared effective by the SEC but thereafter ceases to be effective or is suspended for more than fifteen (15) consecutive calendar days or more than an aggregate of twenty (20) calendar days (which need not be consecutive calendar days) during any 12-month period; or (iv) ROCH or ParentCo (as applicable) fails for any reason to satisfy the current public information requirement under Rule 144(c) under the Securities Act and the Pre-Pipe Shares and PIPE Shares are not then registered for resale under the Securities Act during the period commencing from the twelve (12) month anniversary of the closing and ending at such time that all of the Pre-Pipe Shares and PIPE Shares may be sold without the requirement for ROCH or ParentCo (as applicable) to be in compliance with Rule 144(c)(1) under the Securities Act and otherwise without restriction or limitation pursuant to Rule 144 under the Securities Act. The additional payments by ROCH or ParentCo (as applicable) will accrue on the applicable Pre-Pipe Shares and PIPE Shares at a rate of 1.0% of the aggregate purchase price paid for such shares per month, subject to certain terms and limitations (including a cap of 6.0% of the aggregate purchase price paid for such shares pursuant to the Subscription Agreements).
10
Founder Support Agreement
In connection with the execution of the Merger Agreement, certain of the Initial Stockholders entered into the Founder Support Agreement with ROCH, ParentCo, and PCT, pursuant to which such Initial Stockholders agreed to vote all shares of Common Stock beneficially owned by them in favor of each of the Proposals, to use their reasonable best efforts to take all actions reasonably necessary to consummate the Business Combination and to not take any action that would reasonably be expected to materially delay or prevent the satisfaction of the conditions to the Business Combination set forth in the Merger Agreement. In addition, such Initial Stockholders also agreed that they would not sell, assign or otherwise transfer any of the Insider Shares (as defined therein) unless the buyer, assignee or transferee executes a joinder agreement to the Founder Support Agreement. We agreed that we would not register any sale, assignment or transfer of such Insider Shares on our transfer ledger (book entry or otherwise) that is not in compliance with the Founder Support Agreement.
Company Support Agreement
In connection with the execution of the Merger Agreement, PCT Unitholders representing at least 70% of the issued and outstanding Company LLC Interests entered into the Company Support Agreement with ROCH, ParentCo, and PCT, pursuant to which such PCT Unitholders agreed to vote all LLC Interests beneficially owned by them in favor of each of the Proposals, to use their reasonable best efforts to take all actions reasonably necessary to consummate the Business Combination and to not take any action that would reasonably be expected to materially delay or prevent the satisfaction of the conditions to the Business Combination set forth in the Merger Agreement. In addition, such PCT Unitholders also agreed that they would not sell, assign or otherwise transfer any of the Company LLC Interests held by them, with certain limited exceptions, unless the buyer, assignee or transferee executes a joinder agreement to the Company Support Agreement.
11
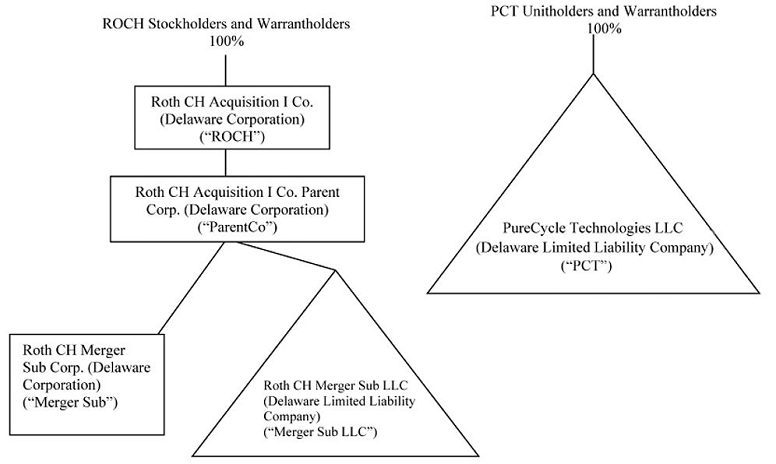
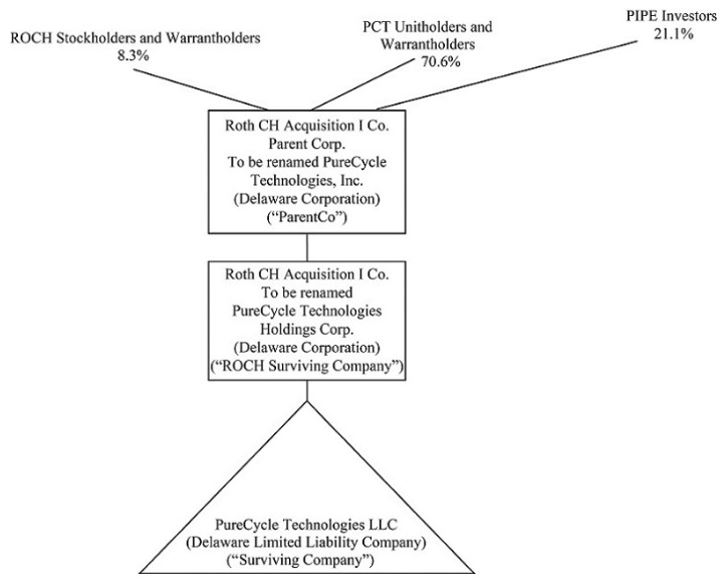
Ownership Structure
The following diagram illustrates the ownership structure of ROCH, ParentCo, Merger Sub LLC, Merger Sub Corp and PCT prior to the Business Combination and then after the Business Combination.
Prior to the Business Combination

12
After the Business Combination
13
Anticipated Accounting Treatment
The Business Combination will be accounted for as a “reverse recapitalization” in accordance with GAAP. Under this method of accounting ROCH will be treated as the “acquired” company for financial reporting purposes. This determination is primarily based on the fact that subsequent to the Business Combination, the PCT Unitholders are expected to have a majority of the voting power of the Combined Company, PCT will comprise all of the ongoing operations of the Combined Company, PCT will comprise a majority of the governing body of the Combined Company, and PCT’s senior management will comprise all of the senior management of the Combined Company. Accordingly, for accounting purposes, the Business Combination will be treated as the equivalent of PCT issuing shares for the net assets of ROCH, accompanied by a recapitalization. The net assets of ROCH will be stated at historical costs. No goodwill or other intangible assets will be recorded. Operations prior to the Business Combination will be those of PCT.
14
SELECTED HISTORICAL FINANCIAL INFORMATION OF ROCH
ROCH’s balance sheet data as of September 30, 2020 and statement of operations data for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 are derived from ROCH’s unaudited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. ROCH’s balance sheet data as of December 31, 2019 and statement of operations data for the period from February 13, 2019 (inception) through December 31, 2019 are derived from ROCH’s audited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus.
The historical results of ROCH included below and elsewhere in this prospectus are not necessarily indicative of the future performance of ROCH. You should read the following selected financial data in conjunction with the financial statements and the related notes appearing elsewhere in this prospectus.
| Nine Months Ended September 30, | 2020 | For the Period from February 13, 2019 (inception) through December 31, 2019 | ||||||
| Formation and operating costs | $ | 246,843 | 1,594 | |||||
| Loss from operations | (246,843 | ) | — | |||||
| Other income | — | |||||||
| Interest income | 23,547 | — | ||||||
| Net loss | (224,032 | ) | (1,594 | ) | ||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding – basic and diluted | 2,409,765 | 1,875,000 | ||||||
| Basic and diluted net loss per common share | $ | (0.09 | ) | (0.00 | ) | |||
| Balance Sheet Data: | As of September 30, 2020 | As of December 31, 2019 | ||||||
| Trust Account | $ | 76,522,615 | $ | — | ||||
| Total assets | 77,078,250 | 280,908 | ||||||
| Total liabilities | 2,802,189 | 257,502 | ||||||
| Common stock subject to possible redemption | 69,276,060 | — | ||||||
| Stockholders’ equity | 5,000,001 | 280,908 | ||||||
15
SELECTED HISTORICAL FINANCIAL INFORMATION OF PCT
The information presented below is derived from PCT’s unaudited condensed consolidated interim financial statements and audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and September 30, 2019 and the fiscal years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 and the balance sheet data as of September 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019 and 2018. In the opinion of PCT’s management, the unaudited condensed consolidated interim financial information reflects all adjustments necessary for a fair statement of the financial information in those statements.
The historical results presented below are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for any future period. You should read carefully the following selected information in conjunction with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and PCT’s historical consolidated financial statements and accompanying footnotes, included elsewhere in this prospectus.
For the Years Ended December 31 | Nine Months Ended September 30, | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2020 | 2019 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||||||
| Statement of Operations Data | ||||||||||||||||
| Revenue | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
| Costs and Expenses | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating Costs | $ | 7,040 | $ | 4,901 | $ | 5,966 | $ | 1,222 | ||||||||
| Research and Development | 528 | 509 | 526 | 786 | ||||||||||||
| Selling, General and Administrative | 6,293 | 10,082 | 11,478 | 2,097 | ||||||||||||
| Total Operating Costs and Expenses | 13,861 | 15,492 | 17,970 | 4,105 | ||||||||||||
| Interest Expense | 1,827 | 400 | 1,012 | — | ||||||||||||
| Other (Income) Expense, net | (100 | ) | 330 | 330 | — | |||||||||||
| Net Loss | $ | (15,588 | ) | $ | (16,222 | ) | $ | (19,312 | ) | $ | (4,105 | ) | ||||
| Net Loss per Unit(1) | $ | (7.91 | ) | $ | (7.03 | ) | $ | (8.42 | ) | $ | (1.86 | ) | ||||
| As of December 31, (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| As of September 30, | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | |||||||||
| Balance Sheet Data | ||||||||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents | $ | 108 | $ | 150 | $ | 101 | ||||||
| Working Capital(2) | (15,742 | ) | (7,622 | ) | (4,226 | ) | ||||||
| Total Assets | 37,954 | 33,281 | 25,738 | |||||||||
| Total Liabilities | 31,119 | 30,901 | 19,544 | |||||||||
| Total Members’ Equity | 6,835 | 2,380 | 6,194 | |||||||||
(1) PCT follows the two-class method when computing net loss per common units when units are issued that meet the definition of participating securities. The two-class method requires income available to common unitholders for the period to be allocated between common and participating securities based upon their respective rights to receive dividends as if all income for the period had been distributed. The two-class method also requires losses for the period to be allocated between common and participating securities based on their respective rights if the participating security contractually participates in losses. As holders of participating securities do not have a contractual obligation to fund losses, undistributed net losses are not allocated to Class B Preferred Units, Class B-1 Preferred Units and Class C Units for purposes of the loss per unit calculation.
(2) PCT defines working capital as total current assets minus total current liabilities.
16
SUMMARY UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED FINANCIAL INFORMATION
The following summary unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information (the “Summary Pro Forma Information”) gives effect to the Business Combination. The Business Combination will be accounted for as a reverse recapitalization in accordance with GAAP. Under this method of accounting, ROCH will be treated as the “acquired” company for financial reporting purposes. Accordingly, the Business Combination will be reflected as the equivalent of PCT issuing stock for the net assets of ROCH, accompanied by a recapitalization whereby no goodwill or other intangible assets are recorded. Operations prior to the Business Combination will be those of PCT. The summary unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet data as of September 30, 2020 gives effect to the Business Combination as if it had occurred on September 30, 2020. The summary unaudited pro forma condensed combined statements of operations data for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and combined statements of operations data for the year ended December 31, 2019 give effect to the Business Combination as if it had occurred on January 1, 2019.
The following Summary Pro Forma Information has been prepared in accordance with Article 11 of Regulation S-X as amended by the final rule, Release No. 33-10786 “Amendments to Financial Disclosures about Acquired and Disposed Businesses”. The Summary Pro Forma Information has been derived from, and should be read in conjunction with, the more detailed unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information of the post-combination company appearing elsewhere in this prospectus and the accompanying notes to the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information. The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information is based upon, and should be read in conjunction with, the historical financial statements and related notes of ROCH and PCT for the applicable periods included in this prospectus. The Summary Pro Forma Information has been presented for informational purposes only and is not necessarily indicative of what the Combined Company’s financial position or results of operations actually would have been had the Business Combination been completed as of the dates indicated. In addition, the Summary Pro Forma Information does not purport to project the future financial position or operating results of the Combined Company.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information has been prepared using the assumptions below with respect to the potential redemption into cash of Common Stock:
| • | Assuming Minimum Redemptions: This presentation assumes that no Public Stockholders of ROCH exercise redemption rights with respect to their Public Shares for a pro rata share of the funds in the Trust Account. |
| • | Assuming Maximum Redemptions: This presentation assumes that Public Stockholders holding 6.9 million of the Public Shares will exercise their redemption rights for their pro rata share (approximately $10.00 per share) of the funds in the Trust Account. This scenario gives effect to public share redemptions for aggregate redemption payments of $69.3 million using a per share redemption price of $10.00 per share. The Merger Agreement includes as a condition to closing the Business Combination that, at the closing, ROCH will have a minimum of $250.0 million in cash comprising (i) the cash held in the Trust Account after giving effect to ROCH share redemptions and proceeds from the PIPE Investment and (ii) a minimum of $5.0 million of net tangible assets. Additionally, this presentation also contemplates that ROCH’s Initial Stockholders have agreed to waive their redemption rights with respect to their Founder Shares, Private Shares and Public Shares in connection with the completion of a Business Combination. |
17
Summary Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Statement of Operations Data
Nine Months Ended September 30, 2020 (in thousands except share and per share data) | Pro
Forma Combined (Assuming No Redemption) | Pro
Forma Combined (Assuming Maximum Redemption) | ||||||
| Revenue | $ | — | $ | — | ||||
| per share – basic and diluted | $ | (0.11 | ) | $ | (0.11 | ) | ||
| average common shares outstanding – basic and diluted | 118,328,000 | 111,400,394 | ||||||
Summary Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Statement of Operations Data
Year Ended December 31, 2019 (in thousands except share and per share data) | Pro
Forma Combined (Assuming No Redemption) | Pro
Forma Combined (Assuming Maximum Redemption) | ||||||
| Revenue | $ | — | $ | — | ||||
| Net loss per share – basic and diluted | $ | (0.14 | ) | $ | (0.15 | ) | ||
| Weighted-average common shares outstanding – basic and diluted | 118,328,000 | 111,400,394 | ||||||
Summary Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined
Balance Sheet Data as of September 30, 2020 (in thousands) | Pro
Forma Combined (Assuming No Redemption) | Pro
Forma Combined (Assuming Maximum Redemption) | ||||||
| Total assets | $ | 724,516 | $ | 655,240 | ||||
| Total liabilities | $ | 311,851 | $ | 311,851 | ||||
| Total stockholders’ equity | $ | 412,665 | $ | 343,389 | ||||
18
The following table sets forth summary historical comparative share information for ROCH and PCT and unaudited pro forma condensed combined per share information after giving effect to the Business Combination. The pro forma book value information reflects the Business Combination as if it had occurred on September 30, 2020. The weighted average shares outstanding and net earnings per share information reflect the Business Combination as if they had occurred on January 1, 2019.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined earnings per share information should be read in conjunction with, the historical financial statements and related notes of ROCH and PCT for the applicable periods included in this prospectus. The unaudited pro forma condensed combined earnings per share information has been presented for informational purposes only and is not necessarily indicative of what the Combined Company’s results of operations actually would have been had the Business Combination been completed as of the dates indicated. In addition, the unaudited pro forma combined book value per share information does not purport to project the future financial position or operating results of the Combined Company.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information has been prepared using the assumptions below with respect to the potential redemption into cash of Common Stock:
| • | Assuming Minimum Redemptions: This presentation assumes that no Public Stockholders of ROCH exercise redemption rights with respect to their Public Shares for a pro rata share of the funds in the Trust Account. |
| • | Assuming Maximum Redemptions: This presentation assumes that Public Stockholders holding 6.9 million of the Public Shares will exercise their redemption rights for their pro rata share (approximately $10.00 per share) of the funds in the Trust Account. This scenario gives effect to public share redemptions for aggregate redemption payments of $69.3 million using a per share redemption price of $10.00 per share. The Merger Agreement includes as a condition to closing the Business Combination that, at the closing, ROCH will have a minimum of $250.0 million in cash comprising (i) the cash held in the Trust Account after giving effect to ROCH share redemptions and proceeds from the PIPE Investment and (ii) a minimum of $5.0 million of net tangible assets. Additionally, this presentation also contemplates that ROCH’s Initial Stockholders have agreed to waive their redemption rights with respect to their Founder Shares, Private Shares and Public Shares in connection with the completion of a Business Combination. |
| Combined Pro Forma | PureCycle
Equivalent Per Share Pro Forma(3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCT (Historical) | ROCH (Historical) | Pro
Forma Combined (Assuming No Redemption) | Pro
Forma Combined (Assuming Maximum Redemption) | Pro
Forma Combined (Assuming No Redemption) | Pro
Forma Combined (Assuming Maximum Redemption) | |||||||||||||||||||
| As of and for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Book Value per share(1) | $ | 2.65 | $ | 2.07 | $ | 3.49 | $ | 3.08 | $ | 37.69 | $ | 33.27 | ||||||||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding of common stock – basic and diluted | 2,581,282 | 2,409,765 | 118,328,000 | 111,400,394 | 27,879,167 | 27,879,163 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net income per share of Class A common stock – basic and diluted | $ | (7.91 | ) | $ | (0.09 | ) | $ | (0.11 | ) | $ | (0.11 | ) | $ | (1.14 | ) | $ | (1.21 | ) | ||||||
| As of and for the Year ended December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Book Value per share(1) | $ | 0.92 | $ | 0.01 | $ | N/A(2 | ) | $ | N/A(2 | ) | $ | N/A(2 | ) | $ | N/A(2 | ) | ||||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding of common stock – basic and diluted | 2,581,282 | 1,875,000 | 118,328,000 | 111,400,394 | 27,879,167 | 27,879,167 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net income per share of Class A common stock – basic and diluted | $ | (8.42 | ) | $ | — | $ | (0.14 | ) | $ | (0.15 | ) | $ | (1.52 | ) | $ | (1.61 | ) | |||||||
(1) Book value per share = (Total equity)/common shares outstanding.
(2) Pro Forma balance sheet fur year ended December 31, 2019 not required and as such, no such calculation included in this table.
(3) The equivalent pro forma basic and diluted per share data for PCT is calculated based on an expected exchange ratio of 10.80 under both the no redemption and maximum redemption scenarios that is inherent in the Business Combination.
19
The Offering
| Issuer | Roth CH Acquisition I Co. Parent Corp., to be renamed PureCycle Technologies, Inc. in connection with the Business Combination. | |
| Shares that may be offered and sold from time to time by the Selling Stockholders named herein | 25,000,000 shares of ParentCo Common Stock. | |
| ParentCo Common Stock to be issued and outstanding after the consummation of the Business Combination (assuming no redemptions and excluding shares issuable upon exercise of outstanding warrants)(1) | 118,324,000 shares | |
| Use of proceeds | All of the shares of ParentCo Common Stock offered by the Selling Stockholders pursuant to this prospectus will be sold by the Selling Stockholders for their respective accounts. We will not receive any of the proceeds from these sales. | |
| Proposed NASDAQ Capital Market symbol | “PCT” | |
| Risk Factors | Investing in ParentCo Common Stock involves a high degree of risk. See “Risk Factors” beginning on page 23 and the other information in this prospectus for a discussion of the factors you should consider carefully before you decide to invest in ParentCo Common Stock. |
(1) Represents the number of shares of ParentCo Common Stock outstanding at Closing assuming that none of ROCH’s public stockholders exercise their redemption rights in connection with the Special Meeting. Excludes 4,000,000 shares of ParentCo Common Stock which may be issued to the current owners of PCT subject to the achievement of certain stock price targets and upon commissioning of an industrial facility in Ironton, Ohio.
20
Our business is subject to a number of risks and uncertainties, including those highlighted in the section entitled “Risk Factors” immediately following this summary. Some of these principal risks include the following and may be further exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic:
| • | Risks Related to PCT’s Business |
| • | PCT is an early commercial stage emerging growth company with no revenue, and may never achieve or sustain profitability. |
| • | PCT’s business is not diversified. |
| • | The License Agreement sets forth certain performance targets which, if missed, could result in a termination or conversion of the license granted under the License Agreement. |
| • | PCT’s outstanding secured and unsecured indebtedness (including at the Project level), ability to incur additional debt and the provisions in the agreements governing PCT’s debt, and certain other agreements, could have a material adverse effect on PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. |
| • | PCT’s projections are subject to significant risks, assumptions, estimates and uncertainties. As a result, PCT’s projected revenues, expenses and profitability may differ materially from expectations. |
| • | PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects may be adversely affected by the impact of the global outbreak of COVID-19. |
| • | Construction of the Phase II Facility may not be completed in the expected timeframe or in a cost-effective manner. Any delays in the construction of the Phase II Facility could severely impact PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. |
| • | Initially, PCT will rely on a single facility for all of its operations. |
| • | There is no guarantee the Technology is scalable to commercial-scale operation. |
| • | PCT may be unable to sufficiently protect its proprietary rights and may encounter disputes from time to time relating to its use of the intellectual property of third parties. |
| • | PCT may not be successful in finding future strategic partners for continuing development of additional offtake and feedstock opportunities. |
| • | PCT’s failure to secure waste polypropylene could have a negative impact on PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. |
| • | Because PCT’s global expansion requires sourcing feedstock and supplies from around the world, including Europe, changes to international trade agreements, tariffs, import and excise duties, taxes or other governmental rules and regulations could adversely affect PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. |
| • | The market for UPRP is still in the development phase and the acceptance of UPRP by manufacturers and potential customers is not guaranteed. |
| • | Certain of PCT’s offtake agreements are subject to index pricing, and fluctuation in index prices may adversely impact PCT’s financial results. |
| • | Competition could reduce demand for PCT’s products or negatively affect PCT’s sales mix or price realization. |
| • | PCT may not be able to meet applicable regulatory requirements for the use of PCT’s UPRP in food grade applications, and, even if the requirements are met, complying on an ongoing basis with the numerous regulatory requirements applicable to the UPRP and our facilities will be time-consuming and costly. |
| • | The operation of and construction of the Project is subject to governmental regulation. |
21
| • | Risks Related to Human Capital Management |
| • | PCT is dependent on management and key personnel, and PCT’s business would suffer if it fails to retain its key personnel and attract additional highly skilled employees. |
| • | While ROCH and PCT work to complete the business combination, management’s focus and resources may be diverted from operational matters and other strategic opportunities. |
| • | PCT’s management has limited experience in operating a public company. |
| • | Risks Related to the Combined Company’s Common Stock |
| • | There can be no assurance that the Combined Company’s Common Stock will be approved for listing on NASDAQ upon the Closing, or if approved, that the Combined Company will be able to comply with the continued listing standards of NASDAQ. |
| • | The exercise of registration rights may adversely affect the market price of the Combined Company’s Common Stock. |
| • | Future offerings of debt or offerings or issuances of equity securities by the Combined Company may adversely affect the market price of the Combined Company’s Common Stock or otherwise dilute all other stockholders. |
| • | General Risk Factors |
| • | Each of ROCH and PCT have incurred and will incur substantial costs in connection with the Business Combination and related transactions, such as legal, accounting, consulting and financial advisory fees. |
| • | The Combined Company is an emerging growth company, and the Combined Company cannot be certain if the reduced reporting requirements applicable to emerging growth companies will make its shares less attractive to investors. |
| • | Following the consummation of the Business Combination, the Combined Company will incur significant increased expenses and administrative burdens as a public company. |
22
Upon consummation of the Business Combination, the resulting Combined Company will be subject to a number of risks. You should carefully consider the following risk factors, together with all of the other information included in this prospectus, before you decide whether to invest in ParentCo Common Stock. Following the closing of the Business Combination, the market price of the Combined Company’s common stock could decline due to any of these risks, in which case you could lose all or part of your investment. In assessing these risks, you should also refer to the other information included in this prospectus, including the consolidated financial statements of ROCH and PCT and the accompanying notes. The Combined Company’s business, financial condition or results of operations could be affected materially and adversely by any of the risks discussed below.
Risks Related to PCT’s Business
Risks Related to PCT’s Status as an Early Commercial Stage Emerging Growth Company
PCT is an early commercial stage emerging growth company with no revenue, and may never achieve or sustain profitability.
PCT is commercializing a recycling technology that was developed by The Procter & Gamble Company (“P&G”). P&G granted PCT a worldwide license under an Amended and Restated Patent License Agreement dated July 28, 2020, between P&G and PCT (the “License Agreement”) for a proprietary process of restoring waste polypropylene into ultra-pure recycled polypropylene (“UPRP”) through an extraction and filtration purification process (the “Technology”).
PCT relies principally on the commercialization of UPRP as well as the Technology and related licenses to generate future revenue growth. To date, such products and services have delivered no revenue. Also, UPRP product offerings and partnering revenues are in their very early stages. PCT believes that commercialization success is dependent upon the ability to significantly increase the number of production plants, feedstock suppliers and offtake partners as well as strategic partners that utilize UPRP and the Technology via licensing agreements. If demand for UPRP and the Technology does not increase as quickly as planned, PCT may be unable to increase revenue levels as expected. PCT is currently not profitable. Even if PCT succeeds in increasing adoption of UPRP products by target markets, maintaining and creating relationships with existing and new offtake partners, feedstock suppliers and customers, and developing and commercializing additional plants, market conditions, particularly related to pricing and feedstock costs, may result in PCT not generating sufficient revenue to achieve or sustain profitability.
PCT’s business is not diversified.
PCT’s initial commercial success depends on its ability to profitably operate the solid waste disposal facility and Feedstock Evaluation Unit (the “FEU” or the “Phase I Facility”) and its ability to complete construction and profitably and successfully operate its first commercial scale recycling facility (the “Phase II Facility” and, together with the Phase I Facility, the “Project”). The Project is located in Lawrence County, Ohio. Other than the future production and sale of UPRP, there are currently no other lines of business or other sources of revenue. Such lack of diversification may limit PCT’s ability to adapt to changing business conditions and could have an adverse effect on PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
The License Agreement sets forth certain performance and pricing targets which, if missed, could result in a termination or conversion of the license granted under the License Agreement.
Pursuant to the License Agreement, P&G has granted PCT a license to utilize certain P&G intellectual property. The intellectual property is tied to the proprietary purification process by which waste polypropylene may be converted to UPRP, referred to as the Technology. The License Agreement sets forth certain performance targets for the Phase II Facility which, if missed, could result in a termination of the license granted under the License Agreement (if PCT is unable to make UPRP at certain production volumes and at certain prices within a certain time frame). The License Agreement also sets forth certain performance and pricing targets for the Phase II Facility which, if missed, could result in conversion of the license to a non-exclusive license (if PCT’s UPRP is unable to meet certain purification thresholds within a certain period of time after the start of the Project or PCT is unable or unwilling to provide P&G with UPRP at certain prices from the first plant). In the event the License Agreement is terminated or converted to a non-exclusive license, this could have a material adverse effect on PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
23
PCT’s outstanding secured and unsecured indebtedness (including at the Project level), ability to incur additional debt and the provisions in the agreements governing PCT’s debt, and certain other agreements, could have a material adverse effect on PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
As of September 30, 2020, after giving pro forma effect to the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement, the offering of the Revenue Bonds, and the issuance of $60 million of the Convertible Notes, PCT had total consolidated debt of $312.0 million, including $306.5 million of secured indebtedness (including $235.0 million of indebtedness at the Project level) and $5.5 million of unsecured indebtedness. PCT’s debt service obligations could have important consequences to the Combined Company for the foreseeable future, including the following: (i) PCT’s ability to obtain additional financing for capital expenditures, working capital or other general corporate purposes may be impaired; (ii) a substantial portion of PCT’s cash flow from operating activities must be dedicated to the payment of principal and interest on PCT’s debt, thereby reducing the funds available to us for PCT’s operations and other corporate purposes; and (iii) we may be or become substantially more leveraged than some of PCT’s competitors, which may place us at a relative competitive disadvantage and make us more vulnerable to changes in market conditions and governmental regulations.
PCT is required to maintain compliance with certain financial and other covenants under its debt agreements. There are and will be operating and financial restrictions and covenants in certain of PCT’s debt agreements, including the Loan Agreement and the indenture governing PCT’s Convertible Notes, as well as certain other agreements to which PCT is or may become a party. These limit, among other things, PCT’s ability to incur certain additional debt, create certain liens or other encumbrances, sell assets, and transfer ownership interests and transactions with affiliates of PCT. These covenants could limit PCT’s ability to engage in activities that may be in PCT’s best long-term interests. PCT’s failure to comply with certain covenants in these agreements could result in an Event of Default (as defined therein) under the various debt agreements, allowing lenders to accelerate the maturity for the debt under these agreements and to foreclose upon any collateral securing the debt. An Event of Default would also adversely affect PCT’s ability to access its borrowing capacity and pay debt service on its outstanding debt, likely resulting in acceleration of such debt or in a default under other agreements containing cross-default provisions. Under such circumstances, PCT might not have sufficient funds or other resources to satisfy all of its obligations. In addition, the limitations imposed by PCT’s financing agreements on its ability to pay dividends, incur additional debt and to take other actions might significantly impair PCT’s ability to obtain other financing, generate sufficient cash flow from operations to enable PCT to pay its debt or to fund other liquidity needs. Such consequences would adversely affect PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
PCT’s projections are subject to significant risks, assumptions, estimates and uncertainties. As a result, PCT’s projected revenues, expenses and profitability may differ materially from expectations.
In connection with the Business Combination, the ROCH Board of Directors considered, among other things, internal financial forecasts for the post-Business Combination company. They speak only as of the date made and will not be updated. These financial projections are subject to significant economic, competitive, industry and other uncertainties, including availability of capital, and may not be achieved in full, at all or within projected timeframes. For example, the financial projections provided to the ROCH Board of Directors are derived in part from PCT’s projections of future UPRP production volumes. Those future production volumes include volumes associated with both current and projected feedstock sources. Projected feedstock sources and associated future production volumes and related future cash flows are inherently more uncertain than those related to current volumes, and the impact of that uncertainty increases for periods further from the date of this proxy statement/prospectus. Further, as a result of unprecedented market disruption resulting from the global coronavirus (COVID-19), these projections are even more uncertain in terms of reflecting actual future results. In addition, the failure of PCT’s business to achieve projected results could have a material adverse effect on the Combined Company’s share price and financial position following the Business Combination.
24
Risks Related to PCT’s Operations
PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects may be adversely affected by the impact of the global outbreak of COVID-19.
The United States is being affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, the full effect of which on global financial markets as well as national, state and local economies is unknown. There can be no assurances as to the materiality, severity and duration of negative economic conditions caused by the pandemic.
In addition to keeping PCT employees healthy and safe, the immediate impact of COVID-19 on PCT relates to the challenges that PCT’s suppliers and contractors may be facing. PCT is a party to certain agreements, including construction contracts and certain long-term feedstock agreements that provide for the supply to PCT of post-industrial and post-consumer resin that contains polypropylene as feedstock with guaranteed minimum and maximum volumes at prices linked to an index for virgin polypropylene in a price schedule with collared pricing and a minimum price floor. The feedstock agreements contain typical provisions for termination by either party due to force majeure, breach of contract, and/or company insolvency. The impact of COVID-19 on such agreements, or the applicable agreements’ termination provisions, is uncertain, and could result in the termination of such agreements.
When PCT is producing UPRP, if the pandemic has not abated, the impact of COVID-19, while uncertain, could be manifested in the challenges faced by PCT’s customers. For example, certain UPRP is intended for use in consumer packaging by consumer goods companies, and there could be volatility in the packaged consumer goods market due to interruptions in consumer access to products resulting from government actions that impact the ability of those companies to produce and ship goods. Product demand trends caused by future economic trends are unclear. PCT has executed offtake agreements providing for a combined guaranteed minimum sale of 63 million pounds per year (“MMlb/yr.”) of UPRP and a maximum volume of 138 MMlb/yr at PCT’s option, which reduces the ability of PCT to quickly respond to changes caused by COVID-19, particularly as the amount of UPRP to be provided for sale under each offtake agreement is determined prior to each year as an annual volume commitment.
There may be additional unknown risks presented by the COVID-19 pandemic that could impact PCT’s operating results. For example, the deadly global outbreak and continuing spread of COVID-19 could have an adverse effect on the value, operating results and financial condition of PCT’s business; as well as the ability of PCT to maintain operations and grow revenue generated from offtake partners and customers and could delay or prevent completion of the Phase II Facility or result in additional costs or reduced revenues. In addition, the impact of COVID-19 is likely to cause substantial changes in consumer behavior and has caused restrictions on business and individual activities, which are likely to lead to reduced economic activity. Extraordinary actions taken by international, federal, state, and local public health and governmental authorities to contain and combat the outbreak and spread of COVID-19 in regions throughout the world, including travel bans, quarantines, “stay-at-home” orders, and similar mandates for many individuals and businesses to substantially restrict daily activities could have an adverse effect on PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
25
Construction of the Phase II Facility may not be completed in the expected timeframe or in a cost-effective manner. Any delays in the construction of the Phase II Facility could severely impact PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
The Project will constitute the first of its kind. Construction on the Project commenced in 2018 with the construction of the Phase I Facility comprised of the FEU, operating within an 11,000 square foot building located on the Project site. The FEU was brought online on July 1, 2019. Construction of the Phase II Facility has commenced, will include modifications to 150,000 square feet of existing buildings, utilities and the Project storage area, and is expected to be substantially completed by October 2022. The Combined Company might not be able to achieve completion of the Phase II Facility in the expected timeframe, in a cost-effective manner or at all due to a variety of factors, including, but not limited to, a stoppage of work as a result of the COVID-19 outbreak, unexpected construction problems or severe weather. Significant unexpected delays in construction could result in additional costs or reduced revenues, and it could limit the amount of UPRP PCT can produce, which could severely impact PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
The construction and commissioning of any new project is dependent on a number of contingencies some of which are beyond PCT’s control. There is a risk that significant unanticipated costs or delays could arise due to, among other things, errors or omissions, unanticipated or concealed Project site conditions, including subsurface conditions, unforeseen technical issues or increases in plant and equipment costs, insufficiency of water supply and other utility infrastructure, or inadequate contractual arrangements. Should significant unanticipated costs arise, this could have a material adverse impact on PCT’s business, financial performance and operations. No assurance can be given that construction will be completed, will be completed on time or will be completed at all, or as to whether PCT, which has provided a Guaranty of Completion of the Project, will have sufficient funds available to complete construction. If the Project is not completed, funds are not likely to be available to pay debt service on PCT’s outstanding debt.
Initially, PCT will rely on a single facility for all of its operations.
Initially, PCT will rely solely on the operations at the Project. Adverse changes or developments affecting the Project could impair PCT’s ability to produce UPRP and its business, prospects, financial condition and results of operations. Any shutdown or period of reduced production at the Project, which may be caused by regulatory noncompliance or other issues, as well as other factors beyond its control, such as severe weather conditions, natural disaster, fire, power interruption, work stoppage, disease outbreaks or pandemics (such as COVID-19), equipment failure or delay in supply delivery, would significantly disrupt PCT’s ability to grow and produce UPRP in a timely manner, meet its contractual obligations and operate its business. PCT’s equipment is costly to replace or repair, and PCT’s equipment supply chains may be disrupted in connection with pandemics, such as COVID-19, trade wars or other factors. If any material amount of PCT’s machinery were damaged, it would be unable to predict when, if at all, it could replace or repair such machinery or find co-manufacturers with suitable alterative machinery, which could adversely affect PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. Performance guarantees may not be sufficient to cover damages or losses, or the guarantors under such guarantees may not have the ability to pay. Any insurance coverage PCT has may not be sufficient to cover all of its potential losses and may not continue to be available to PCT on acceptable terms, or at all.
Cyber risk and the failure to maintain the integrity of PCT’s operational or security systems or infrastructure, or those of third parties with which PCT does business, could have a material adverse effect on PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
PCT is subject to an increasing number of information technology vulnerabilities, threats and targeted computer crimes which pose a risk to the security of its systems and networks and the confidentiality, availability and integrity of data. Disruptions or failures in the physical infrastructure or operating systems that support PCT’s businesses, offtake partners, feedstock suppliers and customers, or cyber attacks or security breaches of PCT’s networks or systems, could result in the loss of customers and business opportunities, legal liability, regulatory fines, penalties or intervention, reputational damage, reimbursement or other compensatory costs, and additional compliance costs, any of which could materially adversely affect PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. While PCT attempts to mitigate these risks, PCT’s systems, networks, products, solutions and services remain potentially vulnerable to advanced and persistent threats.
PCT also maintains and has access to sensitive, confidential or personal data or information in its business that is subject to privacy and security laws, regulations and customer controls. Despite PCT’s efforts to protect such sensitive, confidential or personal data or information, PCT’s facilities and systems and those of its customers, offtake partners, feedstock suppliers and third-party service providers may be vulnerable to security breaches, theft, misplaced or lost data, programming and/or human errors that could lead to the compromise of sensitive, confidential or personal data or information or improper use of
PCT’s systems and software.
26
PCT may be unable to sufficiently protect its proprietary rights and may encounter disputes from time to time relating to its use of the intellectual property of third parties.
PCT relies on its proprietary intellectual property, including numerous patents and registered trademarks, as well as its licensed intellectual property under the License Agreement and others to market, promote and sell UPRP products. PCT monitors and protects against activities that might infringe, dilute, or otherwise harm its patents, trademarks and other intellectual property and relies on the patent, trademark and other laws of the U.S. and other countries. However, PCT may be unable to prevent third parties from using its intellectual property without authorization. In addition, the laws of some non-U.S. jurisdictions, particularly those of certain emerging markets, provide less protection for PCT’s proprietary rights than the laws of the U.S. and present greater risks of counterfeiting and other infringement. To the extent PCT cannot protect its intellectual property, unauthorized use and misuse of PCT’s intellectual property could harm its competitive position and have a material adverse effect on PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Despite PCT’s efforts to protect these rights, unauthorized third parties may attempt to duplicate or copy the proprietary aspects of its technology and processes. PCT’s competitors and other third parties independently may design around or develop similar technology or otherwise duplicate PCT’s services or products such that PCT could not assert its intellectual property rights against them. In addition, PCT’s contractual arrangements may not effectively prevent disclosure of its intellectual property and confidential and proprietary information or provide an adequate remedy in the event of an unauthorized disclosure. Measures in place may not prevent misappropriation or infringement of PCT’s intellectual property or proprietary information and the resulting loss of competitive advantage, and PCT may be required to litigate to protect its intellectual property and proprietary information from misappropriation or infringement by others, which is expensive, could cause a diversion of resources and may not be successful.
PCT also may encounter disputes from time to time concerning intellectual property rights of others, and it may not prevail in these disputes. Third parties may raise claims against PCT alleging that PCT, or consultants or other third parties retained or indemnified by PCT, infringe on their intellectual property rights. Some third-party intellectual property rights may be extremely broad, and it may not be possible for PCT to conduct its operations in such a way as to avoid all alleged violations of such intellectual property rights. Given the complex, rapidly changing and competitive technological and business environment in which PCT operates, and the potential risks and uncertainties of intellectual property-related litigation, an assertion of an infringement claim against PCT may cause PCT to spend significant amounts to defend the claim, even if PCT ultimately prevails, pay significant money damages, lose significant revenues, be prohibited from using the relevant systems, processes, technologies or other intellectual property (temporarily or permanently), cease offering certain products or services, or incur significant license, royalty or technology development expenses.
Moreover, it has become common in recent years for individuals and groups to purchase intellectual property assets for the sole purpose of making claims of infringement and attempting to extract settlements from companies such as PCT. Even in instances where PCT believes that claims and allegations of intellectual property infringement against it are without merit, defending against such claims is time consuming and expensive and could result in the diversion of time and attention of PCT’s management and employees. In addition, although in some cases a third party may have agreed to indemnify PCT for such costs, such indemnifying party may refuse or be unable to uphold its contractual obligations. In other cases, insurance may not cover potential claims of this type adequately or at all, and PCT may be required to pay monetary damages, which may be significant.
27
Risks Related to PCT’s Production of UPRP
There is no guarantee the Technology is scalable to commercial-scale operation.
The Technology is based upon generally available commercial equipment to process contaminated polypropylene into clean recycled polypropylene product. Certain of the equipment to be utilized in the Phase II Facility has not operated with the same feedstock in a commercial mode. While PCT has constructed the FEU to demonstrate the process using the same equipment (except at a smaller scale) as the commercial- scale Phase II Facility, the FEU does not operate at a commercial-scale. The collective test data was used to design the Phase II Facility equipment for commercial-scale and testing under the intended operating conditions and configuration for the commercial-scale operation to verify reproducibility of results including color, melt flow index, moldability (tensile modulus and other measures) and the odor of the final PCT- produced polypropylene product. While that testing indicated that the FEU can generate recycled polypropylene product that on average meets all of its key parameter targets, PCT cannot guarantee these results will be achieved in commercial-scale operation. Further, of the four quality parameters for UPRP, odor is the most difficult to characterize and measure. PCT’s goal is to generate product that will significantly reduce the odor of the offtake and be comparable or nearly comparable to virgin polypropylene with respect to level of odor, but PCT cannot guarantee that the Project will be capable of achieving the performance guarantees or meeting the requirements of the currently applicable environmental permits. The Project’s failure to achieve the performance guarantees or meet the requirements of the currently applicable environmental permits could impact PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects if the possible shortfalls versus specification are not effectively remedied per contract.
PCT may not be successful in finding future strategic partners for continuing development of additional offtake and feedstock opportunities.
PCT may seek to develop additional strategic partnerships to increase feedstock supply and offtake amount due to capital costs required to develop the UPRP product or manufacturing constraints. PCT may not be successful in efforts to establish such a strategic partnerships or other alternative arrangements for the UPRP product or Technology because PCT’s research and development pipeline may be insufficient, PCT’s product may be deemed to be at too early of a stage of development for collaborative effort or third parties may not view PCT’s product as having the requisite potential to demonstrate commercial success.
If PCT is unable to reach agreements with suitable collaborators on a timely basis, on acceptable terms or at all, PCT may have to curtail the development of UPRP product, reduce or delay the development program, delay potential commercialization, reduce the scope of any sales or marketing activities or increase expenditures and undertake development or commercialization activities at PCT’s own expense. If PCT elects to fund development or commercialization activities on its own, PCT may need to obtain additional expertise and additional capital, which may not be available on acceptable terms or at all. If PCT fails to enter into collaborations and does not have sufficient funds or expertise to undertake the necessary development and commercialization activities, PCT may not be able to further develop product candidates and PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects may be materially and adversely affected.
PCT’s failure to secure waste polypropylene could have a negative impact on PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
PCT’s ability to procure a sufficient quantity and quality of post-industrial and post-consumer resin that contains polypropylene as feedstock is dependent upon certain factors outside of PCT’s control including, but not limited to, changes to pricing levels for waste polypropylene, recycled polypropylene and non-recycled polypropylene, shortages in supply, interruptions affecting suppliers (including those due to operational restraints, industrial relations, transportation difficulties, accidents or natural disasters), or the introduction of new laws or regulations that make access to waste polypropylene more difficult or expensive. PCT has entered into four feedstock supply agreements each for a term of three years with automatic one-year renewals for 17 years, and one feedstock supply agreement for a term ending October 31, 2023 (collectively, the “Feedstock Supply Agreements”). The Feedstock Supply Agreements are subject to prior termination by either party upon ninety days’ notice prior to expiration of the current term. The Feedstock Supply Agreements provide for a combined guaranteed minimum of 60 MMlb/yr. of feedstock and at PCT’s option for a combined maximum of 195 MMlb/yr., and up to a combined 210 MMlb/yr. as an option to be mutually agreed to. The amount of feedstock to be supplied each year by each supplier is determined prior to each year in an Annual Volume Commitment (as defined therein). The feedstock suppliers guarantee that they will not sell to other parties or otherwise dispose of any portion of feedstock up to the Annual Volume Commitment. While there are no penalties stated in the Feedstock Supply Agreements for failure of either party to deliver and/or accept the committed quantity of feedstock, PCT may terminate an agreement by giving notice of nonrenewal as indicated above. While PCT believes it has sourced sufficient feedstock of desirable quality, it cannot guarantee that feedstock suppliers will have sufficient quantities available and at the appropriate specifications in accordance with their respective agreements with PCT. If feedstock is not available to PCT in sufficient quantity and of requisite quality, PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects could be materially adversely impacted.
28
Because PCT’s global expansion requires sourcing feedstock and supplies from around the world, including Europe, changes to international trade agreements, tariffs, import and excise duties, taxes or other governmental rules and regulations could adversely affect PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
PCT’s global expansion model will require sourcing feedstock from suppliers around the world. The U.S. federal government or other governmental bodies may propose changes to international trade agreements, tariffs, taxes and other government rules and regulations. If any restrictions or significant increases in costs or tariffs are imposed related to feedstock sourced from Europe, or elsewhere, as a result of amendments to existing trade agreements, and PCT’s supply costs consequently increase, PCT may be required to raise UPRP prices, which may result in decreased margins, the loss of customers, and a material adverse effect on PCT’s financial results. The extent to which PCT’s margins could decrease in response to any future tariffs is uncertain. PCT continues to evaluate the impact of effective trade agreements, as well as other recent changes in foreign trade policy on its supply chain, costs, sales and profitability. PCT is actively working through strategies to mitigate such impact, including reviewing feedstock sourcing options and working with feedstock suppliers. In addition, COVID-19 has resulted in increased travel restrictions and the extended shutdown of certain businesses throughout the world. The impact of COVID-19 on PCT’s business is uncertain at this time and will depend on future developments; however, prolonged closures in Europe, and elsewhere, may disrupt the operations of certain feedstock suppliers, which could, in turn, negatively impact PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. Any such impact could be material.
Risks Related to the Market for UPRP
The market for UPRP is still in the development phase and the acceptance of UPRP by manufacturers and potential customers is not guaranteed.
The customer approval process for the UPRP product may take longer than expected and certain potential customers may be slow to accept the product produced by PCT or may not accept it at all. PCT has agreed to a strategic partnership term sheet to enter into an offtake agreement with a term of 20 years, whereby PCT guarantees the UPRP product to meet specific criteria for color and opacity. There is no odor specification in the offtake agreements. Any such changes may require modifications to its executed offtake agreements, which provide for a combined guaranteed minimum sale of 63 MMlb/yr of UPRP at PCT’s option, and a combined maximum of 138 MMlb/yr. The amount of UPRP to be provided for sale under each agreement is determined prior to each year as an Annual Volume Commitment. PCT must provide samples of the product to each customer so that the customer may determine if the product meets specifications, regulatory and legal requirements, customer’s internal policies, and technical, safety, and other qualifications for UPRP use in the customer’s products. Upon delivery, the customer will have 30 days to inspect the UPRP and either accept or reject the material. Provided PCT has sufficient feedstock and that the UPRP meets the product specifications and conditions as determined in each offtake agreement, PCT should have sufficient product offtake capacity to accommodate a production rate of 107 MMlb/yr. The inability of PCT to provide, and there is no guarantee that PCT will be able to provide, product of sufficient quantity and quality for sale pursuant to the offtake agreements is likely to materially adversely affect PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Certain of PCT’s offtake agreements are subject to index pricing, and fluctuation in index prices may adversely impact PCT’s financial results.
While PCT expects the price of its UPRP to continue to command a premium over the price of virgin resin and not be subject to fluctuations in the price of virgin PP, there is no guarantee of this result. Offtake agreements contain pricing for PCT’s products at both fixed prices and Index prices. PCT is using Information Handling Services provided by IHS Market Ltd (“IHS”) as it relates to the monthly market movement price mechanism index known as “Global Plastics & Polymers Report, Month-End: Polypropylene (PP)” and “Homopolymer (GP Inj. Mldg.),” with the price description terms of “Contract-market; HC Bulk, Delivered; Ex-Discounts, rebates” (delivered via railcar), based on the lower value listed in “Cts/Lb.” Over the last two years the index has been as high as $0.93 in October 2018 and as low as $0.54 in April 2020. Should the modeled index price forecasted by IHS be materially lower than the IHS estimate, PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects may be materially adversely impacted.
29
Competition could reduce demand for PCT’s products or negatively affect PCT’s sales mix or price realization. Failure to compete effectively by meeting consumer preferences, developing and marketing innovative solutions, maintaining strong customer service and distribution relationships, and expanding solutions capabilities and reach could adversely affect PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
While PCT expects to produce a unique product in its UPRP, PCT operates in a competitive global market for polypropylene sources — virgin and recycled polypropylene. Competitors or new entrants might develop new products or technologies which compete with PCT and its proprietary Technology. PCT cannot predict changes that might affect its competitiveness or whether existing competitors or new entrants might develop products that reduce demand for PCT’s UPRP. The development of new products or technologies which compete with PCT’s UPRP may have a material adverse effect on PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
In addition, PCT has granted a sublicense of P&G intellectual property back to P&G under the terms of the License Agreement, with a limited right to sublicense by P&G (the “Grant Back”). Under the Grant Back, for five years after the effective date of the License Agreement, the aggregate tonnage that may be produced under the Grant Back will be capped at a certain level per year worldwide. Beyond year 5, that aggregate annual tonnage will be expanded for each of the six regions worldwide. P&G has agreed that territory under the Grant Back will exclude the start of construction of a plant within a certain radius of the Project for five years from the effective date of the License Agreement. If PCT is able to establish production, either on its own or through a sublicense agreement with another partner, in any territory, P&G production will remain capped within that territory beyond the 5 years. If P&G sublicenses the P&G intellectual property under the Grant Back to other manufacturers, UPRP production and supply could increase, adversely impacting PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Risks Related to Regulatory Developments
PCT may not be able to meet applicable regulatory requirements for the use of PCT’s UPRP in food grade applications, and, even if the requirements are met, complying on an ongoing basis with the numerous regulatory requirements applicable to the UPRP and PCT’s facilities will be time-consuming and costly.
The use of UPRP in food grade applications is subject to regulation by various government agencies, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”). The FDA has established certain guidelines for the use of recycled plastics in food packaging, as set forth in the FDA’s Guidance for Industry: Use of Recycled Plastics in Food Packaging (Chemistry Considerations). In order for the UPRP to be used in food grade applications, it must receive a No Objection Letter (“NOL”) from the FDA. The process for obtaining an NOL will include FDA evaluation of both the PCT purification process, the Technology, as well as the recycled feedstock resin. As such, PCT will seek multiple NOLs for type of use and for each categorically different source of feedstock. In addition, as needed, individual migration studies will be conducted to simulate articles in contact with food.
We cannot guarantee the receipt of the NOLs and a failure to receive the requested NOLs will have an adverse effect on PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Furthermore, changes in regulatory requirements, laws and policies, or evolving interpretations of existing regulatory requirements, laws and policies, may result in increased compliance costs, delays, capital expenditures and other financial obligations that could adversely affect PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We expect to encounter regulations in most if not all of the countries in which we may seek to expand, and we cannot be sure that we will be able to obtain necessary approvals in a timely manner or at all. If PCT’s UPRP does not meet applicable regulatory requirements in a particular country or at all, then we may face limited market demand in those countries and PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects will be adversely affected.
The various regulatory schemes applicable to PCT’s UPRP will continue to apply following initial approval.
30
Monitoring regulatory changes and ensuring our ongoing compliance with applicable requirements is time-consuming and may affect our business, financial condition, results of operation and prospects. If we fail to comply with such requirements on an ongoing basis, we may be subject to fines or other penalties, or may be prevented from selling our UPRP, and PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operation and prospects may be harmed.
The operation of and construction of the Project is subject to governmental regulation.
Under the loan agreement entered into in connection with PCT’s outstanding Revenue Bonds (the “Loan Agreement”), PCT must: (i) not commence construction or operation of the Project prior to receipt of all applicable permits and easements required for the particular phase of construction or operation; (ii) abide by the terms and conditions of all such permits and easements; and (iii) operate the Project at all times in the manner required or permitted by such permits and easements.
PCT has not identified any technical or engineering circumstances that it believes would prevent the issuance of the key permits and approvals required for construction and operation of the Project in the ordinary course consistent with the planned construction of the Project. Delays in or failure to obtain and maintain any required permit or approval, or delay in satisfying or failure to satisfy any condition or requirement or any approval or permit could delay or prevent completion of the Project or result in additional costs or reduced revenues. Federal, state and local statutory and regulatory requirements applicable to construction and operation of the Project are subject to change. No assurance can be given that PCT or any other affected party will be able to comply with such changes. Additional statutory or regulatory requirements may be imposed upon the Project in the future, which might materially increase costs of operation or maintenance.
Legislative, regulatory or judicial developments could affect PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
PCT is subject to extensive air, water and other environmental laws and regulations at the federal and state level, as well as foreign regulatory schemes in Europe, such as the European Food Safety Authority. In addition, PCT will be subject to additional regulatory regimes upon expanding to new regions, such as Asia. Some of these laws require or may require PCT to operate under a number of environmental permits. These laws, regulations and permits can often require pollution control equipment or operational changes to limit actual or potential impacts to the environment. These laws, regulations and permit conditions may change and become more difficult to comply with. A violation of these laws, regulations or permit conditions could result in substantial fines, damages, criminal sanctions, permit revocations and/or a plant shutdown. Any such action may have a material adverse effect on PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects and result in the Company’s inability to pay debt service on its outstanding debt.
Risks Related to Human Capital Management
PCT is dependent on management and key personnel, and PCT’s business would suffer if it fails to retain its key personnel and attract additional highly skilled employees.
PCT’s success is dependent on the specialized skills of its management team and key operating personnel. This may present particular challenges as PCT operates in a highly specialized industry sector, which may make replacement of its management team and key operating personnel difficult. A loss of the managers or key employees, or their failure to satisfactorily perform their responsibilities, could have an adverse effect on PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
PCT’s future success will depend on its ability to identify, hire, develop, motivate and retain highly qualified personnel for all areas of its organization, particularly research and development, recycling technology, operations and sales. Trained and experienced personnel are in high demand and may be in short supply. Many of the companies with which PCT competes for experienced employees have greater resources than PCT does and may be able to offer more attractive terms of employment. In addition, PCT invests significant time and expense in training employees, which increases their value to competitors that may seek to recruit them. PCT may not be able to attract, develop and maintain the skilled workforce necessary to operate its business, and labor expenses may increase as a result of a shortage in the supply of qualified personnel, which will negatively impact PCT’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
31
While ROCH and PCT work to complete the Business Combination, management’s focus and resources may be diverted from operational matters and other strategic opportunities.
Successful completion of the Business Combination may place a significant burden on management and other internal resources. The diversion of management’s attention and any difficulties encountered in the transition process could harm the new Combined Company’s business financial condition, results of operations and prospects. In addition, uncertainty about the effect of the Business Combination on PCT’s systems, employees, customers, partners, and other third parties, including regulators, may have an adverse effect on the new Combined Company. These uncertainties may impair the new Combined Company’s ability to attract, retain and motivate key personnel for a period of time after the completion of the Business Combination.
PCT’s management has limited experience in operating a public company.
PCT’s executive officers and directors have limited experience in the management of a publicly traded company subject to significant regulatory oversight and the reporting obligations under federal securities laws. PCT’s management team may not successfully or effectively manage its transition to a public company following the Merger. Their limited experience in dealing with the increasingly complex laws pertaining to public companies could be a significant disadvantage in that it is likely that an increasing amount of their time may be devoted to these activities which will result in less time being devoted to the management and growth of PCT. It is possible that the Combined Company will be required to expand its employee base and hire additional employees to support its operations as a public company, which will increase its operating costs in future periods.
Risks Related to the Combined Company’s Common Stock
An active trading market for the Combined Company’s Common Stock may never develop or be sustained, which may make it difficult to sell the shares of the Combined Company’s Common Stock you purchase.
An active trading market for the Combined Company’s Common Stock may not develop or continue or, if developed, may not be sustained, which would make it difficult for you to sell your shares of the Combined Company’s Common Stock at an attractive price (or at all). The market price of the Combined Company’s Common Stock may decline below your purchase price, and you may not be able to sell your shares of the Combined Company’s Common Stock at or above the price you paid for such shares (or at all).
There can be no assurance that Combined Company’s Common Stock will be approved for listing on NASDAQ upon the Closing, or if approved, that the Combined Company will be able to comply with the continued listing standards of NASDAQ.
ROCH’s Common Stock is currently listed on NASDAQ. In connection with the Closing, we intend to apply to list the ParentCo Common Stock, warrants and units on NASDAQ upon the Closing under the symbol “PCT”, “PCTTW” and “PCTTU”, respectively. As part of the application process, we are required to provide evidence that we are able to meet the initial listing requirements of NASDAQ, which are more rigorous than NASDAQ’s continued listing requirements and include, among other things, a requirement that the Combined Company have 300 or more unrestricted round lot holders, at least 150 of which hold unrestricted shares with a minimum value of $2,500, and meet a minimum public float. The Combined Company’s ability to meet these listing requirements may depend, in part, on the number of shares of Common Stock that are redeemed in connection with the Business Combination, as the number of redemptions may impact whether the Combined Company has at least 300 unrestricted round lot holders upon the Closing, among other initial listing requirements. The Combined Company’s application has not yet been approved, and may not be approved if we are unable to provide evidence satisfactory to NASDAQ that the Combined Company will meet these listing requirements.
If the Combined Company’s Common Stock is not approved for listing on NASDAQ or, after the Closing, NASDAQ delists the Combined Company’s shares from trading on its exchange for failure to meet the listing standards, the Combined Company and its stockholders could face significant material adverse consequences including:
| • | a limited availability of market quotations for the Combined Company’s securities; |
32
| • | reduced liquidity for the Combined Company’s securities; |
| • | a determination that the Combined Company’s Common Stock is a “penny stock” which will require brokers trading in the Combined Company’s Common Stock to adhere to more stringent rules and possibly result in a reduced level of trading activity in the secondary trading market for the Combined Company’s securities; |
| • | a limited amount of news and analyst coverage; and |
| • | a decreased ability to issue additional securities or obtain additional financing in the future. |
The market price of the Combined Company’s common stock is likely to be highly volatile, and you may lose some or all of your investment.
Following the Business Combination, the market price of Combined Company’s common stock is likely to be highly volatile and may be subject to wide fluctuations in response to a variety of factors, including the following:
| • | the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on PCT’s business; |
| • | the inability to obtain or maintain the listing of the Combined Company’s shares of Common Stock on NASDAQ; |
| • | the inability to recognize the anticipated benefits of the Business Combination, which may be affected by, among other things, competition, PCT’s ability to grow and manage growth profitably, and retain its key employees; |
| • | changes in applicable laws or regulations; |
| • | risks relating to the uncertainty of PCT’s projected financial information; |
| • | risks related to the organic and inorganic growth of PCT’s business and the timing of expected business milestones; and |
| • | the amount of redemption requests made by ROCH’s stockholders. |
In addition, the stock markets have experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations that have affected and continue to affect the market prices of equity securities of many companies. These fluctuations have often been unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of those companies. Broad market and industry factors, as well as general economic, political, regulatory and market conditions, may negatively affect the market price of the Combined Company’s Common Stock, regardless of the Combined Company’s actual operating performance.
Volatility in the Combined Company’s share price could subject the Combined Company to securities class action litigation.
In the past, securities class action litigation has often been brought against a company following a decline in the market price of its securities. If the Combined Company faces such litigation, it could result in substantial costs and a diversion of management’s attention and resources, which could harm its business.
If securities or industry analysts do not publish research or reports about the Combined Company, or publish negative reports, the Combined Company’s stock price and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for the Combined Company’s common stock will depend, in part, on the research and reports that securities or industry analysts publish about the Combined Company. The Combined Company does not have any control over these analysts. If the Combined Company’s financial performance fails to meet analyst estimates or one or more of the analysts who cover the Combined Company downgrade its common stock or change their opinion, the Combined Company’s stock price would likely decline. If one or more of these analysts cease coverage of the Combined Company or fail to regularly publish reports on the Combined Company, it could lose visibility in the financial markets, which could cause the Combined Company’s stock price or trading volume to decline.
33
Because the Combined Company does not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future, capital appreciation, if any, would be your sole source of gain.
The Combined Company currently anticipates that it will retain future earnings for the development, operation and expansion of its business and do not anticipate declaring or paying any cash dividends for the foreseeable future. As a result, capital appreciation, if any, of the Combined Company’s shares of common stock would be your sole source of gain on an investment in such shares for the foreseeable future.
The exercise of registration rights or sales of a substantial amount of the Combined Company’s Common Stock after the Business Combination may adversely affect the market price of the Combined Company’s Common Stock.
In connection with the consummation of the Business Combination, the Merger Agreement provides that Roth Capital Partners, LLC (“Roth”), Craig-Hallum Capital Group, LLC (“C-H”), the Combined Company and certain Initial Stockholders and PCT Unitholders (collectively, the “IRA Holders”) will enter into an Investor Rights Agreement pursuant to which the Combined Company will be obligated to file a registration statement to register the resale of certain securities of the Combined Company held by the IRA Holders. IRA Holders will have certain demand rights and “piggy-back” registration rights, subject to certain requirements and customary conditions. The Combined Company also has agreed to register the shares of the Combined Company’s Common Stock issued in connection with the PIPE prior to the consummation of the Business Combination.
In connection with its issuance of Convertible Notes, PCT has entered into a registration rights agreement (the “Magnetar Registration Rights Agreement”) with a series of funds affiliated with Magnetar Capital LLC (the “Magnetar Investors”). Pursuant to the Magnetar Registration Rights Agreement, PCT, ROCH, or an affiliate thereof is required to file a registration statement to register the resale of the Common Stock (as defined therein) held by the Magnetar Investors upon conversion of the Convertible Notes no later than 60 days following the consummation of the Business Combination, and is required to have such registration statement declared effective by a certain period of time or pay liquidated damages. The Magnetar Investors also have certain demand rights, subject to certain requirements and customary conditions.
The registration and availability of such a significant number of securities for trading in the public market may have an adverse effect on the market price of the Combined Company’s Common Stock. See “Shares Eligible for Future Sale.”
Future offerings of debt or offerings or issuances of equity securities by the Combined Company may adversely affect the market price of the Combined Company’s Common Stock or otherwise dilute all other stockholders.
In the future, we may attempt to obtain financing or to further increase the Combined Company’s capital resources by issuing additional shares of the Combined Company’s Common Stock or offering debt or other equity securities, including commercial paper, medium-term notes, senior or subordinated notes, debt securities convertible into equity or shares of preferred stock. We also expect to grant equity awards to employees, directors, and consultants under the Combined Company’s stock incentive plans. Future acquisitions could require substantial additional capital in excess of cash from operations. The Combined Company would expect to obtain the capital required for acquisitions through a combination of additional issuances of equity, corporate indebtedness and/or cash from operations.
Issuing additional shares of the Combined Company’s Common Stock or other equity securities or securities convertible into equity may dilute the economic and voting rights of the Combined Company’s existing stockholders or reduce the market price of the Combined Company’s Common Stock or both. Upon liquidation, holders of such debt securities and preferred shares, if issued, and lenders with respect to other borrowings would receive a distribution of the Combined Company’s available assets prior to the holders of the Combined Company’s Common Stock. Debt securities convertible into equity could be subject to adjustments in the conversion ratio pursuant to which certain events may increase the number of equity securities issuable upon conversion. Preferred shares, if issued, could have a preference with respect to liquidating distributions or a preference with respect to dividend payments that could limit the Combined Company’s ability to pay dividends to the holders of the Combined Company’s Common Stock. The Combined Company’s decision to issue securities in any future offering will depend on market conditions and other factors beyond the Combined Company’s control, which may adversely affect the amount, timing and nature of the Combined Company’s future offerings.
34
Certain provisions of the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and the Amended and Restated Bylaws (both as defined in “Description of Securities to be Registered”) could hinder, delay or prevent a change in control of the Combined Company, which could adversely affect the price of the Combined Company’s Common Stock.
Certain provisions of the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and the Amended and Restated Bylaws could make it more difficult for a third party to acquire the Combined Company without the consent of the Combined Company’s board of directors. These provisions include:
| • | authorizing the issuance of undesignated preferred stock, the terms of which may be established and the shares of which may be issued without stockholder approval, and which may include super voting, special approval, dividend, or other rights or preferences superior to the rights of the holders of the Combined Company’s Common Stock; |
| • | prohibiting stockholder action by written consent, requiring all stockholder actions be taken at a meeting of our stockholders; |
| • | providing that the board of directors is expressly authorized to make, alter or repeal the Amended and Restated Bylaws; |
| • | until the fifth anniversary of the effectiveness of the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, providing that directors may be removed only for cause and then only by the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the voting power of the outstanding shares then entitled to vote in an election of directors, voting together as a single class; |
| • | providing that vacancies on the Combined Company’s board of directors, including newly-created directorships, may be filled only by a majority vote of directors then in office; |
| • | prohibiting stockholders from calling special meetings of stockholders; |
| • | until the fifth anniversary of the effectiveness of the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, requiring the affirmative vote of the holders of at least 66 2∕3% in voting power of the outstanding shares then entitled to vote in an election of directors, voting together as a single class, to amend certain provisions of the Amended and Restated Bylaws and certain provisions of the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation; |
| • | establishing advance notice requirements for nominations for elections to our board of directors or for proposing matters that can be acted upon by stockholders at stockholder meetings; and |
| • | establishing a classified board of directors until the fifth anniversary of the effectiveness of the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, as a result of which our board of directors will be divided into three classes, with each class serving for staggered three-year terms, which prevents stockholders from electing an entirely new board of directors at an annual meeting. |
In addition, these provisions may make it difficult and expensive for a third party to pursue a tender offer, change in control or takeover attempt that is opposed by our management or our board of directors. Stockholders who might desire to participate in these types of transactions may not have an opportunity to do so, even if the transaction is favorable to them. These anti-takeover provisions could substantially impede your ability to benefit from a change in control or change our management and board of directors and, as a result, may adversely affect the market price of the Combined Company’s Common Stock and your ability to realize any potential change of control premium. See “Description of Securities to be Registered — Anti-Takeover Effects of the Combined Company’s Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws and Certain Provisions of Delaware Law.”
General Risk Factors
Each of ROCH and PCT have incurred and will incur substantial costs in connection with the Business Combination and related transactions, such as legal, accounting, consulting and financial advisory fees.
As part of the Business Combination, each of ROCH and PCT are utilizing professional service firms for legal, accounting and financial advisory services. Although the parties have been provided with estimates of the costs for each advisory firm, the total actual costs may exceed those estimates. In addition, the companies are retaining consulting services to assist in the integration of the businesses, including but not limited to organizational decisions, Combined Company business process design, cultural integration and go-to-market integration. These consulting services may extend beyond the current estimated time frame thus resulting in higher than expected costs.
35
The Combined Company may be unable to obtain additional financing to fund the operations and growth of the business following the consummation of the Business Combination.
The Combined Company may require additional financing to fund its operations or growth following the consummation of the Business Combination. The failure to secure additional financing could have a material adverse effect on the continued development or growth of the Combined Company. Such financings may result in dilution to stockholders, issuance of securities with priority as to liquidation and dividend and other rights more favorable than common stock, imposition of debt covenants and repayment obligations, or other restrictions that may adversely affect its business. In addition, the Combined Company may seek additional capital due to favorable market conditions or strategic considerations even if it believes that it has sufficient funds for current or future operating plans. There can be no assurance that financing will be available to the Combined Company on favorable terms, or at all. The inability to obtain financing when needed may make it more difficult for the Combined Company to operate its business or implement its growth plans.
The Combined Company will be an emerging growth company, and the Combined Company cannot be certain if the reduced reporting requirements applicable to emerging growth companies will make its shares less attractive to investors.
After the completion of the Business Combination, the Combined Company will be an emerging growth company, as defined in the JOBS Act. For as long as the Combined Company continues to be an emerging growth company, it may take advantage of exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not “emerging growth companies,” including exemption from compliance with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404, reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation and exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. The Combined Company will remain an emerging growth company until the earlier of (1) the date (a) May 7, 2025, (b) in which the Combined Company has total annual gross revenue of at least $1.07 billion or (c) in which the Combined Company is deemed to be a large accelerated filer, which means the market value of shares of the Combined Company’s common stock that are held by non-affiliates exceeds $700 million as of the prior June 30th, and (2) the date on which the Combined Company has issued more than $1.0 billion in non-convertible debt during the prior three-year period.
In addition, under the JOBS Act, emerging growth companies can delay adopting new or revised accounting standards until such time as those standards apply to private companies. The Combined Company has irrevocably elected not to avail itself of this exemption from new or revised accounting standards and, therefore, the Combined Company will be subject to the same new or revised accounting standards as other public companies that are not emerging growth companies.
Even after the Combined Company no longer qualifies as an emerging growth company, it may still qualify as a “smaller reporting company,” which would allow it to take advantage of many of the same exemptions from disclosure requirements including exemption from compliance with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404 and reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in this proxy statement and the Combined Company’s periodic reports and proxy statements.
The Combined Company cannot predict if investors will find its common stock less attractive because the Combined Company may rely on these exemptions. If some investors find the Combined Company’s common stock less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for the common stock and its market price may be more volatile.
36
PCT identified certain material weaknesses in its internal control over financial reporting. If PCT is unable to remediate these material weaknesses, or if PCT identifies additional material weaknesses in the future or otherwise fails to maintain an effective system of internal controls, PCT may not be able to accurately or timely report its financial condition or results of operations, which may adversely affect PCT’s business and stock price.
In connection with the preparation and audit of PCT’s consolidated financial statements for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 and the balance sheet data as of September 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019 and 2018, certain material weaknesses were identified in PCT’s internal control over financial reporting. A material weakness is a deficiency, or combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of PCT’s interim or annual consolidated financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. The material weaknesses were as follows:
| • | PCT did not have sufficient, qualified personnel to determine the appropriate accounting treatment for its complex agreements or transactions that required technical accounting analysis; |
| • | PCT’s lack of sufficient personnel also resulted in inadequate segregation of duties in the design and operation of the internal controls over financial reporting; |
| • | PCT’s lack of formal processes and controls resulted in an ineffective control environment, which led to an inadequate review of the financial statements and financial reporting; |
| • | PCT did not design and maintain effective controls over certain information technology (“IT”) controls for information systems that are relevant to the preparation of its financial statements, specifically with respect to user access, to ensure appropriate segregation of duties that adequately restrict user access to financial applications, programs, and data to appropriate company personnel; and |
| • | PCT did not design and maintain effective controls surrounding the completeness and cutoff of expenses and payables, such that certain expenses paid by a related entity on behalf of PCT were not appropriately allocated to PCT, and certain transactions were recorded in the period when the invoice was received rather than accrued in the period when the activity took place. |
These material weaknesses could result in a misstatement of substantially all of PCT’s accounts or disclosures, which would result in a material misstatement to the interim or annual consolidated financial statements that would not be prevented or detected. PCT has begun implementation of a plan to remediate the material weaknesses described above. Those remediation measures are ongoing and include the following:
| • | In 2018 and 2019 there were two accounting employees; both were part time, and one of which was an accounts payable clerk. PCT management is increasing staffing and has brought in outside resources. PCT has since hired a CFO, a Vice President of Finance, and a Controller and is looking to hire an Executive VP Finance to support the CFO and provide leadership to the accounting team. PCT has also engaged a public accounting firm to assist with financial reporting and advise on technical accounting issues; |
| • | PCT is making certain changes to its IT systems, including the development of formal access policies, the development of an audit of administrator activity and the reassignment of administrator privileges over PCT’s accounting system outside PCT’s accounting department; and |
| • | PCT is establishing a process to maintain checklists tracking related entity payments as part of its monthly close processes and is instituting policies to strengthen its receipt and processing of purchase orders to monitor accrual determinations. Furthermore, payment for almost all PCT expenses has been moved to PCT, with only a limited number of expenses paid by a related entity for situations where there is a shared contract. |
PCT plans to continue to assess its internal controls and procedures and intends to take further action as necessary or appropriate to address any other matters it identifies or are brought to its attention. PCT cannot assure you that the measures it has taken to date and may take in the future will be sufficient to remediate the control deficiencies that led to PCT’s material weaknesses in internal control over financial reporting or that PCT will prevent or avoid potential future material weaknesses. The effectiveness of PCT’s internal control over financial reporting is subject to various inherent limitations, including cost limitations, judgments used in decision making, assumptions about the likelihood of future events, the possibility of human error and the risk of fraud. If PCT is unable to remediate the material weaknesses, its ability to record, process and report financial information accurately, and to prepare financial statements within the time periods specified by the forms of the SEC, could be adversely affected which, in turn, may adversely affect PCT’s reputation and business and the market price of the Combined Company’s Common Stock.
In addition, any such failures could result in litigation or regulatory actions by the SEC or other regulatory authorities, loss of investor confidence, delisting of the Combined Company’s securities and harm to the Combined Company’s reputation and financial condition, or diversion of financial and management resources from the operation of PCT’s business.
37
Following the consummation of the Business Combination, the Combined Company will incur significant increased expenses and administrative burdens as a public company, which could have an adverse effect on its business, financial condition and results of operations.
Following the consummation of the Business Combination, the Combined Company will face increased legal, accounting, administrative and other costs and expenses as a public company that PCT does not incur as a private company. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (the “Sarbanes-Oxley Act”), including the requirements of Section 404, as well as rules and regulations subsequently implemented by the SEC, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 and the rules and regulations promulgated and to be promulgated thereunder, the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) and the securities exchanges, impose additional reporting and other obligations on public companies. Compliance with public company requirements will increase costs and make certain activities more time-consuming. A number of those requirements will require the Combined Company to carry out activities PCT has not done previously. For example, the Combined Company will create new board committees and adopt new internal controls and disclosure controls and procedures. In addition, additional expenses associated with SEC reporting requirements will be incurred. Furthermore, if any issues in complying with those requirements are identified (for example, if the auditors identify material weaknesses in addition to those disclosed herein or a significant deficiency in the internal control over financial reporting), the Combined Company could incur additional costs rectifying those issues, and the existence of those issues could adversely affect the Combined Company’s reputation or investor perceptions of it. It may also be more expensive to obtain director and officer liability insurance in such a situation. Risks associated with the Combined Company’s status as a public company may make it more difficult to attract and retain qualified persons to serve on the board of directors or as executive officers. The additional reporting and other obligations imposed by these rules and regulations will increase legal and financial compliance costs and the costs of related legal, accounting and administrative activities. These increased costs will require the Combined Company to divert a significant amount of money that could otherwise be used to expand the business and achieve strategic objectives. Advocacy efforts by stockholders and third parties may also prompt additional changes in governance and reporting requirements, which could further increase costs.
The Combined Company’s failure to timely and effectively implement controls and procedures required by Section 404(a) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act that will be applicable to it after the Business Combination is consummated could negatively impact its business.
PCT is currently not subject to Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. However, following the consummation of the Business Combination, the Combined Company will be required to provide management’s attestation on internal controls. The standards required for a public company under Section 404(a) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act are significantly more stringent than those required of PCT as a privately held company. Management may not be able to effectively and timely implement controls and procedures that adequately respond to the increased regulatory compliance and reporting requirements that will be applicable after the Business Combination. If the Combined Company is not able to implement the additional requirements of Section 404(a) in a timely manner or with adequate compliance, it may not be able to assess whether its internal controls over financial reporting are effective, which may subject it to adverse regulatory consequences and could harm investor confidence and the market price of its securities.
38
We will not receive any proceeds from the sale of the ParentCo Common Stock by the Selling Stockholders.
39
unaudited pro forma condensed combined Financial Information
Defined terms included below shall have the same meaning as terms defined and included elsewhere in this prospectus.
Introduction
ParentCo is providing the following unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information to aid you in your analysis of the financial aspects of the Business Combination.
In May 2020, the SEC adopted Release No. 33-10786 “Amendments to Financial Disclosures about Acquired and Disposed Businesses.” Release No. 33-10786 is effective on January 1, 2021; however, voluntary early adoption is permitted. ParentCo has elected to early adopt the provisions of Release No. 33-10786, and the Summary Pro Forma Information is presented in accordance therewith.
ROCH is a special purpose acquisition company whose purpose is to acquire, through a merger, share exchange, asset acquisition, stock purchase, reorganization or other similar business combination with one or more businesses. ROCH was incorporated in Delaware on February 13, 2019, as Roth CH Acquisition I Co. On May 4, 2020, ROCH consummated its IPO. The IPO, of 7,500,000 of its Units, each consisting of one share of Common Stock and three quarters of a Warrants, generated gross proceeds to ROCH of $75.0 million. Simultaneously with the consummation of the IPO, ROCH completed the private sale of 262,500 Private Units (consisting of Private Shares and related Private Warrants) at a purchase price of $10.00 per unit to its Initial Stockholders generating gross proceeds of $2.6 million. Each Private Unit consists of one share of ParentCo Common Stock and three quarters of a warrant to purchase shares of ParentCo Common Stock at an exercise price of $11.50. Following the closing of the IPO on May 7, 2020, an amount of $75.0 million ($10.00 per Unit) from the net proceeds of the sale of the Units in the IPO and the sale of the Private Units was placed in a Trust Account which will be invested only in U.S. government securities, within the meaning set forth in Section 2(a)(16) of the Investment Company Act of 1940, with a maturity of 180 days or less or in a money market fund meeting the conditions of Rule 2a-7 of the Investment Company Act. On May 26, 2020, in connection with the underwriters’ election to partially exercise their over- allotment option, ROCH sold an additional 150,000 Units at a purchase price of $10.00 per Unit, generating gross proceeds of $1.5 million. In addition, in connection with the underwriters’ partial exercise of their over-allotment option, ROCH also consummated the sale of an additional 3,000 Private Units at a purchase price of $10.00 per Private Unit, generating gross proceeds of $30,000. Following such closing, an additional $1.5 million was deposited into the Trust Account, resulting in $76.5 million being held in the Trust Account. ROCH has 18 months from the closing of the IPO (by November 7, 2021) to complete an initial business combination.
PCT and its wholly owned subsidiaries, Purecycle: Ohio LLC, PCT Managed Services LLC and PCO Holdco LLC, are businesses whose planned principal operations are to conduct business as a plastics recycler using a patented recycling process. Developed and licensed by P&G (as defined herein), the patented recycling process separates color, odor and other contaminants from plastic waste feedstock to transform it into virgin-like resin, referred to as ultra-pure recycled polypropylene (“UPRP”). PCT is currently constructing its Phase II Facility and conducting research and development activities to operationalize the Technology.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet as of September 30, 2020 combines the historical balance sheet of ROCH and the historical balance sheet of PCT on a pro forma basis as if the Business Combination and the related transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement, summarized below, had been consummated on September 30, 2020. The unaudited pro forma combined statements of operations for the year ended December 31, 2019 and condensed combined statement of operations for the nine months ended September 30, 2020, combine the historical statements of operations of ROCH and PCT for such periods on a pro forma basis as if the Business Combination and the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement, summarized below, had been consummated on January 1, 2019, the beginning of the earliest period presented. The transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement that are given pro forma effect include:
| • | PCT Adjustments represent transactions that have occurred in anticipation of the Business Combination that are required to be presented to illustrate the effects of the Business Combination on a Pro Forma basis, including the following: |
40
| • | The net proceeds from the issuance of the Convertible Notes and the issuance of Class A and Class B-1 equity; and |
| • | Payment of certain PCT debt with the Convertible Notes and equity issuance proceeds. |
| • | Transaction accounting adjustments represent adjustments that are expected to occur in connection with the Closing of the Business Combination, including the following: |
| • | The reverse recapitalization between Merger Sub LLC and PCT; |
| • | The net proceeds from the issuance of ParentCo Common Stock in the PIPE Investment; and |
| • | The net proceeds from the issuance of Revenue Bonds that are made available to the Combined Company upon Closing of the Business Combination. |
The pro forma condensed combined financial information may not be useful in predicting the future financial condition and results of operations of the Combined Company. The actual financial position and results of operations may differ significantly from the pro forma amounts reflected herein due to a variety of factors.
The historical financial information of ROCH was derived from the unaudited and audited financial statements of ROCH as of and for the nine months ended September 30, 2020, and for the year ended December 31, 2019, which are included elsewhere in this prospectus. The historical financial information of PCT was derived from the unaudited and audited consolidated financial statements of PCT as of and for the nine months ended September 30, 2020, and for the year ended December 31, 2019, which are included elsewhere in this prospectus. This information should be read together with ROCH’s and PCT’s unaudited and audited financial statements and related notes, the section titled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and other financial information included elsewhere in this prospectus.
The Business Combination will be accounted for as a reverse recapitalization, in accordance with GAAP. Under this method of accounting, ROCH will be treated as the “acquired” company for financial reporting purposes. Accordingly, the Business Combination will be treated as the equivalent of PCT issuing stock for the net assets of ROCH, accompanied by a recapitalization. The net assets of ROCH will be stated at historical cost, with no goodwill or other intangible assets recorded. Operations prior to the Business Combination will be those of PCT.
PCT has been determined to be the accounting acquirer based on evaluation of the following facts and circumstances under both the minimum and maximum redemption scenarios:
| • | PCT will have the largest single voting interest block in the Combined Company under the minimum redemption scenario and the maximum redemption scenario; |
| • | PCT will have the ability to nominate the majority of the members of the board of directors following the closing; |
| • | PCT will hold executive management roles for the Combined Company and be responsible for the day-to-day operations; |
| • | The Combined Company will assume PCT’s name; and |
| • | The intended strategy of the Combined Company will continue PCT’s current strategy of being a leader in plastics recycling. |
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information has been prepared using the assumptions below with respect to the potential redemption into cash of Common Stock:
| • | Assuming Minimum Redemptions: This presentation assumes that no public stockholders of ROCH exercise redemption rights with respect to their Public Shares for a pro rata share of the funds in the Trust Account. |
| • | Assuming Maximum Redemptions: This presentation assumes that stockholders holding 6.9 million of the Public Shares will exercise their redemption rights for their pro rata share (approximately $10.00 per share) of the funds in the Trust Account. This scenario gives effect to Public Share redemptions for aggregate redemption payments of $69.3 million using a $10.00 per share redemption price. The Merger Agreement includes as a condition to closing the Business Combination that, at the closing, ROCH will have a minimum of $250.0 million in cash comprising (i) the cash held in the Trust Account after giving effect to ROCH share redemptions and (ii) proceeds from the PIPE Investment and a minimum of $5.0 million of net tangible assets. Additionally, this presentation also contemplates that ROCH’s Initial Stockholders have agreed to waive their redemption rights with respect to their Founder Shares, Private Shares and Public Shares in connection with the completion of a Business Combination. |
41
Description of the Business Combination
The aggregate consideration for the Business Combination will be $1,156.9 million, payable in the form of shares of the ParentCo Common Stock and assumed indebtedness.
The following summarizes the merger consideration in both the minimum redemption and maximum redemption scenarios:
| Total shares transferred* | 83,500,000 | |||
| Value per share | 10.00 | |||
| Total Share Consideration | $ | 835,000,000 | ||
| Assumed indebtedness | ||||
| Revenue Bonds | 249,600,000 | |||
| The Convertible Notes | 60,000,000 | |||
| Term Loan | 313,500 | |||
| Related Party Promissory Note | 12,000,000 | |||
| Total merger consideration | $ | 1,156,913,500 |
* Amount excludes the issuance of 4.0 million earnout shares to certain unitholders of PCT as a result of the Combined Company satisfying the performance and operational targets subsequent to the closing of the Business Combination
The following summarizes the pro forma ParentCo Common Stock outstanding under the two redemption scenarios (in thousands):
| Assuming Minimum Redemptions (Shares) | % | Assuming Maximum Redemptions (Shares) | % | |||||||||||||
| PCT Shareholders | 83,500 | 70.6 | % | 83,500 | 75.0 | % | ||||||||||
| Total PCT Inc Merger Shares | 83,500 | 70.6 | % | 83,500 | 75.0 | % | ||||||||||
| ROCH Public Shares | 7,645 | 6.5 | % | 717 | 0.6 | % | ||||||||||
| ROCH Founder and Private Shares | 2,183 | 1.8 | % | 2,183 | 2.0 | % | ||||||||||
| Total ROCH Shares | 9,828 | 8.3 | % | 2,900 | 2.6 | % | ||||||||||
| PIPE investors | 25,000 | 21.1 | % | 25,000 | 22.4 | % | ||||||||||
| Pro Forma ParentCo Common Stock at September 30, 2020 | 118,328 | 100.0 | % | 111,400 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||
The two redemption scenarios exclude PCT’s outstanding warrants, options, and unvested Class C Units. Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, 143,619 outstanding warrants will be canceled and such agreement terminated pursuant to the issuance of conditional replacement warrants by ParentCo. An agreement for the future issuance of 6,347 Class A Units, with the option to purchase an additional 7,990 Class A Units will be amended to allow for the future issuance and purchase of shares of ParentCo Common Stock. The 144,366 outstanding unvested Class C Units will be ParentCo’s restricted shares, subject to the same vesting schedule and forfeiture restrictions as the unvested PCT Class C Units.
The following unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet as of September 30, 2020 and the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statements of operations for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and combined statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2019 are based on the historical financial statements of ROCH and PCT. The unaudited pro forma adjustments are based on information currently available, and assumptions and estimates underlying the unaudited pro forma adjustments are described in the accompanying notes. Actual results may differ materially from the assumptions used to present the accompanying unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information.
42
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED BALANCE SHEET AS OF SEPTEMBER 30, 2020
(in thousands)
| As
of September 30, 2020 | As
of September 30, 2020 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| As of September 30, 2020 | Transaction Accounting Adjustments | Pro Forma Combined | Transaction Accounting Adjustments | Pro Forma Combined | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCT (Historical) | PCT Adjustments | PCT As Adjusted | ROCH (Historical) | (Assuming No Redemption) | (Assuming No Redemption) | (Assuming Maximum Redemption) | (Assuming Maximum Redemption) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 108 | $ | — | A | $ | 52,645 | $ | 409 | $ | 76,523 | F | $ | 362,053 | $ | (69,276 | ) | N | $ | 292,777 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | (5,063 | ) | B | | | 250,000 | G | | | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | 57,600 | C | | | (2,677 | ) | H | | | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | (14,847 | ) | I | | | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted Cash | — | 30,000 | D | 89,775 | — | 237,428 | J | 327,203 | — | | 327,203 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | 59,775 | E | | | | | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prepaid royalties | 2,100 | — | | 2,100 | — | — | | 2,100 | — | | 2,100 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 2,964 | — | | 2,964 | 146 | (2,732 | ) | J | 378 | — | | 378 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total current assets | 5,172 | 142,312 | | 147,484 | 555 | 543,695 | | 691,734 | (69,276 | ) | | 622,458 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-current assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketable securities held in Trust Account | — | — | | — | 76,523 | (76,523 | ) | F | — | — | | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Property and equipment, net | 32,782 | — | | 32,782 | — | — | | 32,782 | — | | 32,782 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intangible assets | — | — | | — | — | — | | — | — | | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total non-current assets | 32,782 | — | | 32,782 | 76,523 | (76,523 | ) | | 32,782 | — | | 32,782 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | 37,954 | 142,312 | | 180,266 | 77,078 | 467,172 | | 724,516 | (69,276 | ) | | 655,240 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LIABILITIES, TEMPORARY EQUITY AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT | | | | | | | | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts payable | 1,865 | — | | 1,865 | 1 | — | | 1,866 | — | | 1,866 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accrued expenses | 2,772 | (77 | ) | B | 2,695 | 124 | (618 | ) | I | 2,201 | — | | 2,201 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Notes payable – current | 4,277 | (4,086 | ) | B | 191 | — | — | | 191 | — | | 191 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Due to related party | — | — | | — | — | — | | — | — | | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related party notes payable | 12,000 | — | | 12,000 | — | — | | 12,000 | — | | 12,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accrued and other current liabilities | — | — | | — | — | — | | — | — | | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total current liabilities | 20,914 | (4,163 | ) | | 16,751 | 125 | (618 | ) | | 16,258 | — | | 16,258 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-current liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred research and development obligation | 1,000 | — | | 1,000 | — | — | | 1,000 | — | | 1,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Notes Payable | 1,022 | (900 | ) | B | 122 | — | 234,696 | J | 234,818 | — | | 234,818 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Redeemable warrants | 8,183 | (8,183 | ) | A | — | — | — | | — | — | | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Convertible Promissory Notes | — | 59,775 | E | 59,775 | — | — | | 59,775 | — | | 59,775 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred underwriting fee payable | — | — | | — | 2,677 | (2,677 | ) | H | — | — | | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total non-current liabilities | 10,205 | 50,692 | | 60,897 | 2,677 | 232,019 | | 295,593 | — | | 295,593 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total liabilities | 31,119 | 46,529 | | 77,648 | 2,802 | 231,401 | | 311,851 | — | | 311,851 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commitment and Contingencies | | | | | | | | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Temporary equity: | | | | | | | | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common stock subject to possible redemption | — | — | | — | 69,276 | (69,276 | ) | K | — | — | | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity (deficit): | | | | | | | | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class A Common stock | — | — | | — | — | 7 | K | 113 | (7 | ) | N | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | 25 | G | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | 81 | L | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class A Common Units | 387 | 29,418 | D | 87,405 | — | (87,405 | ) | L | — | — | | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | 57,600 | C | | | | | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class B Preferred Units | 1,898 | 8,183 | A | 10,081 | — | (10,081 | ) | L | — | — | | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class B-1 Preferred Units | 41,162 | — | | 41,162 | — | (41,162 | ) | L | — | — | | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class C Profits Units | 6,590 | 717 | C | 7,889 | — | (7,889 | ) | L | — | — | | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | 582 | D | | | | | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 107 | — | | 107 | 5,225 | 69,269 | K | 459,557 | (69,269 | ) | N | 390,288 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | 249,975 | G | | | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | (11,250 | ) | I | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | (225 | ) | M | | | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | 146,456 | L | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Retained earnings (deficit) | (43,309 | ) | (717 | ) | C | (44,026 | ) | (225 | ) | 225 | M | (47,005 | ) | — | | (47,005 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | (2,979 | ) | I | | | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) | 6,835 | 95,783 | | 102,618 | 5,000 | 305,047 | | 412,665 | (69,276 | ) | | 343,389 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES, TEMPORARY EQUITY AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT | 37,954 | 142,312 | | 180,266 | 77,078 | 467,172 | | 724,516 | (69,276 | ) | | 655,240 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
43
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS FOR THE NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2020
(in thousands, except share and per share data)
For
the |
For
the 2020 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transaction Accounting |
Pro Forma | Transaction Accounting |
Pro Forma | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For the Nine Months Ended September 30, 2020 | Adjustments | Combined | Adjustments | Combined | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCT | PCT | PCT As |
ROCH | (Assuming No |
(Assuming No |
(Assuming Maximum |
(Assuming Maximum |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Historical) | Adjustments | Adjusted | (Historical) | Redemption) | Redemption) | Redemption) | Redemption) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating costs and expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating costs | 7,040 | — | 7,040 | 247 | — | 7,287 | — | 7,287 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative | 6,293 | (1,775 | ) | AA | 4,518 | — | (821 | ) | CC | 3,697 | — | 3,697 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Research and development | 528 | — | 528 | — | — | 528 | — | 528 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total operating costs and expenses | 13,861 | (1,775 | ) | 12,086 | 247 | (821 | ) | 11,512 | — | 11,512 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gain on sale of assets | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loss from operations | (13,861 | ) | 1,775 | (12,086 | ) | (247 | ) | 821 | (11,512 | ) | — | (11,512 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other income (expense): | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other income (expense) | 100 | — | 100 | — | — | 100 | — | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest income (expense) | (1,827 | ) | 739 | BB | (1,088 | ) | 24 | (24 | ) | DD | (1,088 | ) | — | (1,088 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on marketable securities held in Trust Account | — | — | (1 | ) | 1 | DD | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total other income (expense) | (1,727 | ) | 739 | (988 | ) | 23 | (23 | ) | (988 | ) | — | (988 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) before income tax provision | (15,588 | ) | 2,514 | (13,074 | ) | (224 | ) | 798 | (12,500 | ) | — | (12,500 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax provision | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | (15,588 | ) | 2,514 | (13,074 | ) | (224 | ) | 798 | (12,500 | ) | — | (12,500 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Assuming Minimum Redemptions (Note 4) |
Assuming Maximum Redemptions (Note 4) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weighted Common shares outstanding | 2,581,282 | 2,409,765 | 118,328,000 | 111,400,394 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic and diluted net income (loss) per share | $ | (7.91 | ) | $ | (0.09 | ) | $ | (0.11 | ) | $ | (0.11 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
44
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA COMBINED STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS FOR YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2019
(in thousands, except share and per share data)
| For
the Year ended December 31, 2019 | For
the Year ended December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transaction Accounting | Pro Forma | Transaction Accounting | Pro Forma | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For the Year ended December 31, 2019 | Adjustments | Combined | Adjustments | Combined | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCT | PCT | PCT As | ROCH | (Assuming No | (Assuming No | (Assuming Maximum | (Assuming Maximum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Historical) | Adjustments | Adjusted | (Historical) | Redemptions) | Redemptions) | Redemption) | Redemption) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating costs and expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating costs | 5,966 | — | 5,966 | 2 | — | 5,968 | — | 5,968 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative | 11,478 | (6,408 | ) | AA | 5,070 | — | 3,801 | CC | 8,871 | — | 8,871 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Research and development | 526 | — | 526 | — | — | 526 | — | 526 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total operating costs and expenses | 17,970 | (6,408 | ) | 11,562 | 2 | 3,801 | 15,365 | — | 15,365 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loss from operations | (17,970 | ) | 6,408 | (11,562 | ) | (2 | ) | (3,801 | ) | (15,365 | ) | — | (15,365 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other income (expense): | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other income (expense) | (330 | ) | — | (330 | ) | — | — | (330 | ) | — | (330 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | (1,012 | ) | 57 | BB | (955 | ) | — | — | (955 | ) | — | (955 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other income – Interest income on Trust Account | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total other income (expense) | (1,342 | ) | 57 | (1,285 | ) | — | — | (1,285 | ) | — | (1,285 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) before income tax provision | (19,312 | ) | 6,465 | (12,847 | ) | (2 | ) | (3,801 | ) | (16,650 | ) | — | (16,650 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax provision | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | (19,312 | ) | 6,465 | (12,847 | ) | (2 | ) | (3,801) | (16,650 | ) | — | (16,650 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Assuming Minimum Redemptions (Note 4) |
Assuming Maximum Redemptions (Note 4) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weighted Common shares outstanding | 2,581,282 | 1,875,000 | 118,328,000 | 111,400,394 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic and diluted net income (loss) per share | $ | (8.42 | ) | $ | — | $ | (0.14 | ) | $ | (0.15 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
45
NOTES TO UNAUDITED PRO FORMA COMBINED FINANCIAL INFORMATION
1. Basis of Presentation
The Business Combination will be accounted for as a reverse recapitalization in accordance with GAAP. Under this method of accounting, ROCH will be treated as the “acquired” company for financial reporting purposes. Accordingly, the Business Combination will be treated as the equivalent of PCT issuing stock for the net assets of ROCH, accompanied by a recapitalization. The net assets of ROCH will be stated at historical cost, with no goodwill or other intangible assets recorded. Operations prior to the Business Combination will be those of PCT.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet as of September 30, 2020 assumes that the Business Combination occurred on September 30, 2020. The unaudited pro forma condensed combined statements of operations for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and unaudited pro forma combined statements of operations for the year ended December 31, 2019 give pro forma effect to the Business Combination as if it had been completed on January 1, 2019. These periods are presented on the basis of PCT as the accounting acquirer.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet as of September 30, 2020 has been prepared using, and should be read in conjunction with, the following:
| • | ROCH’s unaudited condensed balance sheet as of September 30, 2020 and the related notes for the period ended September 30, 2020, included elsewhere in this prospectus; |
| • | PCT’s unaudited condensed balance sheet as of September 30, 2020 and the related notes for the period ended September 30, 2020, included elsewhere in this prospectus. |
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 has been prepared using, and should be read in conjunction with, the following:
| • | ROCH’s unaudited condensed statement of operations for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and the related notes, included elsewhere in this prospectus; and |
| • | PCT’s unaudited condensed statement of operations for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and the related notes, included elsewhere in this prospectus. |
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2019 has been prepared using, and should be read in conjunction with, the following:
| • | ROCH’s audited statement of operations for the twelve months ended December 31, 2019 and the related notes, included elsewhere in this prospectus; and |
| • | PCT’s audited statement of operations for the twelve months ended December 31, 2019 and the related notes, included elsewhere in this prospectus. |
Management has made significant estimates and assumptions in its determination of the pro forma adjustments. As the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information has been prepared based on these preliminary estimates, the final amounts recorded may differ materially from the information presented.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information does not give effect to any anticipated synergies, operating efficiencies, tax savings, or cost savings that may be associated with the Business Combination.
The pro forma adjustments reflecting the consummation of the Business Combination are based on certain currently available information and certain assumptions and methodologies that ROCH believes are reasonable under the circumstances. The unaudited condensed combined pro forma adjustments, which are described in the accompanying notes, may be revised as additional information becomes available and is evaluated. Therefore, it is likely that the actual adjustments will differ from the pro forma adjustments and it is possible the difference may be material. ROCH believes that its assumptions and methodologies provide a reasonable basis for presenting all of the significant effects of the Business Combination based on information available to management at this time and that the pro forma adjustments give appropriate effect to those assumptions and are properly applied in the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information.
46
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information is not necessarily indicative of what the actual results of operations and financial position would have been had the Business Combination taken place on the dates indicated, nor are they indicative of the future consolidated results of operations or financial position of the Combined Company. The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information should be read in conjunction with the historical financial statements and notes thereto of ROCH and PCT.
2. Accounting Policies
Upon consummation of the Business Combination, the Combined Company will perform a comprehensive review of the two entities’ accounting policies. As a result of the review, management may identify differences between the accounting policies of the two entities which, when conformed, could have a material impact on the financial statements of the Combined Company. ROCH’s historical Accounts payable and accrued expenses of $0.1 million was reclassified as Accrued expense to conform to PCT’s balance sheet presentation.
3. Adjustments to Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Financial Information
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information has been prepared to illustrate the effect of the Business Combination and has been prepared for informational purposes only.
The following unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information has been prepared in accordance with Article 11 of Regulation S-X as amended by the final rule, Release No. 33-10786 “Amendments to Financial Disclosures about Acquired and Disposed Businesses.” Release No. 33-10786 replaces the existing pro forma adjustment criteria with simplified requirements to depict the accounting for the transaction (“Transaction Accounting Adjustments”) and present the reasonably estimable synergies and other transaction effects that have occurred or are reasonably expected to occur (“Management’s Adjustments”). ParentCo has elected not to present Management’s Adjustments and will only be presenting Transaction Accounting Adjustments in the following unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information.
The pro forma condensed combined financial information does not include an income tax adjustment. Upon closing of the Business Combination, it is likely that the Combined Company will record a valuation allowance against the full value of U.S. and state deferred tax assets as the recoverability of the tax assets is uncertain. The pro forma combined provision for income taxes does not necessarily reflect the amounts that would have resulted had the Combined Company filed consolidated income tax returns during the periods presented.
The pro forma basic and diluted loss per share amounts presented in the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statements of operations are based upon the number of the Combined Company’s shares outstanding, assuming the Business Combination occurred on January 1, 2019.
Adjustments to Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Balance Sheet
The adjustments included in the unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet as of September 30, 2020 are as follows:
| (A) | Represents the exercise of 210,526 P&G warrants into Class B Preferred Units in contemplation of the Business Combination at an exercise price of $1 per warrant. These Class B Preferred Units are a component of the PCT Units converted into shares of ParentCo Common Stock pursuant to the Merger Agreement. |
| (B) | Represents the repayment of promissory notes including accrued interest to arrive at the Assumed Indebtedness amount per the Merger Agreement. |
| (C) | Represents additional Class A Unit equity investments issued and vested Class C Units subsequent to September 30, 2020, offsetting by equity issuance costs paid to third parties. These additional units are a component of the PCT Units converted into shares of ParentCo Common Stock pursuant to the Merger Agreement. The cash raised is used for operating purposes and this is provided to present the capital structure at the close of the Business Combination. |
47
| (D) | Represents the $30.0 million received in exchange for 346,284 Class A and 50,000 Class C Units issued as a closing condition for the Revenue Bonds. These Class A Units and Class C Units (which vest upon issuance) are a component of PCT Units expected to be converted into shares of ParentCo Common Stock pursuant to the Merger Agreement. The cash raised is expected to be used for operating purposes and this is provided to present the capital structure at the close of the Business Combination. |
| (E) | Represents the net issuance of $59.8 million of Convertible Notes, which include gross proceeds received of $60.0 million and $0.2 million of debt issuance costs recorded against notes payable. The holders of the Convertible Notes have the option to convert the Convertible Notes into Class A Units prior to Closing. Following the consummation of the Business Combination, the holders of the Convertible Notes are entitled to convert the Convertible Notes into approximately 7.5 million shares of the Combined Company, subject to adjustment. |
| (F) | Reflects the reclassification of $76.5 million of marketable securities held in the Trust Account at the balance sheet date that becomes available to fund the Business Combination. |
| (G) | Represents the net proceeds from the private placement of 25 million shares of common stock at $10.00 per share pursuant to the PIPE Investment. |
| (H) | Reflects the settlement of $2.7 million of deferred underwriters’ fees. The fees are expected to be paid at the close of the Business Combination. |
| (I) | Represents preliminary estimated transaction costs of $15.0 million, in addition to the $2.7 million of deferred underwriting fees noted above, inclusive of advisory, banking, printing, legal and accounting fees that are expensed as a part of the Business Combination and equity issuance costs that are capitalized into additional paid-in capital. The unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet reflects these costs as a reduction of cash of $14.8 million as $0.2 million has been paid as of September 30, 2020. $0.6 million was accrued as of September 30, 2020. Equity issuance costs of $11.2 million are offset to additional paid-in capital and the remaining balance is expensed through accumulated deficit. The costs expensed through accumulated deficit are included in the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2019 as discussed below. |
| (J) | Represents the net issuance of $237.4 million of Revenue Bonds, which include gross proceeds to PCT of $244.1 million and the payment $6.7 million of underwriter’s fee and other bond issuance costs. Upon the closing of the Revenue Bonds, the $2.7 million capitalized bond issuance costs from PCT’s historical balance sheet are reclassed from prepaid expense and other current assets to notes payable. The Revenue Bonds proceeds are kept in the Trust Account and are expected to be released to PCT after certain conditions are met on January 31, 2021. The cash raised will be used for construction of the Phase II Facility. |
| (K) | Reflects the reclassification of approximately $69.3 million of common stock subject to possible redemption to permanent equity. |
| (L) | Represents recapitalization of PCT’s Units and the issuance of 83.5 million shares of ParentCo Common Stock to PCT Unitholders as consideration for the reverse recapitalization, less shares reserved for 143,619 PCT outstanding warrants that will be canceled pursuant to the issuance of conditional replacement warrants by ParentCo, an outstanding option for issuance and purchase of 14,337 Class A Units that will be amended to allow for future issuance and purchase of shares of ParentCo Common Stock and 144,366 PCT outstanding unvested Class C Units that will become ParentCo’s restricted shares, subject to the same vesting schedule and forfeiture restrictions as the unvested PCT Class C Units. |
| (M) | Reflects the reclassification of ROCH’s historical accumulated deficit. |
| (N) | Reflects the maximum redemption of 6.9 million ROCH Public Shares for aggregate redemption payments of $69.3 million allocated to Common Stock and additional paid-in capital using par value $0.001 per share and a redemption price of $10.00 per share. This adjustment is recorded after consideration of the $250.0 million minimum cash requirement and $5.0 million minimum net tangible assets requirement for ROCH. |
48
Adjustments to Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Statements of Operations
The pro forma adjustments included in the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statements of operations for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and year ended December 31, 2019 are as follows:
| (AA) | Reflects elimination of historical P&G warrants expense that have been exercised and converted into Class B Preferred Units and will no longer be treated as liability-based instruments after the Business Combination. |
| (BB) | Reflects elimination of historical interest expense on the promissory notes repaid subsequent to the end of the period to arrive at Assumed Indebtedness for the Business Combination. |
| (CC) | Reflects the total estimated transaction costs in the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2019. Transaction costs that were expensed in the historical PCT statement of operations for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 were excluded from the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations for the nine months ended September 30, 2020. Transaction costs are reflected as if incurred on January 1, 2019, the date the Business Combination occurred for the purposes of the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations. This is a non-recurring item. |
| (DD) | Reflects elimination of investment income and unrealized loss on the Trust Account. |
The pro forma adjustments don’t include interest expense on the issuance of the Revenue Bonds and the issuance of Convertible Notes as both are intended for the construction of the Phase II Facility and are expected to be capitalized as property, plant and equipment which is not presented in the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statements of operations. The estimated interest expense on the Revenue Bonds is $13.6 million and $18.1 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and year ended December 31, 2019. The estimated interest expense on the issuance of Convertible Notes is $2.6 million and $3.5 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and year ended December 31, 2019.
4. Loss per Share
Represents the net loss per share calculated using the historical weighted average shares outstanding, and the issuance of additional shares in connection with the Business Combination, assuming the shares were outstanding since January 1, 2019. As the Business Combination and related equity transactions are being reflected as if they had occurred at the beginning of the periods presented, the calculation of weighted average shares outstanding for basic and diluted net income (loss) per share assumes that the shares issuable relating to the Business Combination have been outstanding for the entirety of all periods presented. If the maximum number of shares are redeemed, this calculation is retroactively adjusted to eliminate such shares for the entire period.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information has been prepared assuming two alternative levels of redemption into cash of Common Stock for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and for the year ended December 31, 2019:
| For the Nine Months Ended September 30, 2020 | For the Year ended December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data) | Assuming No Redemption | Assumig Maximum Redemption | Assumig No Redemption | Assuming Maximum Redemption | |||||||||||||||||
| Pro forma net loss | $ | (12,500 | ) | $ | (12,500 | ) | $ | (16,650 | ) | $ | (16,650 | ) | |||||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding of common stock | 118,328,000 | 111,400,394 | 118,328,000 | 111,400,394 | |||||||||||||||||
| Net loss per share (Basic and Diluted) attributable to common stockholders(1) | $ | (0.11 | ) | $ | (0.11 | ) | $ | (0.14 | ) | $ | (0.15 | ) | |||||||||
(1) As PCT had a net loss on a pro forma combined basis, the outstanding warrants and unvested Class C Units had no impact to diluted net loss per share as they are considered anti-dilutive.
49
management’s discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations
The following discussion and analysis provides information which PCT’s management believes is relevant to an assessment and understanding of PCT’s consolidated results of operations and financial condition. The discussion should be read together with “Selected Historical Financial Information of PCT” and the audited annual and unaudited interim condensed consolidated financial statements, together with related notes thereto, included elsewhere in this prospectus. The discussion and analysis should also be read together with our unaudited pro forma consolidated financial information as of December 31, 2019 and for the year ended December 31, 2019, and as of September 30, 2020 and for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 (in the section of this prospectus entitled “Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Financial Information”). This discussion may contain forward-looking statements based upon current expectations that involve risks, uncertainties, and assumptions. Our actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements as a result of various factors, including those set forth under “Risk Factors” or in other parts of this prospectus. Unless the context otherwise requires, references in this “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” to “we”, “us”, “our”, and “the Company” are intended to mean the business and operations of PCT and its consolidated subsidiaries.
Overview
PCT is commercializing a patented purification recycling technology (the “Technology”), originally developed by The Procter & Gamble Company (“P&G”), for restoring waste polypropylene into resin with near-virgin characteristics. We call this resin ultra-pure recycled polypropylene (“UPRP”), which has nearly identical properties and applicability for reuse as virgin polypropylene. PCT has a global license for the technology from P&G. We intend to build our first commercial-scale plant in Ironton, Ohio, which is expected to have nameplate capacity of approximately 107 million pounds/year when fully operational. Production is expected to commence in late 2022 and the plant is expected to be fully operational in 2023. We have secured and contracted all of the feedstock and offtake for this initial plant. Our goal is to create an important new segment of the global polypropylene market that will assist multinational entities in meeting their sustainability goals, provide consumers with polypropylene-based products that are sustainable, and reduce overall polypropylene waste in the world’s landfills and oceans.
PCT intends to build new recycling production facilities globally, with the goal of having 30 commercial lines operational by 2030 and 50 by 2035. In addition to our first plant in Ironton, OH, we expect the next plant to be located in Europe and to commence production in 2023 with a nameplate capacity of approximately 107 million pounds when fully operational. Additional expansion in the United States is expected to include a scaled up commercial line capable of producing over 165 million pounds of UPRP. Pre- engineering for the design and installation of five commercial lines in a single “cluster” site is currently underway and is expected to result in a combined capacity of over 825 million pounds annually. From these first seven plants PCT expects to bring over 1 billion pounds of annual recycled polypropylene production to the market in the next five years, which is less than 1% of the total annual projected demand for virgin and virgin parity resin.
PCT is regarded as a leader in innovation in polymers, sustainability, and recycling by numerous non- government organizations (“NGOs”), trade associations, and a major media publication. Recognition of PCT’s achievements include the American Chemistry Council’s Innovation in Plastics Recycling award (2017), Time Magazine’s “Best Innovations of 2019”, and the 2020 Re|focus Solar Institute Award for Leadership in Innovation awarded by the Plastics Association.
The Business Combination
On November 16, 2020, ROCH, ParentCo, Merger Sub LLC, Merger Sub Corp and PCT entered into the Merger Agreement pursuant to which the Business Combination will be consummated. The consideration payable to PCT Unitholders in connection with the Business Combination consists of a combination of shares of ParentCo and the assumption of all PCT indebtedness. The Business Combination estimates a $835.0 million pre-money valuation, and includes $250.0 million of proceeds from the PIPE Investment. PCT will be deemed the accounting predecessor and the combined entity will be the successor registrant with the SEC, meaning that PCT’s consolidated financial statements for previous periods will be disclosed in ParentCo’s future periodic reports filed with the SEC.
50
While the legal acquirer in the Business Combination Agreement is ParentCo, for financial accounting and reporting purposes under GAAP, PCT will be the accounting acquirer and the Business Combination will be accounted for as a “reverse recapitalization.” A reverse recapitalization does not result in a new basis of accounting, and the consolidated financial statements of the combined entity represent the continuation of the consolidated financial statements of PCT in many respects. Under this method of accounting, ROCH will be treated as the “acquired” company for financial reporting purposes. For accounting purposes, PCT will be deemed to be the accounting acquirer in the transaction and, consequently, the transaction will be treated as a recapitalization of PCT. Accordingly, the consolidated assets, liabilities and results of operations of PCT will become the historical consolidated financial statements of the ParentCo, and ROCH’s assets, liabilities and results of operations will be consolidated with PCT beginning on the acquisition date. Operations prior to the Business Combination will be presented as those of the ParentCo in future reports. The net assets of ROCH will be recognized at historical cost (which is expected to be consistent with carrying value), with no goodwill or other intangible assets recorded upon execution of the Business Combination.
Upon consummation of the Business Combination and the closing of the PIPE, the most significant change in PCT’s future reported financial position and results of operations is expected to be an estimated increase in cash and cash equivalents (as compared to PCT’s condensed consolidated balance sheet at September 30, 2020) to approximately $292.8 million, assuming maximum stockholder redemptions, or $362.1 million, assuming no redemptions, and, in each case, including $250.0 million in gross proceeds from the PIPE Investment, $60.0 million pre-PIPE capital from an investor, net proceeds from the Revenue Bonds of $237.4 million and net proceeds from the Convertible Notes of $59.8 million. Total direct and incremental transaction costs of ROCH and PCT are estimated at approximately $15.0 million, which will be treated as a reduction of the cash proceeds with $11.2 million deducted from Surviving Company additional paid-in capital for equity issuance costs and the remaining balance is expensed through accumulated deficits. See the section entitled “Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Financial Information.”
As a result of the Business Combination, we will become the successor to an SEC-registered and NASDAQ-listed company, which will require us to hire additional personnel and implement procedures and processes to address public company regulatory requirements and customary practices. We expect to incur additional annual expenses as a public company for, among other things, directors’ and officers’ liability insurance, director fees and additional internal and external accounting and legal and administrative resources, including increased personnel costs, audit and legal fees.
Factors Affecting Our Financial Condition and Results of Operations
We are a pre-commercial company and our future financial condition and operating performance will depend on our ability to successfully begin, sustain and expand the manufacturing and sale of UPRP, as discussed below, which in turn is subject to significant risks and challenges, including those described in the section of this prospectus titled “Risk Factors.”
Cutting-Edge Licensed Polypropylene Recycling Technology
We apply a unique resin purification process to produce near-virgin quality polypropylene resin using waste polypropylene feedstock. The physical purification process separates colors, contaminants and odors from waste polypropylene to achieve a “food grade” product while also expanding the range of feedstock quality in comparison to traditional polypropylene recycling. We believe that the Technology is the only proven and economically viable method of recycling polypropylene to virgin quality and that no other technologies can effectively address polypropylene recycling at scale. Upon commencement of production at the Phase II Facility, we expect to become the first global producer of UPRP.
If demand for UPRP continues to increase, as we expect, other companies, some of which may be better capitalized and have access to stronger research and development capabilities, may seek to develop new or improved polypropylene recycling technologies. New technologies may lead to the production of cheaper or higher quality UPRP, which in turn could adversely affect our prospects.
51
Relationship with P&G
P&G, which designed and owns the patents to the Technology for manufacturing UPRP, granted us an exclusive, worldwide license to their patents and other intellectual property for the manufacture of recycled polypropylene (the “License Agreement”). The License Agreement was granted for the duration of the relevant patents and we, in turn, granted back a limited sublicense to P&G for the same period, including to any intellectual property Improvements (as defined in the License Agreement) made by us, allowing P&G to produce or sublicense the production of up to a certain amount of UPRP worldwide per year for a set period of time and up to a certain higher threshold of UPRP per region (the License Agreement defines six separate geographic regions) per year thereafter. The exclusivity period has a life span of 20 years from the date a patent is granted. Under the License Agreement, nine patents were granted in 2017, with four additional patents pending which will reset the exclusivity timeline.
P&G has the right to purchase UPRP, at “most favored nation” pricing, from the Phase II Facility in its first year of operations at a guaranteed minimum amount and a guaranteed minimum amount each year thereafter. Following the opening of our second plant, P&G will have the right to annually purchase a certain amount or maximum percentage of our total manufacturing capacity each year, whichever is greater. The License Agreement provides for royalties to P&G on production sold to third parties, with the royalty rate upon commencement of production driven by the number of plants, product pricing and time. Pursuant to the License Agreement, we prepaid a portion of this royalty amount in April 2019. The License Agreement may be subject to stepped up royalty rates, become non-exclusive or become subject to termination by P&G in certain circumstances, including if we fail to meet mutually agreeable resin technical specifications within six months of the start of operations at the Phase II Facility, are unable or unwilling to provide P&G with the aforementioned UPRP offtake quantity on terms specified in the License Agreement, if we fail to pay required royalties or upon a change of control (excluding the Business Combination). See the section entitled “Description of PCT Business — Intellectual Property.”
If P&G exercises its right to produce or sublicense the production of UPRP using its technology, we may come into competition with P&G or its sublicensees, which will have access to the same technology and may not be subject to royalties or may enjoy preferential royalty terms. Competition may drive down pricing and, to the extent such future competitors are able to produce UPRP more efficiently than we are, our margins and profits could be adversely affected. In addition, any breach by us of certain terms of the License Agreement may entitle P&G to terminate the License Agreement or make it non-exclusive, which would have a material and adverse impact on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Completion of the Phase II Facility and Expansion of Our Manufacturing Footprint
Construction of our first manufacturing plant began in October 2020. The plant, which we refer to as the “Phase II Facility” or “Plant 1,” is on the 26-acre site of a former Dow Chemical plant near the Ohio River and close to rail, highway and barge transportation. We expect the Phase II Facility to be commercially operational by the end of 2022, with an annual production capacity of 107 million pounds.
Our initial testing production line — the Feedstock Evaluation Unit (“FEU” or “Phase I Facility”) — was developed to test and optimize the efficiency and throughput of our recycling process, was completed in July 2019 and will remain a critical component for testing feedstock for polypropylene content. The next phase is to construct, renovate, equip and install an approximately 150,000 square foot facility housing commercial-scale equipment including the repurposing of three existing buildings for feedstock pre-processing and storage. We estimate the total remaining cost to complete the Phase II Facility at approximately $345 million.
The timely completion of our construction of the Phase II Facility depends on several factors, some of which are outside of our control. We have contracted the construction to several third parties. One contractor will repurpose existing buildings, another will construct the core purification process equipment, and several others will supply certain pre-processing equipment. In addition, PCT is required to obtain or modify certain additional construction permits for the timely completion of the Phase II Facility.
While our contractors are subject to performance guarantees that equipment will be free from defects for 12 months and PCT’s key contractors are subject to delay damage liability in the event that the Phase II Facility is not delivered by the fourth quarter of 2022, there is no assurance that the Phase II Facility will be completed at our anticipated cost, that it will become operational on our anticipated timeline, or that any indemnity for delay will be sufficient to compensate us for the consequences of the defect or delay, such as the termination of or loss of exclusivity under the License Agreement. In the event that the Phase II Facility is completed above anticipated cost then PCT is responsible for construction cost overruns.
52
Strong Demand for High Quality Recycled Polypropylene
According to the 2017 United States National Postconsumer Plastic Bottle Recycling Report published by The Association of Plastic Recyclers and the American Chemistry Council, global demand for virgin or near virgin polypropylene is expected to exceed 200 billion pounds by 2024, of which approximately 27% is expected to come from the United States. However, less than 1% of U.S. polypropylene was recycled as of 2019 according to the American Chemistry Council.
Waste polypropylene ends up in landfills and the environment, creating a long-term problem. Regulators and consumers have increasingly focused on the need for polypropylene recycling solutions. Multiple large corporations have specifically committed to reducing their plastics footprint, resulting in premium pricing for recycled polypropylene relative to its virgin counterpart. PCT has entered into legally binding offtake agreements with three blue-chip customers for the purchase of UPRP from the production expected at the Phase II Facility at premium prices relative to virgin polypropylene. These commitments account for a minimum of 47.5 million pounds of the Phase II Facility’s annual production capacity. Combined with the three additional secured offtake agreements, a minimum of 63 million pounds of total capacity is committed at PCT’s sole option, up to a quantity of 138 million pounds per year at PCT’s sole option. The terms of these offtake agreements range from 3 to 7 years and we have entered into several offtake letters of intent with other potential customers. We have also secured the feedstock required to run the Phase II Facility at its 107 million pounds nameplate capacity for at least the first 3 years.
Basis of Presentation
Our consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”). Currently, we conduct business through one operating segment. The consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that we will continue as a going concern. See Note 1 in the accompanying consolidated financial statements for further details.
Components of Results of Operations
Revenue
To date, we have not generated any operating revenue. We expect to begin to generate revenue by the end of 2022, which is when we expect the Phase II Facility to become commercially operational.
Operating Costs
Operating expenses to date have consisted mainly of personnel costs (including wages, salaries and benefits) and other costs directly related to operations at the Phase I Facility, including rent, depreciation, repairs and maintenance, utilities and supplies. Costs attributable to the design and development of the Phase II Facility are capitalized and will be depreciated over the useful life of the Phase II Facility, which we expect to be approximately 40 years. We expect our operating costs to increase substantially as we continue to scale operations and increase headcount.
Research and Development Expense
Research and development expenses consist primarily of costs related to the development of our facilities and licensed product. These include mainly personnel costs and third-party consulting costs. In 2019 and 2020, our research and development expenses were related primarily to the development of the Phase I Facility and design and development of our UPRP Process. We expect our research and development expenses to increase for the foreseeable future as we increase investment in feedstock evaluation, including investment in new frontend feedstock mechanical separators to improve feedstock purity and increase the range of feedstocks PCT can process economically. In addition, we are increasing our in house feedstock analytical capabilities, which will include additional supporting equipment and personnel.
53
Selling, General and Administrative Expense
Selling, general and administrative expenses consist primarily of personnel-related expenses for our corporate, executive, finance and other administrative functions and professional services, including legal, audit and accounting services. We expect our selling, general, and administrative expenses to increase for the foreseeable future as we scale headcount with the growth of our business, and as a result of operating as a public company, including compliance with the rules and regulations of the SEC, legal, audit, additional insurance expenses, investor relations activities, and other administrative and professional services.
Results of Operations
Comparison of nine-month periods ended September 30, 2020 and 2019
The following table summarizes our operating results for the nine-month periods ended September 30, 2020 and 2019:
| Nine months ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except %) | 2020 | 2019 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||
| Costs and expenses | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating costs | $ | 7,040 | $ | 4,901 | $ | 2,139 | 44 | % | ||||||||
| Research and development | 528 | 509 | 19 | 4 | % | |||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative | 6,293 | 10,082 | (3,789 | ) | (38 | )% | ||||||||||
| Total operating costs and expenses | 13,861 | 15,492 | (1,631 | ) | (11 | )% | ||||||||||
| Interest expense | 1,827 | 400 | 1,427 | 357 | % | |||||||||||
| Other (income) expense | (100 | ) | 330 | (430 | ) | (130 | )% | |||||||||
| Net loss | $ | 15,588 | $ | 16,222 | $ | (634 | ) | (4 | )% | |||||||
Operating Costs
Operating costs for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 amounted to $7.0 million, compared to $4.9 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2019, an increase of $2.1 million, or 44%. The increase was primarily attributable to higher depreciation expense of $1.0 million following the Phase I Facility’s placement into service in July 2019, an increase in repairs and maintenance costs of $0.8 million and higher personnel costs of $1.2 million related to wages and salaries and operating outside services, reflecting the hiring of operational staff at the Phase I Facility and filling of key positions in general sales, operations, and human resources. The increase in wages and salaries was offset by the decrease in equity-based compensation expense of $0.7 million.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses for nine months ended September 30, 2020 amounted to $0.5 million compared to $0.5 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2019, representing an increase of $0.019 million or 4%. The research and development expenses remained consistent for each period.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative expenses for nine months ended September 30, 2020 amounted to $6.3 million compared to $10.1 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2019, representing a decrease of $3.8 million or 38%. The decrease was primarily attributable to the decrease in P&G warrants expense of $4.6 million, partially offset by higher professional services expense of $0.9 million, higher legal fees of $0.2 million in addition to higher personnel costs as a result of filling key positions in general sales, operations, and human resources.
54
Interest Expense
Interest expense for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 amounted to $1.8 million compared to $0.4 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2019, representing an increase of $1.4 million. This represents interest expense on current and non-current notes payable. The increase was primarily attributable to the completion of the Phase I Facility, as the interest on the loans related to the Phase I Facility assets was no longer capitalized after June 2019, and the issuance of additional promissory notes in December 2019.
Other Income/Expense
Other income for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 amounted to $0.1 million compared to other expense of $0.3 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2019.
Comparison of years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018
The following table summarizes our operating results for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018:
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except %) | 2019 | 2018 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||
| Costs and expenses | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating costs | $ | 5,966 | $ | 1,222 | $ | 4,744 | 388 | % | ||||||||
| Research and development | 526 | 786 | (260 | ) | (33 | )% | ||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative | 11,478 | 2,097 | 9,381 | 447 | % | |||||||||||
| Total operating costs and expenses | 17,970 | 4,105 | 13,865 | 338 | % | |||||||||||
| Interest expense | 1,012 | — | 1,012 | 100 | % | |||||||||||
| Other expense | 330 | — | 330 | 100 | % | |||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | 19,312 | $ | 4,105 | $ | 15,207 | 370 | % | ||||||||
Operating Costs
Cost of operations for the year ended December 31, 2019 amounted to $6.0 million compared to $1.2 million for the year ended on December 31, 2018, representing an increase of $4.8 million or 388%. The increase was primarily attributable to the increase in employee headcount. As a result of the increase in workforce and increase in Phase II Facility footprint, the associated costs with operations increased. We expect operating costs will continue to increase as PCT continues to expand.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses for year ended December 31, 2019 amounted to $0.5 million compared to $0.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2018, representing a decrease of $0.3 million or 33%. The decrease was primarily attributable to fewer research and development expenses related to the Phase I Facility. We expect research and development expenses to increase in future periods as stated above.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative expenses for year ended December 31, 2019 amounted to $11.5 million compared to $2.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2018, representing an increase of $9.4 million or 447%. The increase was primarily attributable to an increase in P&G warrant expense of $6.4 million, an increase in selling, general and administrative equity-based compensation of $1.9 million, and an increase in professional services expense of $0.5 million which contributed to the increase in selling, general and administrative expenses.
55
Interest Expense
Interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2019 amounted to $1.0 million compared to $0 for the year ended December 31, 2018, representing an increase of $1.0 million or 100%. This represents interest expense on current and non-current notes payable. The increase was primarily attributable to the Phase I Facility, which was determined to be ready for its intended use on June 30, 2019. This resulted in higher interest expense as the interest was no longer capitalized on the loans related to the Phase I Facility assets after June 30, 2019.
Other Expense
Other expense for the year ended December 31, 2019 amounted to $0.3 million compared to $0 for the year ended December 31, 2018, representing an increase of $0.3 million or 100%. The increase was attributable to a disposal of certain equipment.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
We have not yet begun commercial operations and we do not have any sources of revenue. Our ongoing operations have, to date, been funded by a combination of equity and debt financing. As of September 30, 2020, we had cash and cash equivalents on hand of $0.1 million. On a pro forma basis, assuming the consummation of the Business Combination as of September 30, 2020, assuming receipt of $250.0 million in gross proceeds from the PIPE Investment, proceeds of $60.0 million related to pre-PIPE capital from an investor, gross proceeds from the Revenue Bonds of $249.6 million, gross proceeds from the Class A shares raised as a closing condition for the Revenue Bonds of $30.0 million, and Class C Units which vested subsequent to September 30, 2020 which are included as a component of the Company LLC Interests converted into PCT Merger Consideration of $4.7 million, and gross proceeds from the Convertible Notes offering of $60.0 million, less total direct and incremental transaction costs of ROCH and PCT estimated at approximately $12.6 million, we would have cash and cash equivalents of between approximately $362.1 million and $292.8 million, depending on the level of redemptions by ROCH shareholders. We also had $17.3 million in debt as of September 30, 2020. On a pro forma basis, assuming the consummation of the conditions subsequent to the Revenue Bonds financing and Convertible Notes offering described below, we would have had approximately $321.9 million in debt.
Our consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that we will continue as a going concern; however, certain conditions raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to do so. See Note 1 in the accompanying consolidated financial statements for further details. We believe that our existing cash and cash equivalents, the proceeds of the recently consummated Revenue Bonds financing and Convertible Notes offering and the proceeds of the Business Combination and related PIPE Investment, taken together, will be sufficient to meet our projected cash requirements for at least the next 12 months from the date of this prospectus and through the completion of our Phase II Facility and commencement of commercial production. Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including actual construction costs for our Phase II Facility, the construction of additional plants, funding needs to support our business growth and to respond to business opportunities, challenges or unforeseen circumstances. If our forecasts prove inaccurate, we may be required to seek additional equity or debt financing from outside sources, which we may not be able to raise on terms acceptable to us, or at all. If we are unable to raise additional capital when desired, our business, financial condition and results of operations would be adversely affected.
56
Indebtedness
Revenue Bonds
In October 2020, we entered into a project financing arrangement, whereby the Southern Ohio Port Authority (the “Authority”), an Ohio port authority and political subdivision in Scioto County, Ohio, issued Exempt Facility Revenue Bonds, including tax-exempt senior secured bonds in the aggregate principal amount of $219.55 million (“the Series 2020A Bonds” or “the Senior Bonds”), tax-exempt subordinate secured bonds in the aggregate principal amount of $20.0 million (“the Series 2020B Bonds” or “the Tax-Exempt Subordinate Bonds”) and taxable subordinate secured bonds in the aggregate principal amount of $10.0 million (“the Series 2020C Bonds” or “the Taxable Subordinate Bonds” and together with the Series 2020A and Series 2020B Bonds, the “Revenue Bonds”). The Series 2020A Bonds comprised three terms and were issued with a total original discount of $5.5 million, resulting in net proceeds of $214.1 million, while the Series 2020B, issued in two terms, and 2020C bonds, issued in a single term, were issued at par. Issuance costs related to the Revenue Bonds, which will be recognized on a deferred basis over the life of the debt, amounted to $1.36 million.
Pursuant to a loan agreement with the Authority dated as of October 1, 2020 (the “Loan Agreement”), the Authority agreed to loan our indirect, wholly-owned subsidiary Purecycle: Ohio LLC (“Purecycle Ohio”), as borrower, the proceeds of the Revenue Bonds. The Revenue Bonds are special obligations of the Authority issued under an Indenture of Trust dated as of October 1, 2020 (the “Indenture”) between the Authority and UMB Bank, N.A., as trustee (the “Revenue Bonds Trustee”) payable solely from the Trust Estate consisting of the Authority’s right, title and interest in and to Purecycle Ohio’s Gross Revenues (as defined therein) and moneys in certain funds and accounts established by the Indenture or the Loan Agreement and held by the Trustee. The Revenue Bonds are further secured by a mortgage, an equity pledge, a security agreement, a collateral assignment to the Trustee of Purecycle Ohio’s sublicense to the Technology and the Guaranty of Completion described herein. We have entered into a Guaranty of Completion dated as of October 7, 2020 and further described herein, in favor of the Trustee whereby we guarantee the lien free completion of the Phase II Facility and, together with Purecycle Ohio, an Environmental Indemnity Agreement dated October 7, 2020, in favor of the Trustee providing certain indemnities for losses related to environmental matters on the site of Plant 1.
Interest on the Revenue Bonds is payable semi-annually on June 1 and December 1 of each year, until maturity. The Loan Agreement requires Purecycle Ohio to make periodic principal prepayments, reflecting the Authority’s obligation to mandatorily redeem a portion of the Revenue Bonds from time to time (“the sinking fund redemption amounts”), beginning in 2024, according to a sinking fund schedule.
The following table sets forth the original stated principal amounts, interest rates, final maturity dates and mandatory principal repayments according to the sinking fund schedule applicable to Purecycle Ohio’s obligations under the Loan Agreement, in relation to each relevant term of the Revenue Bonds:
| ($ in millions) | Original Principal Amount | Interest Rate | Final Maturity Date | Mandatory Principal Repayment | ||||||||
| Series 2020A | ||||||||||||
| Term 1 | $ | 12.37 | 6.25 | % | December 1, 2025 | Semi-annual payment of $2.9 million beginning on June 1, 2024 and incrementally higher semi-annual payments thereafter | ||||||
| Term 2 | 38.76 | 6.50 | % | December 1, 2030 | Semi-annual payment of $3.3 million beginning on June 1, 2031 and incrementally higher semi-annual payments thereafter | |||||||
| Term 3 | 168.48 | 7.00 | % | December 1, 2042 | Semi-annual payment of $4.6 million beginning on June 1, 2031 and incrementally higher semi-annual payments thereafter | |||||||
| Series 2020B | ||||||||||||
| Term 1 | 10.0 | 10.0 | % | December 1, 2025 | Semi-annual payment of $0.2 million beginning on June 1, 2024 and incrementally higher semi-annual payments thereafter(1) | |||||||
| Term 2 | 10.0 | 10.0 | % | December 1, 2027 | Semi-annual payment of $0.2 million beginning on June 1, 2024 and incrementally higher semi-annual payments thereafter(2) | |||||||
| Series 2020C | 10.0 | 13.0 | % | December 1, 2027 | Semi-annual payment of $0.1 million beginning on June 1, 2024 and incrementally higher semi-annual payments thereafter(3) | |||||||
| Total | $ | 249.6 | ||||||||||
(1) Principal due at December 1, 2025 maturity of $9.5 million.
(2) Principal due at December 1, 2027 maturity of $8.6 million.
(3) Principal due at December 1, 2027 maturity of $8.8 million.
57
The Loan Agreement requires Purecycle Ohio to use the proceeds of the Revenue Bonds exclusively to construct and equip the Phase II Facility, fund a debt service reserve fund for the Series 2020A Bonds, finance capitalized interest, and pay the costs of issuing the Revenue Bonds. Construction of the Phase II Facility has commenced and is expected to be substantially completed by October 2022, and is expected to have an estimated useful life beyond the final maturity of the Revenue Bonds. Pursuant to the Indenture, the proceeds of the Revenue Bonds will be placed in various trust funds and non-interest-bearing accounts established and administered by the Revenue Bonds Trustee. In addition, 100% of Purecycle Ohio’s revenue attributable to the production of the Phase II Facility must be deposited into a revenue escrow fund. Funds in the trust accounts and revenue escrow account will be disbursed by the Revenue Bonds Trustee when certain conditions are met, and will be used to pay costs and expenditures related to the development of the Phase II Facility, make required interest and principal payments (including sinking fund redemption amounts) and, in certain circumstances required under the Indenture, to redeem the Revenue Bonds.
The Revenue Bonds are secured by Purecycle Ohio pursuant to an Open-End Mortgage, Assignment of Leases and Rents, Security Agreement and Fixture Filing and a Security Agreement pursuant to which, among other things, Purecycle Ohio has granted a security interest in all of Purecycle Ohio’s assets and gross revenues. The Revenue Bonds are further secured by Purecycle Ohio’s sublicense rights to certain intellectual property, all right, title and interest to moneys in certain funds and accounts established pursuant to the Indenture and the Loan Agreement, and all equity interests in Purecycle Ohio, held by Purecycle Ohio’s sole member, PCTO Holdco.
We made a $60.0 million equity contribution to Purecycle Ohio in October of 2020 in connection with the Revenue Bond closing. We are also required to make an additional $40.0 million equity contribution to Purecycle Ohio by January 31, 2021. The proceeds of these equity contributions must be used for the construction of the Phase II Facility.
In addition, as of the Revenue Bond closing, we entered into a Guaranty of Completion (the “Guaranty”) with respect to the Phase II Facility, whereby we guaranteed the lien free completion of the Phase II Facility and established a liquidity reserve (the “Guarantor Liquidity Account”) held by U.S. Bank, as Escrow Agent, under an Escrow Agreement dated October 7, 2020. The Guarantor Liquidity Account is to be fully funded by us in the amount of $50.0 million (the “Guarantor Liquidity Reserve Amount”), no later than January 31, 2021; provided, that the Guaranty provides for an alternate funding schedule for the Guarantor Liquidity Account in the event we do not raise $250.0 million of equity by January 31, 2021. Pursuant to the Escrow Agreement, only the Revenue Bonds Trustee, as secured party, can give direction to the Escrow Agent concerning the release or investment of the Guarantor Liquidity Account and sale and liquidation of its investments. We have no right to exercise any control over the Guarantor Liquidity Account and we are required under the Guaranty to replenish the Guarantor Liquidity Account to the Guarantor Liquidity Reserve Amount throughout the term of the Guaranty if funds are withdrawn by the Revenue Bonds Trustee. The Guaranty requires that funds be transferred from the Guarantor Liquidity Account to the Equity Account of the Project Fund (one of the funds created upon the issuance of the Revenue Bond proceeds under the Indenture that is held and maintained by the Revenue Bonds Trustee, which contains certain subaccounts, including the Equity Account, from which funds can be disbursed by the Revenue Bonds Trustee to pay project expenses if certain conditions are met, as further described in the Loan Agreement) held by the Revenue Bonds Trustee under the Indenture if the contingency funds on deposit in the Equity Account are reduced to an amount below $21.2 million in order to maintain the contingency fund at that level. The Guaranty will terminate one year after the Phase II Facility operates at full capacity for 30 consecutive days, as long as we have fulfilled all of our obligations under the Guaranty, and the distribution test set forth in the Loan Agreement is satisfied. Thereafter, our covenant not to finance, develop or construct a plastics recycling plant within a 250-mile radius of the Phase II Facility shall remain in full force and effect until the Revenue Bonds are paid in full; provided we can participate in the financing, development or construction of an expansion and/or addition to the Phase II Facility.
58
In addition, the Guaranty requires us to raise at least $250.0 million in equity no later than January 31, 2021. To the extent we fail to do so, we must deposit into the Guarantor Liquidity Account an amount equal to the difference between $250.0 million and the amount of equity actually raised less the Guarantor Liquidity Reserve Amount, in twelve equal monthly installments, commencing on February 28, 2021, until a total of $200.0 million has been deposited. We must give written evidence of such deposits to the Trustee by the last day of each month, commencing February 28, 2021. The Guaranty provides that (i) we may not use any of the initial $250 million of equity raised for any future project of ours or any of our affiliates at a level greater than 30% of the total project cost prior to the date the Guaranty terminates, and (ii) unless we have provided written evidence to the Trustee that we have $100 million (including the Guarantor Liquidity Reserve Amount) of equity to support our obligations under the Guaranty, we cannot contribute equity to any additional project in an amount greater than 30% of total project costs for such additional project.
We must also have at least $75.0 million and $100.0 million of cash (including the Guarantor Liquidity Account) on our balance sheet by July 31, 2021 and January 31, 2022, respectively, or provide for the issuance of an irrevocable direct-pay letter of credit for the benefit of the Trustee for these amounts.
The Loan Agreement contains certain customary financial and other covenants of Purecycle Ohio, including a prohibition on distributions to its members prior to January 1, 2024, and thereafter only if certain conditions are met, and two financial maintenance covenants. These include a debt service coverage ratio covenant and days cash on hand covenant, which are measured at the end of each fiscal year, commencing with the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023. The following table summarizes the requirements of the debt service coverage ratio and days cash on hand covenants.
| Definition per Indenture | Must retain independent consultant(1) | Event of default | ||||||||
| Debt service ratio | ||||||||||
| Senior Parity Coverage Requirement | The ratio of adjusted income (“net income available for debt service” as defined in the Indenture) to the maximum annual debt service (principal, including mandatory sinking fund redemption amounts, interest and fees) of the Series 2020A Bonds and any parity indebtedness | 150% | 125% | |||||||
| Overall Coverage Requirement | The ratio of adjusted income (“net income available for debt service” as defined in the Indenture) to the maximum annual debt service (principal, including mandatory sinking fund redemption amounts, interest and fees) of all of the Revenue Bonds and any parity indebtedness | 110% | 110% | |||||||
| Days cash on hand | The sum of cash and cash equivalents (as defined in the Indenture, with certain exceptions) divided by one day of operating expenses (calculated based on GAAP, including all scheduled debt service obligations payable during the period, and less depreciation and amortization) | 75 days | 60 days | |||||||
(1) In accordance with the Loan Agreement, in the circumstances displayed in the table, we are required to retain an independent consultant, which must be approved by the majority of bondholders, to make recommendations to increase net income available to debt service or days cash on hand. We are required to transmit a copy of the independent consultant’s report to the Revenue Bonds Trustee and take such actions as will be in substantial conformity with such recommendations.
59
The Loan Agreement also restricts Purecycle Ohio, subject to certain baskets and exceptions, from incurring additional debt or liens, entering into derivatives, making asset sales, acquiring certain assets and making certain investments, licensing or sublicensing certain intellectual property and financing, developing, or constructing plastic recycling plants within a 250-mile radius of the Phase II Facility. We are also required to maintain certain offtake and feedstock supply contracts and are allowed only certain transfers of property, plant and equipment and creation of liens. In addition, Purecycle Ohio is prohibited from making distributions on any membership interests (including to us), license fees or management fees relating to the Phase II Facility, prior to January 1, 2024, and beginning on January 1, 2024, Purecycle Ohio cannot make distributions unless the distribution test is satisfied, under the Loan Agreement.(4)
Certain Revenue Bonds are subject to redemption at Purecycle Ohio’s option at a progressively declining premium to par, beginning on the following dates:
| ($ in millions) | Principal Amount |
Date subject to optional redemption |
Redemption price | |||||||
| Series 2020A | ||||||||||
| Term 3 | $ | 168.5 | December 1, 2027 | 103% beginning on December 1, 2027; price decreases 1% per year until price is at par | ||||||
| Series 2020B | ||||||||||
| Term 1 | 10.0 | December 1, 2024 | 105% | |||||||
| Term 2 | 10.0 | December 1, 2026 | 105% | |||||||
| Series 2020C | 10.0 | December 1, 2025 | 105% if redeemed before December 1, 2026; otherwise 104% | |||||||
| Total | $ | 198.5 | ||||||||
In addition, provided that no Subordinate Bonds shall be redeemed so long as any Senior Bonds remain outstanding, Purecycle Ohio may voluntarily redeem the Revenue Bonds at 103% of principal amount outstanding in the event that the Phase II Facility is damaged or destroyed and becomes inoperable or inaccessible to us resulting from damage to the facility or title taken by condemnation, as further described in the Indenture. The Revenue Bonds are also subject to mandatory redemption upon certain events, including the termination or expiration of the agreements under which we obtain the rights to commercialize UPRP using our licensed technology or Purecycle Ohio’s failure to make the additional $40.0 million equity contribution, or our failure to deposit to the Guarantor Liquidity Account $50.0 million, in each case by January 31, 2021. In addition, the tax-exempt Revenue Bonds are subject to mandatory redemption prior to maturity in whole in the event of the occurrence of a determination of taxability.
Convertible Notes Offering
On October 6, 2020, we entered into a Note Purchase Agreement (the “Note Purchase Agreement”) with certain funds managed by Magnetar Capital LLC or its affiliates (“Magnetar Investors”), providing for the purchase of up to $60.0 million in aggregate principal amount of our Convertible Senior Secured Notes due 2022 (the “Convertible Notes”) issuable under an indenture dated as of October 7, 2020 (the “Magnetar Indenture”) between us and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee and collateral agent.
(4) In order to satisfy the distribution test, all of the following must be met: (A) the Senior Parity Coverage Ratio is at least 150%, the Overall Coverage Requirement is at least 110%, the Days cash on hand is at least 75 days with respect to the fiscal year prior to the date on which distributions are to be made, (B) no event of default has occurred and no condition exists which with the passage of time would constitute or become an Event of Default under the Bond Documents or prior Documents (as defined in the Indenture), (C) Purecycle Ohio has made all required deposits in various funds, and (D) there will remain following any distribution, no less than 75 days cash on hand (“the distribution test”). Contributions from any member of Purecycle Ohio or Affiliate of a member of Purecycle Ohio shall be excluded from any calculations.
60
On October 7, 2020, we issued $48.0 million in aggregate principal amount of Convertible Notes (the “First Tranche Notes”) and expect to issue an additional $12.0 million of aggregate principal amount of Convertible Notes (the “Second Tranche Notes”) to the Magnetar Investors within 45 days after the entry into the Merger Agreement, subject to the satisfaction of customary closing conditions. In the event that the Business Combination is not consummated within 180 days of the entry into the Merger Agreement, the Second Tranche Notes are subject to a special mandatory redemption at a redemption price equal to 100% of their aggregate principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest.
In connection with the Business Combination, the Combined Company and each subsidiary of the Combined Company that is a direct or indirect parent of us (the “Magnetar Guarantors”), is required to unconditionally guarantee, on a senior basis, all of our obligations in respect of the Convertible Notes. The Convertible Notes are our senior obligations and upon the consummation of the Business Combination, will be fully and unconditionally guaranteed by the Combined Company and any of our other direct or indirect parent entities.
Under the Magnetar Indenture for the Convertible Notes, we and the Magnetar Guarantors will, subject to certain exceptions, be restricted from incurring indebtedness that ranks senior in right of payment to the Convertible Notes and if we or the Magnetar Guarantors incur pari passu indebtedness that is secured by a lien, we and such Magnetar Guarantors are required to also provide an equal and ratable lien in favor of the holders of the Convertible Notes. The Convertible Notes are subject to certain customary events of default.
Unless earlier converted, redeemed or repurchased in accordance with the terms of the Magnetar Indenture, the Convertible Notes will mature on October 15, 2022, subject to an extension that may be exercised at our sole discretion to April 15, 2023 with respect to 50% of the then outstanding Convertible Notes. The Convertible Notes will bear interest from their date of issue at a rate of 5.875% per year, payable semi-annually in arrears on April 15 and October 15 of each year, beginning on April 15, 2021. Interest on the Convertible Notes is payable, at our option, entirely in cash or entirely in kind in the form of additional Convertible Notes.
The Convertible Notes are convertible at the option of the holders at any time, until the close of business on the business day immediately preceding the maturity date. Prior to the consummation of the Business Combination, the initial conversion rate for the Convertible Notes is (i) prior to the issuance of the Second Tranche Notes, 12.8403 shares of our Class A Units per $1,000 principal amount of Convertible Notes and (ii) upon issuance of the Second Tranche Notes, 13.1423 shares of such Class A Units per $1,000 principal amount of Convertible Notes. Following the consummation of the Business Combination, the conversion rate per $1,000 principal amount of Convertible Notes will generally be based on 80% of the lesser of (a) $10.00 and (b), if applicable, the weighted average cash price per share of ParentCo Common Stock at which ROCH sells shares of its Common Stock in the PIPE Investment, subject to certain limitations. The conversion rate will increase in the event the equity value of the Business Combination exceeds certain thresholds.
In connection with certain transactions resulting in a change of control (not including the Business Combination), the Convertible Notes will be convertible at the option of the holders until the 35th business day following the change of control becoming effective at an initial conversion rate equal to the quotient of $1,000 and 80% of the per share consideration received by holders of common stock in such change of control transaction. In each case, the conversion rate is subject to adjustment under certain circumstances, including certain dilutive events, in accordance with the terms of the Magnetar Indenture.
If certain fundamental change or change of control transactions occur with respect to us or, following the consummation of the Business Combination, the Combined Company, holders of the Convertible Notes may require the repurchase for cash of all or any portion of their Convertible Notes at a fundamental change repurchase price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the Convertible Notes to be repurchased, plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but excluding, the repurchase date.
61
We may not redeem the Convertible Notes at our option at any time, and no sinking fund is provided for by the Magnetar Indenture.
Cash Flows
A summary of our cash flows for the periods indicated is as follows:
| Years Ended December 31, | Period Ended September 30, | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except %) | 2019 | 2018 | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | $ | (6,315 | ) | $ | (5,427 | ) | $ | (10,784 | ) | $ | (8,421 | ) | ||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | (5,882 | ) | (11,121 | ) | (2,423 | ) | (2,269 | ) | ||||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 12,246 | 16,649 | 13,165 | 10,785 | ||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year | 101 | — | 150 | 101 | ||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of year | $ | 150 | $ | 101 | $ | 108 | $ | 196 | ||||||||
Cash Flows from Operating Activities. Net cash used in operating activities was $10.8 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 compared to $8.4 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2019, representing an increase of $2.4 million or 28%. The increase was primarily attributable to the increase in interest expense of $1.4 million, an increase in depreciation of $1.0 million, increase in wages and salaries of $0.7 million, increase in repairs and maintenance of $0.8 million, and an increase in consulting fees of $0.2 million, offset by a decrease in equity-based compensation of $1.1 million.
Net cash used in operating activities was $6.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to $5.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2018, representing an increase of $0.9 million or 16%. The increase was primarily attributable to our $19.3 million net loss offset by higher equity based compensation of $4.0 million, the issuance of warrants of $6.5 million, an increase in deferred research and development obligation of $1.0 million and an increase in accounts payable and accrued expenses of $2.2 million, which was partially offset by an increase in prepaid royalties of $1.1 million.
Cash Flows from Investing Activities. Net cash used in investing activities was $2.4 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 compared to $2.3 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2019. Our capital asset investment in 2019 was solely attributable to the construction of the Phase I Facility and the capital asset investment in 2020 was attributable to the Phase II Facility.
Net cash used in investing activities was $5.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to $11.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2018, representing a decrease of $5.2 million or 47%. The decrease was primarily attributable to fewer construction costs being incurred due to the completion of the Phase I Facility in June 2019.
Cash Flows from Financing Activities. Net cash provided by financing activities was $13.2 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 compared to $10.8 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2019. In the nine months ended September 30, 2020, we raised $17.5 million from the issuance of preferred equity, and paid down $4.2 million in related parties’ advances and debt. In the nine months ended September 30, 2019, we raised $9.4 million from issuance of preferred equity and obtained a $1.0 million loan from the Enhanced Capital Ohio Rural Fund (“ECORF”).
Net cash provided by financing activities was $12.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to $16.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. During the year ended December 31, 2019, we raised $10.9 million from the issuance of preferred equity, obtained the aforementioned loan from ECORF and a bridge loan from a related party in the amount of $0.6 million. In the year ended December 31, 2018, we raised $12.3 million from the issuance of preferred equity and borrowed $3.2 million from a related party.
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
The following table summarizes our contractual obligations and other commitments as of December 31, 2019, except that the table also reflects the aforementioned debt related to the Revenue Bonds and Convertible Notes issued in October 2020, and the years in which these obligations are due:
62
| Payments Due by Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | Less than 1 Year | 1 – 3 Years | 3 – 5 Years | More than 5 Years | ||||||||||||||||
| Contractual obligations: | (in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Long-Term debt obligations(1) | $ | 329,738 | $ | 6,922 | $ | 72,646 | $ | 650 | $ | 249,520 | ||||||||||
| Interest payments | 2,241 | 1,658 | 554 | 29 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Operating lease obligations(2) | 7,924 | 336 | 672 | 672 | 6,244 | |||||||||||||||
| $ | 339,903 | $ | 8,916 | $ | 73,872 | $ | 1,351 | $ | 255,764 | |||||||||||
(1) Includes principal obligations related to the Revenue Bonds and Convertible Notes we entered into in October 2020 described in the “Liquidity and Capital Resources” section.
(2) Represents future minimum lease payments under our operating lease for office space in Lawrence County, Ohio. The 25 year operating lease was entered with a related party.
The following table summarizes our contractual obligations and other commitments as of September 30, 2020, except that the table also reflects the aforementioned debt related to the Revenue Bonds and Convertible Notes issued in October 2020, and the years in which these obligations are due:
| Payments Due by Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | Less than 1 Year | 1 – 3 Years | 3 – 5 Years | More than 5 Years | ||||||||||||||||
| Contractual obligations: | (in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Long-Term debt obligations(1) | $ | 326,819 | $ | 16,277 | $ | 60,522 | $ | 500 | $ | 249,520 | ||||||||||
| Interest payments | 2,082 | 2,031 | 45 | 6 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Operating lease obligations(2) | 7,672 | 336 | 672 | 672 | 5,992 | |||||||||||||||
| $ | 336,573 | $ | 18,644 | $ | 61,239 | $ | 1,178 | $ | 255,512 | |||||||||||
(1) Includes principal obligations related to the Revenue Bonds and Convertible Notes we entered into in October 2020 described in the “Liquidity and Capital Resources” section.
(2) Represents future minimum lease payments under our operating lease for office space in Lawrence County, Ohio. The 25 year operating lease was entered with a related party.
We have not included our Feedstock agreements in the table above since the payment obligations under these agreements are contingent upon future events, such as the completion of Phase II Facility construction, funding requirements, quantity of feedstocks and IHS Index. The total minimum feedstock volume for all agreements, which are set to commence in 2022, amount to 60 million pounds of feedstock per year. The price per pound on the feedstock is variable, taking into account factors such as the quality of product, initial feedstock price, movements of price based on the fluctuations in the IHS Index, and product delivery point considerations. The Feedstock agreements are legally binding and contain a clause which allows for the termination of the agreement in the event we are unable to obtain sufficient financing by October 31, 2020, which is subject to negotiation and execution of a revised agreement.
We have not included our License Agreement in the table above since the obligations under this agreement are contingent upon future events, such as the completion of the Phase II Facility construction, funding requirements and quantity of P&G orders. P&G will receive royalties during the term of the license as a percentage of net sales to parties other than P&G at certain royalty rates based on the net price of the licensed product. The term of the License Agreement will terminate at the later of (a) the expiry date of the warrants or (b) upon expiration of the licensed patent held by P&G, unless terminated earlier. In addition, P&G has the option to purchase or assign offtake from the Phase II Facility at “most favored nation” pricing up to a certain amount in year one, and up to a certain higher amount per year or a percentage of nameplate capacity, whichever is greater, in each subsequent year of production. In 2019, we made a one-time, non- refundable, royalty-prepayment, which will be used to offset the future royalties payable to P&G under the License Agreement.
In addition, we enter into agreements in the normal course of business with vendors for research and development services and outsourced services, which are generally cancelable upon written notice. These payments are not included in this table of contractual obligations.
63
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We have no off-balance sheet arrangements that have or are reasonably likely to have a current or future effect on our financial condition, changes in financial condition, revenues or expenses, results of operations, liquidity, capital expenditures or capital resources that is material to investors. We do not have any off-balance sheet arrangements or interests in variable interest entities that would require consolidation. Note that while certain legally binding offtake arrangements have been entered into with customers, these arrangements are not unconditional and definitive agreements subject only to customary closing conditions, and do not qualify as off-balance sheet arrangements required for disclosure.
Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, that company’s principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and influenced by that company’s board of directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In connection with the preparation and audit of PCT’s consolidated financial statements for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 and the balance sheet data as of September 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019 and 2018, certain material weaknesses were identified in PCT’s internal control over financial reporting. A material weakness is a deficiency, or combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of PCT’s interim or annual consolidated financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. The material weaknesses were as follows:
| • | PCT did not have sufficient, qualified personnel to determine the appropriate accounting treatment for its complex agreements or transactions that required technical accounting analysis; |
| • | PCT’s lack of sufficient personnel also resulted in inadequate segregation of duties in the design and operation of the internal controls over financial reporting; |
| • | PCT’s lack of formal processes and controls resulted in an ineffective control environment, which led to an inadequate review of the financial statements and financial reporting; |
| • | PCT did not design and maintain effective controls over certain information technology (“IT”) controls for information systems that are relevant to the preparation of its financial statements, specifically with respect to user access, to ensure appropriate segregation of duties that adequately restrict user access to financial applications, programs, and data to appropriate company personnel; and |
| • | PCT did not design and maintain effective controls surrounding the completeness and cutoff of expenses and payables, such that certain expenses paid by a related entity on behalf of PCT were not appropriately allocated to PCT, and certain transactions were recorded in the period when the invoice was received rather than accrued in the period when the activity took place. |
These material weaknesses could result in a misstatement of substantially all of PCT’s accounts or disclosures, which would result in a material misstatement to the interim or annual consolidated financial statements that would not be prevented or detected. PCT has begun implementation of a plan to remediate the material weaknesses described above. Those remediation measures are ongoing and include the following:
| • | In 2018 and 2019 there were two accounting employees; both were part time, and one of which was an accounts payable clerk. PCT management is increasing staffing and has brought in outside resources. PCT has since hired a CFO, a Vice President of Finance, and a Controller and is looking to hire an Executive VP Finance to support the CFO and provide leadership to the accounting team. PCT has also engaged a public accounting firm to assist with financial reporting and advise on technical accounting issues; |
64
| • | PCT is making certain changes to its IT systems, including the development of formal access policies, the development of an audit of administrator activity and the reassignment of administrator privileges over PCT’s accounting system outside PCT’s accounting department; and |
| • | PCT is establishing a process to maintain checklists tracking related entity payments as part of its monthly close processes and is instituting policies to strengthen its receipt and processing of purchase orders to monitor accrual determinations. Furthermore, payment for almost all PCT expenses has been moved to PCT, with only a limited number of expenses paid by a related entity for situations where there is a shared contract. |
PCT plans to continue to assess its internal controls and procedures and intends to take further action as necessary or appropriate to address any other matters it identifies or are brought to its attention. PCT cannot assure you that the measures it has taken to date and may take in the future will be sufficient to remediate the control deficiencies that led to PCT’s material weaknesses in internal control over financial reporting or that PCT will prevent or avoid potential future material weaknesses. The effectiveness of PCT’s internal control over financial reporting is subject to various inherent limitations, including cost limitations, judgments used in decision making, assumptions about the likelihood of future events, the possibility of human error and the risk of fraud. If PCT is unable to remediate the material weaknesses, its ability to record, process and report financial information accurately, and to prepare financial statements within the time periods specified by the forms of the SEC, could be adversely affected which, in turn, may adversely affect PCT’s reputation and business and the market price of the Combined Company’s Common Stock.
In addition, any such failures could result in litigation or regulatory actions by the SEC or other regulatory authorities, loss of investor confidence, delisting of the Combined Company’s securities and harm to the Combined Company’s reputation and financial condition, or diversion of financial and management resources from the operation of PCT’s business.
See the section title “Risk Factors — PCT identified certain material weaknesses in its internal control over financial reporting. If PCT is unable to remediate these material weaknesses, or if PCT identifies additional material weaknesses in the future or otherwise fails to maintain an effective system of internal controls, PCT may not be able to accurately or timely report its financial condition or results of operations, which may adversely affect PCT’s business and stock price.”
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. Although these estimates are based on the Company’s knowledge of current events and actions the Company may undertake in the future, actual results could differ from those estimates and assumptions.
Equity-Based Compensation
The Company issues grants of incentive units to select employees and service providers. The equity- based compensation cost for the incentive units is measured at the grant date based on the fair value of the award over the requisite service period, which is the vesting period on the straight-line basis. In the event of modification, the Company recognizes the remaining compensation cost based on the grant date fair value over the new requisite service period. The Company applies a zero-forfeiture rate for its equity-based awards, as such awards have been granted to a limited number of employees and service providers. The Company revises the forfeiture rate prospectively as a change in an estimate, when a significant forfeiture or an indication that significant forfeiture occurs.
The fair value of the incentive units is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option- pricing model using the following assumptions:
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||
| Expected annual dividend yield | 0.0% | 0.0% | ||||
| Expected volatility | 42.1 – 67.7% | 51.1 – 95% | ||||
| Risk-free rate of return | 0.1 – 1.8% | 1.75 – 2.73% | ||||
| Expected option term (years) | 0.35 – 4.9 | 1.5 – 5.0 |
65
The expected term of the units granted is determined based on the period of time the units are expected to be outstanding. The risk-free rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant. The expected volatility was based on the Company’s capital structure and volatility of similar entities referred to as guideline companies. In determining similar entities, the Company considered industry, stage of life cycle, size and financial leverage. The dividend yield on the Company’s units is assumed to be zero since the Company has not historically paid dividends. The fair value of the underlying Company units was determined using the backsolve method.
Warrants
The Company measures the warrants issued to nonemployees at the fair value of the equity instruments issued as of the warrant issuance date and recognizes that amount as SG&A expense in accordance with the vesting terms of the warrant agreement. In the event that the terms of the warrants qualify as a liability,
the Company accounts for the instrument as a liability recorded at fair value each reporting period through earnings.
The Company has determined the warrants issued to P&G in connection with the patent licensing agreement are liability classified. Accordingly, the warrant units are remeasured at fair value each reporting period. The Company has determined its warrant to be a Level 3 fair value measurement and has used the Black-Scholes option pricing model to calculate its fair value using the following assumptions:
| Expected annual dividend yield | 0.0% | |||
| Expected volatility | 63.8 – 68.34% | |||
| Risk-free rate of return | 0.2 – 0.23% | |||
| Expected option term (years) | 0.5 – 3.9 |
The Company determined the warrants issued in connection with Class B-1 Preferred Unit Purchase Agreement are equity classified. Accordingly, the warrant units are held at their initial fair value with no subsequent remeasurement. The Company has determined its warrant to be a Level 3 fair value measurement and has used the Black-Scholes option pricing model to calculate its fair value using the following assumptions:
| Expected annual dividend yield | 0.0% | |||
| Expected volatility | 54.2 – 63.6% | |||
| Risk-free rate of return | 1.5 – 1.7% | |||
| Expected option term (years) | 4.4 – 4.7 |
The Company has determined the warrants issued to RTI in connection with terms of a professional services agreement are equity classified. Accordingly, the warrant units are held at their initial fair value with no subsequent remeasurement. The Company has determined its warrant to be a Level 3 fair value measurement and has used the Black-Scholes option pricing model to calculate its fair value using the following assumptions:
| Expected annual dividend yield | 0.0% | |||
| Expected volatility | 50.0% | |||
| Risk-free rate of return | 2.82% | |||
| Expected option term (years) | 5.0 |
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See Note 2 to the audited consolidated financial statements and unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus for more information about recent accounting pronouncements, the timing of their adoption, and our assessment, to the extent we have made one, of their potential impact on our financial condition and our results of operations.
66
Emerging Growth Company Election
ROCH is an “emerging growth company” as defined in Section 2(a) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and has elected to take advantage of the benefits of the extended transition period for new or revised financial accounting standards. Following the consummation of the Business Combination, the Combined Company expects to remain an emerging growth company at least through the end of the 2020 fiscal year and the Combined Company expects to continue to take advantage of the benefits of the extended transition period, although it may decide to early adopt such new or revised accounting standards to the extent permitted by such standards. The Combined Company expects to use this extended transition period for complying with new or revised accounting standards that have different effective dates for public and non-public companies until the earlier of the date the Combined Company (i) is no longer an emerging growth company or (ii) affirmatively and irrevocably opts out of the extended transition period provided in the JOBS Act. This may make it difficult or impossible to compare the Combined Company’s financial results with the financial results of another public company that is either not an emerging growth company or is an emerging growth company that has chosen not to take advantage of the extended transition period exemptions because of the potential differences in accounting standards used.
In addition, the Combined Company intends to rely on the other exemptions and reduced reporting requirements provided by the JOBS Act. Subject to certain conditions set forth in the JOBS Act, if, as an emerging growth company, the Combined Company intends to rely on such exemptions, the Combined Company is not required to, among other things: (a) provide an auditor’s attestation report on PCT’s system of internal control over financial reporting pursuant to Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002; (b) provide all of the compensation disclosure that may be required of non-emerging growth public companies under the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010; (c) comply with any requirement that may be adopted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board regarding mandatory audit firm rotation or a supplement to the auditor’s report providing additional information about the audit and the financial statements (auditor discussion and analysis); and (d) disclose certain executive compensation-related items such as the correlation between executive compensation and performance and comparisons of the Chief Executive Officer’s compensation to median employee compensation.
The Combined Company will remain an emerging growth company under the JOBS Act until the earliest of (a) December 31, 2026, (b) the last date of the Combined Company’s fiscal year in which it had total annual gross revenue of at least $1.07 billion, (c) the date on which the Combined Company is deemed to be a “large accelerated filer” under the rules of the SEC or (d) the date on which the Combined Company has issued more than $1.0 billion in non-convertible debt securities during the previous three years.
67
Unless the context otherwise requires, all references in this section to “PCT,” the “Company,” “we,” “us,” or “our” refer to PureCycle Technologies LLC and its subsidiaries prior to the consummation of the Business Combination. Following the Business Combination, the Combined Company’s business will be that of PCT described below.
Overview
PureCycle Technologies LLC (“PCT”) is commercializing a patented purification recycling technology (the “Technology”), originally developed by The Procter & Gamble Company (“P&G”), for restoring waste polypropylene into resin with near-virgin characteristics. We call this resin ultra-pure recycled polypropylene (“UPRP”), which has nearly identical properties and applicability for reuse as virgin polypropylene. PCT has a global license for the technology from P&G. We intend to build our first commercial-scale plant in Ironton, Ohio (referred to herein as “Plant 1” or the “Phase II Facility”), which is expected to have nameplate capacity of approximately 107 million pounds/year when fully operational. Production is expected to commence in late 2022 and the plant is expected to be fully operational in 2023. We have secured and contracted all of the feedstock and product offtake for this initial plant. Our goal is to create an important new segment of the global polypropylene market that will assist multinational entities in meeting their sustainability goals, provide consumers with polypropylene-based products that are sustainable, and reduce overall polypropylene waste in the world’s landfills and oceans.
PCT intends to build new recycling production facilities globally, with the goal of having 30 commercial lines operational by 2030 and 50 by 2035. In addition to our first plant in Ironton, Ohio, we expect the next plant to be located in Europe and to commence production in 2023 with a nameplate capacity of approximately 107 million pounds when fully operational. Additional expansion in the United States is expected to include a scaled up commercial line capable of producing over 165 million pounds. Pre- engineering for the design and installation of five commercial lines in a single “cluster” site is currently underway and will result in a combined capacity of over 825 million pounds annually. From these first seven plants PCT expects to bring over 1 billion pounds of annual recycled polypropylene production to the market in the next five years, which represents less than 1% of the total annual projected demand for virgin and virgin parity resin.
PCT is regarded as a leader in innovation in polymers, sustainability, and recycling by numerous non- government organizations (“NGOs”), trade associations, and major media publications. Recognition of PCT’s achievements include the American Chemistry Council’s Innovation in Plastics Recycling award (2017), Time Magazine’s “Best Innovations of 2019”, and the 2020 Re|focus Solar Institute Award for Leadership in Innovation awarded by the Plastics Association.
Industry Background
Currently, polypropylene is one of the largest contributors to the global plastics waste crisis. Each year more than 150 billion pounds of polypropylene are manufactured and incorporated into a wide array of consumer facing and industrial products. Less than 1% of polypropylene is collected and recycled annually, compared to 20% of polyethylene terephthalate (“PET”), and less than 12% of the overall plastics market is collected and recycled. Many of the advantages attributed to polypropylene (strength, toughness, elasticity) also contribute to its problematic waste stream after initial use. Due to its chemical makeup, polypropylene does not react with diluted bases and acids. As such, it does not break down and can remain a pollutant in our oceans, landfills, and food chain for centuries. Despite these environmental consequences, polypropylene utilization continues to increase, growing at a 5.3% average annual growth rate (“AAGR”) since 2010 with a projected AAGR of 4.3% over the next 5 years.
In response to these issues, multinational companies have partnered with NGOs and trade associations to encourage recycling of plastics. Significant capital has been raised to combat the global plastics crisis, including multinational collaboration, ocean clean-up initiatives, new plastic economies, and global infrastructure investments. For example, over 450 multinationals have signed the Ellen MacArthur Foundation’s New Plastics Economy Global Commitment. This commitment is focused on: (i) eliminating unnecessary packaging waste, (ii) reusing plastic where possible, (iii) making all packaging 100% reusable, recyclable, or compostable, and (iv) the reuse, recycling, or composting of all plastic packaging.
68
Multinationals have taken this pledge even further by committing to reduce the use of virgin plastic packaging by 50% by 2025. These commitments are being driven by consumer demand for sustainable products, which is expected to continue to drive many multinational corporations to source sustainable materials to achieve publicly announced sustainability objectives.
While there are a range of ways that plastics can be recycled today, there are very limited options available for polypropylene. The current options are chemical and mechanical recycling, both of which have significant drawbacks that have resulted in extremely low recycling rates.
Chemical Recycling
Chemical recycling is a type of plastics reclamation that typically creates a chemical reaction to break the molecular bonds of the plastic, resulting in the separated molecules from which plastics are made. This process uses a combination of high energy, heat, pressure, and typically other chemicals to break down the plastic into its most basic monomer form while burning off and removing any contaminants.
In the two most common forms of chemical recycling, the output requires further processing to become a viable product for fuel or plastic. Because additional steps in the supply chain are required to return the output back to plastic, as well the substantially high energy expenditure and carbon dioxide (“CO2”) emissions from the process itself, we do not believe current chemical recycling methods are a true circular solution to the plastics waste crisis. In addition, the cost of the end plastic, once finally returned to its original state, can be inflated due to energy and processing costs.
Mechanical Recycling
Mechanical recycling is the most common recycling method currently performed by solid waste collectors and material reclamation facilities. Mechanical recycling involves several steps, including various levels of optical sortation, manual sortation, washing, density separation or electrostatic separation, shredding, compounding, and pelletizing. The process is currently the most energy efficient recycling solution for polypropylene; however, due to the nature of mechanical reclamation, many of the original additives from within the waste material as well as outside contaminants remain in the end product. Accordingly, the process can lead to wide variations in end product quality and low-value end uses. Currently, mechanically recycled polypropylene can only be downcycled into products with lower specifications that are unable to meet the requirements for food and consumer grade packaging.
We believe the combination of demand for more sustainable products, the growing use of polypropylene, and the inadequacy of existing recycling processes creates a significant opportunity for a company like PCT that has demonstrated that it can turn polypropylene waste into virgin-like polypropylene.
PureCycle’s Solution: Ultra-Pure Recycled Polypropylene
PCT’s recycling technology is a purification recycling process that uses a combination of solvent, temperature and pressure. Waste stream polypropylene is returned to near near-virgin condition through a novel configuration of commercially available equipment and unit operations. The process puts the plastic through a physical extraction process using super critical fluids that both extract and filter out contaminants and purify the color, opacity, and odor of the plastic without altering the physical characteristics of the polymer. By not altering the chemical makeup of the polymer, the Company is able to use significantly less energy and reduce production costs as compared to virgin resin.
69
The unique ‘super-critical fluid’ extraction process does not require chemical reactions and involves the key components shown in the diagram below:
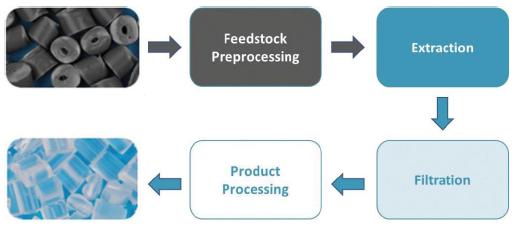
Key benefits of the Technology include:
• all equipment is standard processing equipment, commercially available and widely used;
• use of a physical separation/purification process without chemical reactions;
• operating at conditions comparable to current polyolefin (polypropylene and polyethylene) production conditions;
• expected to utilize ~1∕4 the amount of energy required to produce virgin polypropylene resin; and
• ability to recycle a wide range of polypropylene waste.
Our UPRP technology results in near virgin equivalent quality, color and level of odor. Resin UPRP provides our customers with 100% recycled content without compromising appearance, purity or performance in finished products. UPRP is interchangeable with virgin polypropylene and based on efforts underway, is expected to be approved for use in food-grade applications. UPRP’s characteristics are nearly identical to virgin polypropylene for key plastic resin metrics, including yellowness index value, opacity and melt flow index.
PCT Strengths
Large and Underserved Market
Polypropylene is one of the most-widely produced polymers globally with annual production in excess of 150 billion pounds and expected to exceed 200 billion pounds by 2024. Recycling rates for waste polypropylene are below 1%, compared to almost 20% for PET, resulting in continuous landfilling of nearly all polypropylene waste. The limited polypropylene recycling conducted today is primarily mechanical recycling, which results in a dark, odorous, non-food grade recycled product with limited applications and is not a viable substitute for virgin polypropylene. Consistent with increasing environmental awareness and activism more broadly, there is growing demand for a solution to reduce waste polypropylene by many stakeholders including consumers, corporations, governments and regulators, etc. We believe PCT’s UPRP is a viable substitute and alternative for virgin polypropylene providing a near-term solution to the massive and growing polypropylene waste problem. PCT believes the size of the addressable market for its UPRP is so large that it will only ever be able to serve a small portion. As an example, PCT expects to develop plants with annual UPRP production capacity of approximately 1 billion pounds in the next five years, representing less than 0.5% of the expected global polypropylene market.
70
Proprietary and Proven Technology Developed by Procter & Gamble
PCT utilizes a proprietary purification process that converts waste polypropylene feedstock into UPRP pellets with similar characteristics to virgin polypropylene. The Technology was developed by P&G, and PCT has a global license from P&G. PCT’s process utilizes a broad range of feedstocks including waste carpet, stadium cups and supersacks and produces virgin-quality UPRP pellets that are clear, odorless and contaminant-free, making it suitable for use in almost all polypropylene applications including high-value, food grade consumer products. This patented process was developed by P&G over the course of eight years and has been refined by PCT over the past five years with more than 350 laboratory tests and with over 1,000 pounds of UPRP produced at the Feedstock Evaluation Unit (also called the “FEU” or “Phase I Facility”) since its commissioning in July 2019. In addition, PCT’s purification process and UPRP quality have been validated by independent technical consultants and many of PCT’s strategic partners and initial customers.
High Barriers to Entry
PCT has a global license to P&G’s recycling technology. PCT has spent the last five years developing the actual production process. It has tested over 350 feedstocks and sent samples to large end customers including P&G, Aptar and Total. We have developed a pilot line which we call our Feedstock Evaluation Unit which we use to screen potential feedstock sources and demonstrate that we can process a wide range of polypropylene feedstock. In October 2020, we closed a $250 million Revenue Bonds financing that is expected to substantially fund our first commercial plant, which we expect to start commercial production in late 2022.
Third-Party Validation of Our Product and Process
PCT and independent third parties have validated both PCT’s UPRP production process and finished product. The FEU, commissioned in July 2019, utilizes a smaller scale of the same equipment and processes as PCT’s planned full-scale production plants and serves as a valuable pilot plant with regards to both plant construction and plant operation. The plant design is modular, utilizing well-known and widely utilized industrial processing equipment, but in a novel and proprietary way. All future plants, regardless of size and location, are expected to utilize the same equipment and configuration. The Company has also validated the customer demand for UPRP and signed offtake agreements for up to 20-years for its first plant. Based on signed offtake agreements and Letters of Intent (“LOI”), demand for the first plant is approximately four times greater than the plant’s nameplate capacity. Similarly, PCT secured all required feedstock for its first plant with long-term agreements. With the support of long-term customer offtake and supplier feedstock contracts, highly reputable engineering and construction firms leading the construction, demonstrated success of the FEU and other factors, PCT closed the $250.0 million Revenue Bonds offering in October 2020 to finance a substantial portion of the first plant, with the remaining required capital provided by PCT LLC equity contributions. PCT expects to use a similar approach with future plants to pursue similar project financing arrangements and de-risk the financial profile of each plant and PCT overall.
71
Blue Chip Customers, Partners and Strategic Investors
PCT has developed mutually beneficial relationships and partnerships with many established, blue-chip industry leaders. PCT’s partnership with P&G began in October 2015 with the signing of the License Agreement for the Technology P&G invented. P&G is also a PCT offtake customer, along with a range of other well-known global and regional firms. In addition to P&G, PCT has key partnerships and relationships supporting plant site identification, plant development and construction, research and development, product sales and customer contracts, feedstock sourcing and contracts, operating expertise and other elements of its business. These partners include:
 |
P&G’s initial research yielded the 13 U.S. process patents that form the basis of the Technology. P&G is a longstanding and critical partner for PCT as the patent owner and offtake partner. Additionally, P&G provides continued research and development support, in collaboration with the Company. |
 |
PCT has entered into a strategic partnership with Aptar as the company’s preferred converter. Aptar will continue to play a crucial role in providing product performance studies and recommendations on how the UPRP performs through the transformation process. |
|
|
Nestlé has provided R&D collaboration to develop new packaging materials that help avoid plastic waste, in line with the company’s commitment to make 100% of its packaging recyclable or reusable by 2025. |
 |
Total is a strategic partner of PCT and offtake partner. |
|
Under the company’s strategic partnership, Milliken will be the sole provider of additives to PCT. |
 |
L’Oréal is a strategic partner of PCT and an offtake partner. |
 |
Ravago has an extensive network across the supply chain for both offtake and feedstock and has helped the Company build relationships across the industry. Ravago is both a feedstock supplier to and an offtake purchaser from PCT. |
Experienced Leadership Team
The PCT management team has broad experience across plastics manufacturing, plant development, technology, R&D, sales, marketing, accounting and finance. PCT Chief Executive Officer Mike Otworth has over 23 years’ experience leading and scaling early stage companies, holding multiple senior management positions with a proven track record of founding and capitalizing startups. Chief Financial Officer Michael Dee was a senior executive at Morgan Stanley and has over 30 years of public markets, corporate finance, and M&A experience. Chief Science Officer John Scott holds a dual Ph.D. in Physics and Astrophysics, authored over 60 academic papers, and was the CEO of the XL TechGroup, the precursor company of Innventure LLC, an affiliate of PCT. Chief Commercial Officer David Brenner brings over 15 years’ experience leading transformational projects in a range of industries and was a Senior Manager at Deloitte prior to joining PCT. Director of Technology Jason Vititoe holds two product patents in polystyrene and decades of engineering leadership experience working for Americas Styrenics and Dow Chemical Company. Senior Director of Operations Chris Talarek has over 20 years of operations leadership at BP Oil, P&G, and Timbertech. Combined, the PCT executive team has over 100 years’ experience leading operations and over 70 years operating equipment.
Attractive Plant Economics
PCT is offering a unique UPRP product to a large and growing global polypropylene market and expects market demand to far exceed supply into the foreseeable future. This demand / supply dynamic supports PCT’s planned buildout strategy and supports premium pricing for UPRP that PCT is realizing today and expects to continue to realize in the future. As a result, PCT expects to sell much of the production volume for each new plant prior to construction. Primary components of PCT’s operating costs include feedstock, labor, utilities, and other variable process inputs. These costs are relatively fixed on a per unit basis, providing significant upside to increasing prices. Through its cluster plant strategy, PCT expects to realize capital investment and operational efficiencies for future plants, reducing the investment per pound of capacity produced and allowing capacity to be added more quickly. PCT expects that rapid volume scale-up, long-term fixed price contracts and stable unit cost economics will result in strong EBITDA margins, which combined with limited maintenance capital expenditure requirements should provide significant and growing cash flow as plant construction is completed.
72
PCT Strategy
Fully Unlock and Develop Polypropylene Circular Economy
PCT’s mission is to fully unlock the circular economy for polypropylene at sustainable economics across the supply chain. Comprising approximately 28% of annual global plastic production, polypropylene represents one of the largest challenges in plastics recycling and the plastics waste crisis. PCT’s patented and licensed Technology provides a truly unique waste-plastic-to-virgin-plastic solution to increase polypropylene recycling rates and allow stakeholders to achieve sustainability goals. As global demand for recycled polypropylene continues to grow, PCT expects demand for its UPRP to grow exponentially and support continued premium pricing compared to virgin polypropylene.
Complete Development and Commissioning of Plant 1 in Ironton, Ohio
PCT intends to address the world’s growing appetite for recycled polypropylene with the construction of its first commercial production facility located in Ironton, Ohio. After securing funding through a $250 million solid waste Revenue Bonds offering, construction commenced on the Plant 1 in October 2020. This includes site construction and issuance of long-lead time purchase orders from key equipment and system vendors. Plant 1 leverages the existing infrastructure of PCT’s pilot facility known as the Feedstock Evaluation Unit (FEU), which became operational in 2019. PCT’s plants use standardized equipment that is used in large plants globally, further facilitating scale-up of production. Additionally, PCT is supported by global construction and engineering partners that have commenced development on Plant 1 and are expected to be leveraged in the development of future plants. Plant 1 is expected to be operational in late 2022 and will have a nameplate capacity of 107 million pounds per year of UPRP.
Global Plant Development Buildout
To meet the growing global supply-demand gap for virgin-like recycled polypropylene, PCT aims to expand its annual production capacity to over one billion pounds by late 2024. PCT will leverage its extensive network of strategic partners and customers to support its global plant buildout strategy. We believe this expansion plan is achievable due PCT’s underlying technology, which is comprised of commercially available equipment as well as top tier construction partners that operate globally. PCT’s second plant is expected to be located in Europe where site studies, feedstock, and offtake partner development have already begun. Operations for Plant 2 are expected to start in 2023 with production capacity of 107 million pounds per year. PCT has also begun assessing potential “cluster” sites, which will include five commercial production lines, each with an annual capacity of 165 million pounds of UPRP. This scaled up cluster strategy offers process and construction efficiencies such as leveraging single construction teams to install all five lines, reduced CAPEX from pre-existing infrastructure, reduced operational costs, and a single permitting process for all five lines. The first cluster site is expected to be located in the United States, beginning construction in 2021, and with its first unit beginning operations in 2023. Further site expansion plans include 30 commercial lines operational by 2030 and 50 by 2035 in key global markets and targeting over 8 billion pounds of UPRP production.
Continue Identifying New Customers / Product Applications and Additional Feedstocks / Sources
To support its global expansion, PCT plans to invest in its sales and offtake partner development to identify new potential partners and unique product applications whose value to end consumers can be enhanced by the inclusion of UPRP. Already, PCT has seen significant interest from potential offtake partners willing to pay premium pricing for its UPRP production, including over 200 non-solicited offtake inquiries, including many top global producers. As global sustainability trends continue, the pursuit of optimal feedstocks will be critical to the company’s success. To date, PCT has evaluated over 145 various feedstocks through its FEU. PCT intends to further expand its universe of acceptable feedstocks through strategic partnerships with waste collectors for post-consumer waste (PCR), manufacturers for post industrial waste (PIR), and inclusion of the latest pre-processing and sortation technologies.
73
Maintain Capital Structure Flexibility to Finance Plant Buildout
PCT plans to develop global production plants with over one billion pounds of capacity by 2025. The Company recently issued $250 million non-recourse Revenue Bonds to partially fund Plant 1 along with PCT LLC equity. PCT expects to finance future plants primarily with a combination of debt and equity financing. The Company, supported by its ESG profile, believes there is significant interest and demand from debt and equity sources, including traditional debt and equity, strategic partners, government grants and loans, etc. As the initial plants become operational, PCT expects to generate cash flow that could also support funding for future plant development.
The Product: UPRP
Polypropylene has multiple applications including packaging and labeling for consumer products, piping, ropes, cabling and plastic parts for many industries and, in particular, the automotive industry. It is one of the most commonly used plastics in the world due to its flexibility as a “living hinge” on consumer product lids (shampoo, ketchup) since it typically will not break when bent even after multiple movements and ranges of motion.
PCT’s unique purification separates colors, odors, and contaminants through a physical separation process. This process and end product quality have been tested and validated by P&G, prospective offtake partners, and independent third party labs. When compared to virgin resin, PCT’s UPRP expresses near identical mechanical properties across Melt Flow Index (a measure of viscosity), Tensile Modulus (measure of stiffness), and Impact Strength (a measure of sudden resistance to force).
PCT has leveraged strategic partners with expertise in operations, the use of additives to improve the physical properties of polymers, and Consumer Packaged Goods companies to conduct early testing to confirm that the product meets the expectations of the end users and offtake partners.
Offtake and Customers
Based on current offtake subscription agreements and LOIs, PCT intends to market and sell the UPRP to a wide range of industries, including but not limited to: resin distributors, resin converters, consumer goods manufacturers, food and beverage producers, toy manufacturers and personal care goods producers. Polypropylene is used in a variety of end markets, including consumer packaged goods, electronics, automotive, building & construction, household goods and agriculture. Due to a growing awareness around sustainability and many multinational companies shifting their strategic focus to sustainability as a key differentiator, PCT intends to provide UPRP to a diversified customer base across end markets over time.
Certain offtake pricing agreements are established based on a monthly index published by the IHS Global Plastics and Polymers Report. Since PCT began accepting LOIs from other potential offtake customers, PCT has received significant interest for its UPRP at a premium price to commodity polypropylene pricing. The premium pricing demonstrated in the LOIs supports a de-linking of UPRP pricing from the price of virgin polypropylene. Assuming the continuation of current trends in global sustainability and lack of competing alternatives, PCT expects the price of its UPRP to continue to command a premium over the price of virgin resin and not be subject to fluctuations in the price of virgin PP. For each of the offtake agreements, PCT guarantees the UPRP product to meet specific criteria for both color, opacity and other key technical targets such as MFI (Melt Flow Index) and tensile strength (aka tensile modulus).
The Company has entered into minimum offtake subscriptions agreements for UPRP from its first plant in the amount of 63 million pounds per year, and at PCT’s sole option, up to a quantity of 138 million pounds per year. In addition to the fully executed contracts for these volumes, an additional volume of 35 million pounds annually is secured pursuant to agreements with three strategic partners at their option. Additionally, PCT has entered into LOIs with over twenty-five companies, including large global consumer product companies, distributors and manufacturers that use polypropylene. These LOIs would secure a minimum of 94 million additional pounds of volume and up to 250 million pounds at the Company’s option. The Company continues to maintain active dialogue with potential offtake customers to secure additional volume for future plants.
74
Feedstock Supply
Over 150 billion pounds of polypropylene waste feedstocks are generated every year across multiple industries. Most of these feedstocks are untapped by the market today and are disposed of in landfills and oceans. These feedstocks include flexible & rigid packaging, plastic waste from textiles, and large business segments including consumer products, medical, automotive, industrial, and agricultural.
PCT has tested over 145 feedstocks from over 35 suppliers and reached definitive feedstock agreements with five suppliers representing 60 million minimum and up to 210 million pounds at PCT’s option, with pricing linked in part to the IHS Markit Index that tracks the prices of General Purpose Homopolymer prices and is reported out on a monthly basis (the “IHS Index”). Each supplier agreement includes multiple waste streams across post-industrial and post-consumer polypropylene resin. Each year, the Company will request a quantity of feedstock between the minimum and maximum quantities specified in each feedstock supply agreement. The feedstock price will be linked in part to changes in the index for virgin polypropylene in a price schedule that contains a fixed, collared price around an index price range that is also known as the “baseline” price. These contract prices are linked to the IHS Index which provides a tracking mechanism and collar for feedstock prices. Additionally, the contract prices are tied to tranches based on the percentage of polypropylene in the feedstock supplied to ensure and incentivize suppliers to provide the highest percent of polypropylene. The price schedule also contains a minimum price floor.
PCT has chosen to process most polypropylene feedstock sources across film, fiber, and rigids. Each feedstock type has immediate advantages as well as long-term benefits for PCT:
| • | Rigids, commonly referred to as post-consumer recycled plastic, are the most commonly reclaimed plastics in the industry today. Existing recycling infrastructure in the United States today provides a range of opportunities to acquire rigid feedstocks through mixed bales with price transparency. Though traditional mixed bales are not currently desirable as an alternative option for obtaining additional feedstock supply. The implementation of China’s National Sword, a regulatory policy enacted in 2018 that stopped China’s importation of mixed plastics/trash has created a market need to find alternative buyers for recycled polypropylene. Increased social awareness has resulted in a specific focus on recycling polypropylene and efforts like The Recycling Partnership have created a $35 million fund to help grow polypropylene collection domestically. |
| • | Film is typically not processed by traditional reclaimers, resulting in a favorable acquisition price for PCT. Today, only 15% of film is reclaimed, which represents a strong opportunity for PCT to expand in the future. The Technology allows PCT to unlock the value of this feedstock at a favorable cost. |
| • | Fiber is the least recycled of the 3 waste streams, due to the limited infrastructure, innovation, and market for this material. Each year, approximately four billion pounds of carpet head to the landfill, which represents approximately 500 million pounds of polypropylene. |
The Processing Facilities
The Feedstock Evaluation Unit
The FEU (also called the “Phase I Facility”) is an 11,000 square foot facility located in Ironton in Lawrence County, Ohio with over 1 mile of stainless-steel piping. The facility was completed in July 2019 and has been producing UPRP product since that time. The FEU is considered a pilot scale replica of the larger commercial line being developed at Plant 1. It serves the strategic purpose of determining if new feedstock streams are of sufficient quality before introducing them into the commercial line at Plant 1 initially, and later facilities as built. The FEU is designed to protect the throughput and uptime of the commercial line. It can also serve as a limited, supplemental production source, adding capacity to Plant 1 as needed. Quantities of offtake from the FEU have been provided to offtake partners for evaluation. To date, the product produced is within ranges acceptable under contractual offtake agreements. When the commercial line is operational, the FEU will remain a critical component for testing feedstock.
75
Plant 1
Located on the same site as the FEU, PCT commenced construction in October 2020 on its first commercial scale recycling facility (“Plant 1” or the “Phase II Facility”). The property is formerly owned by The Dow Chemical Company, where a plant is no longer in operation, but significant infrastructure remains. PCT intends to construct, renovate, equip and install an approximately 150,000 square foot facility housing commercial-scale equipment designed to process 182 tons per day of waste polypropylene, including the repurposing of three existing buildings for feedstock pre-processing and storage. Once operational, Plant 1 should be capable of annual production of 107 million pounds of UPRP when operating at 90% capacity and with expected process losses. We expect Plant 1 to begin production in late 2022 and are using the same team that brought the Phase I Facility online, specifically:
| • | The core process, known as the Inside Battery Limit (“ISBL”), is comprised of process equipment, extruders, pelletizers, and related equipment and is to be provided under an equipment supply contract with Koch Modular Process Systems, LLC (“KMPS”), a leading global engineering, procurement and construction group. |
| • | Denham-Blythe Company, Inc., (“Denham-Blythe”), a provider of architectural, engineering, construction management, general contracting, and start-up services, has been selected to serve as the Outside Battery Limit (“OSBL”) and will perform all civil and structural construction aspects of Plant 1, in addition to plant components related to materials handling and transfer. |
| • | M. A. Mortenson Company, a construction company, will be the Company’s agent responsible for, among other things, coordinating PCT, Denham-Blythe and its subcontractor, EN Engineering, Inc., and KMPS. |
Most importantly, each of KMPS and Denham-Blythe, among other suppliers and third party vendors are providing process guarantees, warrantees of performance, and/or have entered into agreements with liquidated damage provisions if certain progress milestones are not reached.
Government Regulation
PCT is subject to laws and regulations administered by various federal, state and local government agencies in the United States, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”), the Federal Trade Commission, the Environmental Protection Agency, and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
Under various federal statutes and implementing regulations, these agencies, among other things, prescribe the requirements and establish the standards for quality and safety and regulate PCT’s products and the manufacturing, labeling, marketing, promotion, and advertising thereof.
PCT is also subject to labor and employment laws, laws governing advertising, privacy laws, safety regulations, marketing claims and other laws, including but not limited to consumer protection regulations that regulate retailers or govern the promotion and sale of merchandise. PCT’s operations, and those of its suppliers, are subject to various laws and regulations relating to environmental protection and worker
health and safety matters.
FDA Letter of No Objection
PCT has followed the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) Guidance for Industry: Use of Recycled Plastics in Food Packaging (Chemistry Considerations). It is expected that the FDA will provide, but PCT cannot guarantee receipt of, a Letter of No Objection (“NOL”) in 2021, which would permit the Company’s UPRP to be used in food grade applications. The process for obtaining an NOL will include FDA evaluation of both the PCT purification process as well as the recycled feedstock resin. As such, PCT will seek multiple NOLs for type of use and for each categorically different source of feedstock. This process will provide necessary data to the FDA with the end goal of understanding the substances of interest in certain feedstocks and the level of removal from the purification process. And, in addition, as needed, individual migration studies will be conducted to simulate articles in contact with food.
76
Intellectual Property
Pursuant to the License Agreement, P&G has granted PCT a license to utilize P&G’s intellectual property and PCT, subject to the Grant Back, licenses back to P&G a right to sublicense, subject to volume and geographic restrictions, the P&G technology. PCT has a limited right to sublicense the technology to PCT affiliates and select third parties with the consent of P&G. The intellectual property is tied to the proprietary purification process by which waste polypropylene may be converted to ultra-pure recycled polypropylene. The License Agreement also governs the ownership of process improvements. Improvements (as defined in the License Agreement) invented by PCT are owned by PCT and are licensed back to P&G for the purpose of selling licensed product, while Improvements (as defined in the License Agreement) invented by P&G or jointly by P&G and PCT are owned by P&G and licensed to PCT. The license may become non-exclusive if PCT fails to make payments or undergoes a change of control without the prior written consent of P&G. If PCT defaults under the License Agreement and the License Agreement is terminated, P&G fails to perform its obligations under these agreements, or PCT’s relationship with P&G is otherwise damaged or severed, this could have a material adverse effect on PCT’s business, results of operations or financial performance. In addition, P&G’s failure to consent to future sublicenses by PCT to PCT affiliates and select third parties would limit PCT’s ability to expand as contemplated by its current business plan.
The License Agreement will terminate upon the later of (a) the expiration of the last Licensed Patent (as defined in the License Agreement) to expire and (b) the expiry date of the warrant between PCT and P&G (which was executed on October 16, 2020). Under the License Agreement, nine Utility Patents were filed and granted by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (“USPTO”). Each Utility Patent will expire on the 20-year anniversary of the original application filing date. There are four additional Utility Patents pending which will reset the duration of the License Agreement. Together, these thirteen Utility Patents make up the Licensed Patents.
Facilities
From May 2018 to September 2020, PCT leased the Lawrence County, Ohio property from Innventure LLC, an affiliate of PCT. On October 8, 2020, a PCT subsidiary purchased the land from Innventure LLC. See the section entitled “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions.”
PCT leases its office space, which consists of 2,870 square feet located at 5950 Hazeltine National Drive, Suite 650, Orlando, Florida 32822 expiring September 2022 and 2,714 square feet located at 925 County Road 1A, Bldg 560, Ironton, OH 45638 expiring January 2021.
PCT believes that its current facilities are suitable and adequate to meet its current needs.
Human Capital Resources
Employees & Demographics. As of September 30, 2020, PCT employs 31 employees. None of PCT’s employees are represented by a labor union. With respect to demographics, approximately 30% of our employees are female and 70% are male. There will be additions to our staff in the coming months as our operations expand to support the initial operation of the Project and the contemplated future expansion.
Talent & Turnover. With a focus on talent acquisition, the leadership team seeks out the most qualified candidates for open roles and endeavors to keep them at PCT. We have a robust program for seeking out those candidates, which ranges from sourcing through talent applications, reviewing direct applicants and using internal referrals to fill roles. Additionally, we strive to promote internally, if applicable. Our program has resulted in a low turnover rate of 6% to date.
Compensation Practice & Pay Equality. As PCT evolves and expands operations, Human Resources in partnership with the leadership team will continue to evaluate the existing workforce to ensure that best practices are maintained across the entire team without risk of inequality. Pay structures will be reviewed annually to ensure best practices in a competitive market and, as part of that review, compensation will be realigned where appropriate for existing employees and new hires.
77
Legal Proceedings
As of the date of this prospectus, PCT was not party to any material legal proceedings. In the future, PCT may become party to legal matters and claims arising in the ordinary course of business, the resolution of which PCT does not anticipate would have a material adverse impact on its financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
78
References in this section to “we”, “our”, “us” and the “Company” generally refer to PCT and its consolidated subsidiaries prior to the Business Combination and ParentCo and its consolidated subsidiaries after giving effect to the Business Combination, also referred to as the Combined Company.
Executive Officers and Directors After the Business Combination
The following persons are expected to serve as the Combined Company’s executive officers and directors following the Business Combination.
| Name | Age | Position | ||
| Executive Officers | ||||
| Michael Otworth | 58 | Chairman, Chief Executive Officer and Director | ||
| Michael Dee | 64 | Chief Financial Officer, Secretary and Treasurer | ||
| David Brenner | 35 | Chief Commercial Officer | ||
| Non-Employee Directors | ||||
| Tanya Burnell | 43 | Director | ||
| Richard Brenner | 66 | Director | ||
| Dr. John Scott | 69 | Director | ||
| Jeffrey Fieler | 51 | Director | ||
| Timothy Glockner | 44 | Director |
Michael Otworth will serve as the Combined Company’s Chairman and Chief Executive Officer and as a member of the Combined Company’s board of directors. Mr. Otworth has served as Chief Executive Officer of Innventure LLC, an affiliate of PCT, and PCT and as a member of PCT’s board of directors since October 2015. Previously, Mr. Otworth served as President and Founding Partner of Green Ocean Innovation from 2008 to 2015, which provided technology sourcing and innovation strategy and development services to Lilly/Elanco Animal Health primarily focusing on therapeutics, diagnostics and various medical devices. Prior to Green Ocean Innovation, he served as Vice-President and Founding CEO of multiple start-ups at XL TechGroup (“XLTG”), a venture capital firm, from 1996 to 2000. Additionally, Mr. Otworth was a key senior management leader of XLTG, which founded, capitalized and advanced companies successfully to late stage funding from 2000 to 2008. He began his career on Capitol Hill working as a legislative aide and committee staff member in the U.S. House of Representatives after Graduating from Otterbein University with a B.A. in Political Science & Biology. We believe Mr. Otworth is qualified to serve as Chief Executive Officer of the Combined Company and as a member of the Combined Company’s board due to his more than 24 years of experience leading start-ups in the technology industry.
Michael Dee will serve as the Combined Company’s Chief Financial Officer. Mr. Dee joined as the Company’s Chief Financial Officer in October 2020. Previously, Mr. Dee served as the Managing Member of Bird Creek Capital LLC, a consulting services company, providing advice and services to the Company. Before joining the Company, Mr. Dee served as the President and Chief Financial Officer and a member of the board of directors of Graf Industrial Corp., a special purpose acquisition company from October 2018 to September 2020, which acquired a lidar technology company in September 2020. Previously, Mr. Dee was involved in a number of personal investment and philanthropic activities. In 2015 and 2016, Mr. Dee was a Senior Advisor to the President for Finance of the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, a $100 billion multilateral development bank, and served as a member of its Management and Investment Committee. From 2010 to 2015, Mr. Dee managed various private investments, including providing advice to SeaOne Maritime Corp., a startup focused on the monetization of natural gas and gas liquids. Mr. Dee was Senior Managing Director - International of Temasek Holdings Private Limited, Singapore’s sovereign investment company, from 2008 to 2010 and also served as a senior member of its Management Committee and Investment Committee. Prior to joining Temasek, Mr. Dee worked at Morgan Stanley from 1981 to 2007 in a variety of senior positions in its capital markets, mergers and acquisitions and firm management divisions, including acting as Head of Fixed Income Capital Markets, Sovereign and Financial Institutions Coverage for Asia, Regional Chief Executive Officer for Southeast Asia and as Head of Morgan Stanley’s regional office in Houston. He was also appointed Singapore’s Honorary Consul General in Houston. Mr. Dee received a Bachelor of Science degree in Economics from the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania in 1981. Mr. Dee’s qualifications include his extensive global experience in public markets, corporate finance, and mergers and acquisitions.
79
David Brenner will serve as the Combined Company’s Chief Commercial Officer. Mr. Brenner has served as the Company’s Chief Commercial Officer since August 2020. He also served as PCT’s Chief Integration Officer from January 2017 to August 2020. Prior to joining PCT, Mr. Brenner was a Senior Solution Manager, from September 2016 to November 2016, and a Manager, from September 2012 to September 2016, at Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited, a division of a multinational professional services network. Mr. Brenner’s prior experience also includes leading the implementation of Electronic Medical Records for orthopedic surgeons, modernizing flagship applications for the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, and supporting the implementation of the Affordable Care Act at Health Care Service Corporation. He earned his MBA from Texas A&M and holds a B.A. in Business Administration, Operations Management from The University of Texas.
Non-Employee Directors
Tanya Burnell will serve as a member of the Combined Company’s board of directors. Ms. Burnell has been a member of the board of directors of PCT since August 2020. Since June 2013, Ms. Burnell has served as a Director of CC Industries, Inc., an affiliate of Henry Crown and Company, a privately owned investment company that invests in public and private securities, real estate, and operating companies. In her role, Ms. Burnell focuses primarily on sourcing and executing new investment opportunities, and providing strategic, financial and operational oversight to operating companies. We believe Ms. Burnell is well-qualified to serve as a member of the Combined Company’s board due to her expertise and experience in finance, operational oversight, and strategy.
Richard Brenner will serve as a member of the Combined Company’s board of directors. Mr. Brenner has served as the Chief Operating Officer of Innventure LLC, an affiliate of PCT, and as a member of the board of directors of PCT since October 16, 2015. Previously, he was the CEO and Co-founder of SPRIM Strategy & Intelligent Innovation, a strategy consulting firm, from 2012 to March 2017, where he oversaw the company’s business operations and ensured the company had effective operational and financial procedures in place. Earlier in his career, Mr. Brenner served as Marketing Director at P&G for Noxzema skin care, followed by Secret and Sure antiperspirants in Cincinnati. He earned his MBA from Northwestern University and his B.S. in Business Administration from the University of Maryland. We believe Mr. Brenner is well-qualified to serve as a member of the Combined Company’s board due to his experience in strategy marketing, finance and operations.
Dr. John Scott will serve as a member of the Combined Company’s board of directors. Dr. Scott is the Founder and Principal of the Company and has served as PCT’s Chief Science Officer and as a member of the Company’s board of directors since October 2015. Additionally, he has served as a senior scientific advisor to PCT’s management team since 2015. Additionally, Dr. Scott is a founder of XLTG and served as its CEO from 1993 to 2013. For the early part of his career, Dr. Scott was an academic scientist for various universities and government labs including the Universities of Maryland, North Carolina and Arizona and the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Additionally, he served as a scientific consultant to six national governments and has advised NATO and the Institute for Defense Analysis. Based on these experiences, Dr. Scott devised a systematic methodology for founding, funding and scaling start-up disruptive technology companies. He is a dual program Ph.D. in Physics/Astrophysics with over 60 papers published. We believe Dr. Scott is qualified to serve as a member of the Combined Company’s board due to his vast scientific expertise and his over 45 years of experience in scientific development, consulting and leadership.
Jeffrey Fieler will serve as a member of the Combined Company’s board of directors. From June 2010 to March 2018, Mr. Fieler served as the Founder and Portfolio Manager of Sylebra Capital Management, a global investment manager, where he managed an active portfolio in the global technology, media and telecommunications sectors with assets under management in excess of $1.5 billion. From May 2003 until June 2010, Mr. Fieler served as a Senior Partner (from January 2007 until June 2010) and Partner (from May 2003 until January 2007) at Coatue Management, a global investment manager, where he managed investment research and portfolio positions related to the internet, media and telecom industries. From March 2000 until May 2003, Mr. Fieler was a Managing Director and Senior Internet Analyst at Bear Stearns, an investment bank. Mr. Fieler has an MBA from the New York University Stern School of Business and a B.A. from Brown University. We believe Mr. Fieler is well-qualified to serve as a member of the Combined Company’s board due to his broad experience in finance and investing.
Timothy Glockner will serve as a member of the Combined Company’s board of directors. Since 2019, Mr. Glockner has served as the president of Glockner Enterprises, a transportation finance, insurance and investment company. Mr. Glockner served as Vice President of Glockner Enterprises from 2002 until 2019. We believe Mr. Glockner is well-qualified to serve as a member of the Combined Company’s board due to his over 18 years of experience in operations, leadership and company development.
80
Company Related Party Transactions
Other than described below, there are no related party transactions between the Company and the anticipated executive officers and directors of the Combined Company.
Mr. Fieler agreed to purchase 1,000,000 shares of ROCH Common Stock in the PIPE for an aggregate purchase price of $10.0 million, which amount was reduced to 700,000 shares for an aggregate purchase price of $7.0 million in connection with the finalization of the PIPE Placement allocations.
For more details regarding the related party transactions between the Company and its other anticipated executive officers and directors, see the section entitled “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions.”
Corporate Governance
We will structure our corporate governance in a manner the Combined Company believes will closely align our interest with those of our stockholders following the Business Combination. Notable features of this corporate governance include:
| • | we will have independent director representation on our audit, compensation and nominating and corporate governance committees immediately at the time of the Business Combination, and our independent directors will meet regularly in executive sessions without the presence of our corporate officers or non-independent directors; and | |
| • | at least one of our directors will qualify as an “audit committee financial expert” as defined by the SEC. |
Election of Officers
Each executive officer serves at the discretion of our board of directors and holds office until his or her successor is duly appointed or until his or her earlier resignation or removal. Other than Richard Brenner and David Brenner, who are father and son, respectively, there are no family relationships among any of our directors and executive officers.
Board Composition
Our board of directors will consist of directors upon closing of the Business Combination. Each of the Combined Company’s directors will continue to serve as a director until the election and qualification of his or her successor or until his or her earlier death, resignation or removal. The authorized number of directors may be changed by resolution of our board of directors. Vacancies on our board of directors can be filled by resolution of our board of directors.
Our board of directors is divided into three classes, each serving staggered, three-year terms until the date (the “Sunset Date”) of the first annual meeting of the stockholders that is held after the fifth anniversary of the effectiveness of the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation:
| • | our Class I directors will be , and their terms will expire at the first annual meeting of stockholders following the date of this prospectus; |
| • | our Class II directors will be , and their terms will expire at the second annual meeting of stockholders following the date of this prospectus; and |
| • | our Class III directors will be , and their terms will expire at the third annual meeting of stockholders following the date of this prospectus. |
Each of and Mr. Fieler is a director designated by certain of the ROCH Investors (as defined therein) and the Pre-PIPE Investors (as defined therein), respectively, pursuant to the Investor Rights Agreement. Pursuant to the Investor Rights Agreement, one of the two directors will be designated by certain of the ROCH Investors for two years following the date of the Investor Rights Agreement and, in that two year period, the other director will be designated by certain of the Pre-PIPE Investors until the Pre- PIPE Investors no longer hold 10% or more of the Combined Company’s outstanding Common Stock (the “Threshold”). Following the end of the above-mentioned two year period and until the Pre-PIPE Investors no longer hold the Threshold, certain of the Pre-PIPE Investors shall continue to have the right to designate one director to the Combined Company’s board of directors. Ms. Burnell is a director designated by Pure Crown LLC pursuant to the Pure Crown Letter Agreement. For more details, see the section entitled “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions — Class A Unit Purchase Agreement with Pure Crown LLC.”
81
Prior to the Sunset Date and as a result of the staggered board, only one class of directors will be elected at each annual meeting of stockholders, with the other classes continuing for the remainder of their respective terms. At any meeting of stockholders at which directors are to be elected prior to the Sunset Date, the number of directors elected may not exceed the greatest number of directors then in office in any class of directors. The directors first appointed to Class I will hold office for a term expiring at the annual meeting of stockholders to be held in 2021; the directors first appointed to Class II will hold office for a term expiring at the annual meeting of stockholders to be held in 2022; and the directors first appointed to Class III will hold office for a term expiring at the annual meeting of stockholders to be held in 2023, with the members of each class to hold office until their successors are elected and qualified. At each succeeding annual meeting of the stockholders of the Combined Company held prior to the Sunset Date, the successors to the class of directors whose term expires at that meeting will be elected by plurality vote of all votes cast at such meeting to hold office for a term expiring at the annual meeting of stockholders held in the third year following the year of their election and until their successors are elected and qualified. All directors elected at annual meetings of stockholders held on or after the Sunset Date will be elected for terms expiring at the next annual meeting of stockholders and will not be subject to the classification provisions set forth above. Subject to the rights, if any, of the holders of any series of preferred stock to elect additional directors under circumstances specified in a preferred stock designation, directors may be elected by the stockholders only at an annual meeting of stockholders.
Our board of directors will be chaired by Mr. Otworth, the current Chief Executive Officer of PCT. Our board of directors believes that combining the positions of Chief Executive Officer and Chairman helps to ensure that our board of directors and management act with a common purpose. In addition, our board of directors believes that a combined Chief Executive Officer and Chairman is better positioned to act as a bridge between management and our board of directors, facilitating the regular flow of information. Our board of directors also believes that it is advantageous to have a chairperson with significant history with and extensive knowledge of PCT, as is the case with Mr. Otworth.
Independence of our Board of Directors
Our board of directors has undertaken a review of the independence of each director. Based on information provided by each director concerning his or her background, employment, and affiliations, our board of directors has determined that the Combined Company’s board of directors will meet independence standards under the applicable rules and regulations of the SEC and the listing standards of NASDAQ. In making these determinations, our board of directors considered the current and prior relationships that each non- employee director has with our company and all other facts and circumstances our board of directors deemed relevant in determining their independence, including the beneficial ownership of our capital stock by each non-employee director, and the transactions involving them described in the section titled “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions.” In making these determinations, our board of directors considered, among other things, the Glockner Line of Credit in light of Mr. Timothy Glockner’s position as President of Glockner Enterprises, an affiliate of Glockner Finance and Auto Now Acceptance Co., LLC. The interest expense paid by the Company in connection with the Glockner Line of Credit was less than the greater of $200,000 or 5% of the annual consolidated gross revenues of Glockner Enterprises in the current year and in each of the past three fiscal years. Our board of directors ultimately concluded that this relationship did not impair Mr. Timothy Glockner’s independence.
Board Committees
Our board of directors has three standing committees: an audit committee; a compensation committee and a nominating and corporate governance committee. Each of the committees will report to the board of directors as it deems appropriate and as the board of directors may request. The expected composition, duties and responsibilities of these committees are set forth below. In the future, our board of directors may establish other committees, as it deems appropriate, to assist it with its responsibilities.
82
Audit Committee
The audit committee provides assistance to our board of directors in fulfilling its legal and fiduciary obligations in matters involving our accounting, auditing, financial reporting and legal compliance functions by approving the services performed by our independent registered public accounting firm and reviewing their reports regarding our accounting practices and systems of internal accounting controls. The audit committee also oversees the audit efforts of our independent registered public accounting firm and takes those actions as it deems necessary to satisfy itself that the independent registered public accounting firm is independent of management. Subject to phase-in rules and a limited exception, the rules of NASDAQ and Rule 10A-3 of the Exchange Act require that the audit committee of a listed company be comprised solely of independent directors. Our audit committee will meet the requirements for independence of audit committee members under applicable SEC and NASDAQ rules. All of the members of our audit committee meet the requirements for financial literacy under the applicable rules and regulations of the SEC and NASDAQ. In addition, qualifies as our “audit committee financial expert,” as such term is defined in Item 407 of Regulation S-K.
Our board of directors will adopt a new written charter for the audit committee, which will be available on our website after adoption. The information on our website is not intended to form a part of or be incorporated by reference into this prospectus.
Compensation Committee
The compensation committee will determine our general compensation policies and the compensation provided to our officers. The compensation committee will also make recommendations to our board of directors regarding director compensation. In addition, the compensation committee will review and determine security-based compensation for our directors, officers, employees and consultants and will administer our equity incentive plans. Our compensation committee will also oversee our corporate compensation programs. Each member of our compensation committee will be independent, as defined under the NASDAQ listing rules, and will also satisfy NASDAQ’s additional independence standards for compensation committee members. Each member of our compensation committee will be a non-employee director (within the meaning of Rule 16b-3 under the Exchange Act).
Our board of directors will adopt a new written charter for the compensation committee, which will be available on our website after adoption. The information on our website is not intended to form a part of or be incorporated by reference into this prospectus.
Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee
The nominating and corporate governance committee is responsible for making recommendations to our board of directors regarding candidates for directorships and the size and composition of the board. In addition, the nominating and corporate governance committee will be responsible for overseeing our corporate governance and reporting and making recommendations to the board of directors concerning corporate governance matters. Each member of our nominating and corporate governance committee will be independent as defined under the NASDAQ listing rules.
Our board of directors will adopt a new written charter for the nominating and corporate governance committee, which will be available on our website after adoption. The information on our website is not intended to form a part of or be incorporated by reference into this prospectus.
Role of Our Board of Directors in Risk Oversight
One of the key functions of our board of directors is informed oversight of our risk management process. Our board of directors administers this oversight function directly through our board of directors as a whole, as well as through various standing committees of our board of directors that address risks inherent in their respective areas of oversight. In particular, our board of directors is responsible for monitoring and assessing strategic risk exposure, and our audit committee will have the responsibility to consider and discuss our major financial risk exposures and the steps our management has taken to monitor and control these exposures, including guidelines and policies to govern the process by which risk assessment and management is undertaken. The audit committee will also have the responsibility to review with management the process by which risk assessment and management is undertaken, monitor compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, and review the adequacy and effectiveness of our internal controls over financial reporting. Our nominating and corporate governance committee will be responsible for periodically evaluating our company’s corporate governance policies and systems in light of the governance risks that our company faces and the adequacy of our company’s policies and procedures designed to address such risks. Our compensation committee will assess and monitor whether any of our compensation plans, policies and programs comply with applicable legal and regulatory requirements.
83
Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation
Other than our Chief Executive Officer’s, Mr. Otworth’s, service on the board of managers of Innventure LLC, where ParentCo director Mr. Rick Brenner is an executive officer, no interlocking relationship exists between our board of directors or compensation committee and the board of directors or compensation committee of any other entity, nor has any interlocking relationship existed in the past. None of the members of our compensation committee has at any time during the prior three years been one of our officers or employees.
Code of Business Conduct and Ethics for Employees, Executive Officers, and Directors
Following the Closing of the Business Combination, our board of directors will adopt a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, or the Code of Conduct, applicable to all of our employees, executive officers and directors, including our Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer and other executive and senior financial officers. The Code of Conduct will be available on our website after adoption. Any amendments to the Code of Conduct, or any waivers of its requirements, are expected to be disclosed on its website to the extent required by applicable rules and exchange requirements. The information on our website is not intended to form a part of or be incorporated by reference into this prospectus.
Compensation of Directors and Officers
Employment Agreements
PCT has entered into employment agreements with certain of its executive officers that are expected to govern certain terms and conditions of such executive officers’ employment following the Business Combination. The employment agreements with Mike Otworth and David Brenner, which were entered into on November 14, 2020, are described below under “PCT Executive Compensation — Employment Agreements/Arrangements with our NEOs — New Employment Agreements” and “PCT Executive Compensation — Severance and Change in Control Compensation.”
Since July 2020 Bird Creek Capital LLC (“Bird Creek”), for which Mr. Dee has served as the Managing Director, has provided advisory services to PCT regarding the negotiation of PCT’s potential financings. In September 2020, PCT entered into a Consulting Services Agreement (the “Bird Creek Agreement”) with Bird Creek to memorialize the terms of his consulting arrangement, including with respect to services provided before the date of the agreement. The fee under the Bird Creek Agreement was to be negotiated between the parties in good faith following the date of the Bird Creek Agreement. Certain payments made pursuant to the Dee Employment Agreement (as defined below) are deemed to satisfy, in full, PCT’s obligations under the Bird Creek Agreement.
On November 15, 2020, in connection with Mr. Dee’s commencement of service as PCT’s Chief Financial Officer, PCT entered into an employment agreement with Mr. Dee (the “Dee Employment Agreement”). The Dee Employment Agreement sets forth the basic terms of Mr. Dee’s employment, including a base salary of $450,000 and eligibility to participate in PCT’s (or its successor’s) annual bonus program, equity award program, and certain employee benefit and fringe benefit plans and programs.
Pursuant to the Dee Employment Agreement, upon the completion of a business combination of PCT with a company formed to raise capital through an initial public offering for the purpose of acquiring an existing company (such as the Business Combination) (a “SPAC Transaction”), Mr. Dee will become entitled to total cash payments of $3,000,000 (the “Negotiated Payment”), payable in two installments during 2021. The Negotiated Payment represents a negotiated fee under the Bird Creek Agreement and reflects the significant contributions made by Mr. Dee with respect to the negotiation of financing transactions to fund working capital and continue construction on the Phase II Facility, as well his contribution to negotiating and structuring the Merger, the pre-PIPE Investment and the PIPE Investment during the term of the Bird Creek Agreement.
84
In further recognition of Mr. Dee’s significant contributions to PCT during the Bird Creek consulting relationship, his considerable public company experience in finance and accounting and his experience in M&A and the capital markets generally and as an inducement to join the PCT management team, the Dee Employment Agreement also provides for the following initial equity awards to Mr. Dee, contingent upon the successful completion of a SPAC Transaction (assumed for purposes of this disclosure to be the Business Combination) and certain other securities law and stock exchange-based conditions:
| • | A stock option with a grant date Black-Scholes value of $7,000,000 and an exercise price equal to the fair market value of the Combined Company’s common stock on the date of grant, which stock option will generally vest in substantially equal installments on each of the first three anniversaries of the grant date and have a term of seven years; |
| • | 1,000,000 restricted shares that will generally vest in substantially equal installments on (1) the date that is six months after the Closing Date, (2) the date that is 12 months after the Closing Date, and (3) the date on which PCT’s Ironton, Ohio plant becomes operational (as certified in accordance with the terms of the Dee Employment Agreement); and |
| • | 200,000 performance-based restricted stock units (“PRSUs”) that will generally vest if, after six months after the Closing and prior to or as of the third anniversary of the Closing, the closing price of the Combined Company's common stock is greater than or equal to $18.00 over any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period. Each PRSU will represent the right to receive one share of common stock of the Combined Company. |
Pursuant to the Dee Employment Agreement, if Mr. Dee’s employment is terminated by PCT without “cause” or by Mr. Dee for “good reason” (as such terms are defined in Mr. Dee’s employment agreement), Mr. Dee will be entitled to receive: (1) continued base salary payments for six months and (2) reimbursement of COBRA continuation coverage premiums for up to six months to the extent they exceed the premiums paid by similarly situated active executives of PCT. Payment of these amounts is generally subject to Mr. Dee’s compliance with certain restrictive covenants and execution of a customary release of claims in favor of PCT. In addition, the Dee Employment Agreement provides that if his employment is terminated by PCT without “cause” or by him for “good reason,” his initial equity awards (as described above) will vest in full (and, in the case of the initial option award, remain exercisable until the earlier of two years after the date of such termination and the original expiration date of such option). If Mr. Dee’s employment is terminated due to his death or “disability” (as defined in his employment agreement), Mr. Dee will be entitled to receive a lump sum cash payment equal to the annual bonus that he would have earned for the calendar year of termination based on actual performance achievement for the full performance year, pro-rated based on his period of service during such year.
The Dee Employment Agreement has an initial two-year term, after which the agreement will be automatically extended for successive one-year terms unless either party provides 30 days’ prior notice of its intention not to extend the term. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the Dee Employment Agreement will terminate if the Business Combination (or another similar SPAC transaction) is not completed on or before December 31, 2021.
Overview of Anticipated Executive Compensation Program
Following the closing of the Business Combination, decisions with respect to the compensation of our executive officers, including our named executive officers, will be made by the compensation committee of our board of directors. The following discussion is based on the present expectations as to the compensation of our named executive officers and directors following the Business Combination. The actual compensation of our named executive officers will depend on the judgment of the members of the compensation committee and may differ from that set forth in the following discussion. Such compensation will also generally be governed by our executive officers’ employment agreements, as in effect from time to time, including as described above.
We anticipate that compensation for our executive officers will have the following components: base salary, cash bonus opportunities, equity compensation, employee benefits, executive perquisites and severance benefits. Base salaries, employee benefits, executive perquisites and severance benefits will be designed to attract and retain senior management talent. We will also use annual cash bonuses and equity awards to promote performance-based pay that aligns the interests of our named executive officers with the long-term interests of our equity-owners and to enhance executive retention.
85
Annual Bonuses
We expect that we will use annual cash incentive bonuses for the named executive officers to motivate their achievement of short-term performance goals and tie a portion of their cash compensation to performance. We expect that, near the beginning of each year, the compensation committee will select the performance targets, target amounts, target award opportunities and other terms and conditions of annual cash bonuses for the named executive officers, subject to the terms of their employment agreements. Following the end of each year, the compensation committee will determine the extent to which the performance targets were achieved and the amount of the award that is payable to the named executive officers.
Stock-Based Awards
We expect to use stock-based awards in future years to promote our interest by providing these executives with the opportunity to acquire equity interests as an incentive for their remaining in our service and aligning the executives’ interests with those of our equity holders.
Other Compensation
We expect to continue to offer various employee benefit plans currently offered by PCT (or similar plans). We may also provide our named executive officers with perquisites and personal benefits that are not generally available to all employees.
Director Compensation
Following the Business Combination, our non-employee directors will receive varying levels of compensation for their services as directors and members of committees of our board of directors. We anticipate determining director compensation in accordance with industry practice and standards.
Limitation on Liability and Indemnification of Directors and Officers
The Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, which will be effective upon consummation
of the Business Combination, will limit a directors’ liability to the fullest extent permitted under the Delaware General Corporation Law (“DGCL”). The DGCL provides that directors of a corporation will not be personally liable for monetary damages for breach of their fiduciary duties as directors, except for liability:
| • | for any transaction from which the director derives an improper personal benefit; |
| • | for any act or omission not in good faith or that involves intentional misconduct or a knowing violation of law; |
| • | for any unlawful payment of dividends or redemption of shares; or |
| • | for any breach of a director’s duty of loyalty to the corporation or its stockholders. |
If the DGCL is amended to authorize corporate action further eliminating or limiting the personal liability of directors, then the liability of the directors will be eliminated or limited to the fullest extent permitted by the DGCL, as so amended.
Delaware law and the Amended and Restated Bylaws provide that ParentCo will, in certain situations, indemnify its directors and officers and may indemnify other employees and other agents, to the fullest extent permitted by law. Any indemnified person is also entitled, subject to certain limitations, to advancement, direct payment, or reimbursement of reasonable expenses (including attorneys’ fees and disbursements) in advance of the final disposition of the proceeding.
In addition, ParentCo will enter into separate indemnification agreements with its directors and officers. These agreements, among other things, require ParentCo to indemnify its directors and officers for certain expenses, including attorneys’ fees, judgments, fines, and settlement amounts incurred by a director or officer in any action or proceeding arising out of their services as one of its directors or officers or any other company or enterprise to which the person provides services at its request.
86
ParentCo plans to maintain a directors’ and officers’ insurance policy pursuant to which its directors and officers are insured against liability for actions taken in their capacities as directors and officers. We believe these provisions in the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation Amended and Restated Bylaws and these indemnification agreements are necessary to attract and retain qualified persons as directors and officers.
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act may be permitted to directors, officers, or control persons, in the opinion of the SEC, such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and is therefore unenforceable.
87
This section discusses the material components of the fiscal year 2019 executive compensation programs for the executive officers of PCT who were “named executive officers” for 2019. This discussion may contain forward-looking statements that are based on PCT’s current plans, considerations, expectations and determinations regarding future compensation programs. Actual compensation programs that PCT adopts following the completion of the Business Combination may differ materially from the existing and currently planned programs summarized or referred to in this discussion.
As an emerging growth company, PCT has opted to comply with the executive compensation disclosure rules applicable to “smaller reporting companies” as such term is defined in the rules promulgated under the Securities Act, which, in general, require compensation disclosure for PCT’s principal executive officer and its two other most highly compensated executive officers, referred to herein as our named executive officers (the “NEOs”).
Mike Otworth was PCT’s principal executive officer for the entirety of fiscal 2019. The two most highly compensated executive officers of PCT that were serving in such capacity at the end of fiscal 2019 (other than Mr. Otworth) were David Brenner and Dr. John Scott.
Therefore, for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2019, PCT’s NEOs were:
| • | Mike Otworth, Chief Executive Officer; |
| • | David Brenner, Chief Commercial Officer; and |
| • | Dr. John Scott, Chief Science Officer, Founder and Principal. |
Mr. Otworth and David Brenner are expected to continue to serve as executive officers of the Combined Company following the consummation of the Business Combination
The following table provides information regarding the compensation of PCT’s NEOs for the 2019 fiscal year.
2019 Summary Compensation Table
| Non-Equity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock | Option | Incentive Plan | All Other | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fiscal | Salary | Bonus | Awards | Awards | Compensation | Compensation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name and Principal Position | Year | ($)(1) | ($) | ($)(2) | ($) | ($) | ($) | Total ($) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mike Otworth | 2019 | 255,000 | — | 936,600 | — | — | — | 1,191,600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chief Executive Officer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dr. John Scott | 2019 | 57,500 | — | 669,000 | — | — | — | 726,500 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chief Science Officer, Founder and Principal(3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| David Brenner | 2019 | 187,751 | — | — | — | — | — | 187,751 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chief Commercial Officer(4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
88
(1) For Mr. Otworth and David Brenner, amounts represent base salary earned during 2019. For Dr. Scott, the amount represents payments to Corporate Development Group (a corporation solely owned by Dr. Scott) with respect to Dr. Scott’s consulting services to PCT during 2019. In April 2019, David Brenner’s base salary was increased from $158,000 to $200,000.
(2) Amounts in this column reflect the aggregate grant date fair value of Incentive Unit (as defined below) awards, in each case calculated in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification Topic 718 (“ASC 718”). For information regarding assumptions underlying the valuation of equity awards, see the discussion under “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations — Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates — Equity- Based Compensation” included elsewhere in this prospectus.
(3) Dr. Scott, Chief Science Officer of Innventure LLC, has provided services to PCT in a consulting capacity.
(4) During 2019 and until April 2019, David Brenner served as VP, Operations of PCT. From April 2019 until August 2020, David Brenner served as Chief Integration Officer of PCT. In August 2020, he was appointed Chief Commercial Officer of PCT.
Employment Agreements/Arrangements with our NEOs
Agreements in Effect During 2019
Prior to the execution of David Brenner’s New Employment Agreement (as defined below), Innventure Management Services LLC was party to an employment agreement, dated April 25, 2018, with Mr. Brenner (the “Prior Brenner Agreement”). The Prior Brenner Agreement provided for, among other things, an initial base salary rate of $150,000 per year. Pursuant to the Prior Brenner Agreement, either Innventure Management Services LLC or Mr. Brenner could terminate Mr. Brenner’s employment at any time, upon which Mr. Brenner would have received any accrued but unpaid base salary and any unpaid business expense reimbursements, but would not have received any severance compensation or benefits. The Prior Brenner Agreement included customary employee and customer non-solicitation provisions that extended for one year following Mr. Brenner’s termination of employment, as well as customary confidentiality, intellectual property and non-disparagement provisions in favor of Innventure Management Services LLC.
Mr. Otworth did not have an employment or consulting agreement during 2019. Mr. Scott did not have a formal agreement regarding his consulting services to PCT during 2019, except with respect to the project fee described below under “— Other Cash Compensation Arrangements.”
New Employment Agreements
On November 14, 2020, PCT entered into employment agreements with Mr. Otworth and David Brenner (the “New Employment Agreements”). Notwithstanding the terms described below, the New Employment Agreements will terminate if a business combination of PCT with a company formed to raise capital through an initial public offering for the purpose of acquiring an existing company (such as the Business Combination) (a “SPAC Transaction”) is not completed on or before December 31, 2021.
Mr. Otworth’s New Employment Agreement provides that Mr. Otworth serves as the Chief Executive Officer of PCT and will be nominated to serve on PCT’s Board of Directors as Chairman during his term as Chief Executive Officer. Mr. Otworth’s base salary under his New Employment Agreement is $750,000, subject to increase as determined by the Board of Directors of PCT. Mr. Otworth is also entitled to a cash bonus equal to $5,000,000 in the event that a SPAC Transaction is successfully completed and Mr. Otworth remains continuously employed with PCT through the completion of the SPAC Transaction. The initial term of Mr. Otworth’s New Employment Agreement ends on November 14, 2022, but the term will be automatically extended for additional one-year periods thereafter unless either party provides written notice of non-renewal at least 90 days prior to the end of the applicable term.
David Brenner’s New Employment Agreement, which supersedes and replaces the Prior Brenner Agreement, provides that Mr. Brenner serves as the Chief Commercial Officer of PCT. Mr. Brenner’s base salary under his New Employment Agreement is $340,000, subject to annual review by the Board of Directors of PCT. The initial term of Mr. Brenner’s New Employment Agreement ends on November 14, 2022, but the term will be automatically extended for additional one-year periods thereafter unless either party provides written notice of non-renewal at least 30 days prior to the end of the applicable term.
89
Under the New Employment Agreements, Mr. Otworth and David Brenner are each eligible to receive, for each calendar year during the term of the executive’s employment beginning with the calendar year in which a SPAC Transaction is consummated, an annual bonus upon terms determined in the discretion of PCT’s Board of Directors. For 2021, Mr. Brenner’s annual bonus will consist of cash payments of $33,333.33 that will be earned upon successful completion of each of the following objectives, subject to the closing of a SPAC Transaction and Mr. Brenner’s continued employment through the date of completion of the applicable objective: (1) a SPAC Transaction closes in 2021; (2) all feedstock is contracted for PCT’s second commercial plant in 2021; and (3) all product offtake is contracted for PCT’s second commercial plant in 2021.
Also during their term of employment beginning with the calendar year in which a SPAC Transaction is consummated, Mr. Otworth and Mr. Brenner will be eligible to participate in PCT’s equity compensation plans as determined by PCT’s Board of Directors or the compensation committee thereof. Throughout the term of the New Employment Agreement, each of Mr. Otworth and Mr. Brenner will be entitled to fringe benefits and other perquisites consistent with those provided to similarly situated executives of PCT and to employee benefit participation on a basis that is no less favorable than other similarly situated executives of PCT. Under the New Employment Agreements, each of Mr. Otworth and Mr. Brenner agree to enter into a restrictive covenants agreement with PCT, which agreement includes customary non-competition, non-solicitation, and confidentiality provisions.
The New Employment Agreements provide for certain severance benefits for Mr. Otworth or Mr. Brenner in the event of certain terminations of employment, as further described below under “— Severance and Change in Control Compensation.”
In addition to the New Employment Agreements, PCT also entered into an employment agreement with Michael Dee (who is not an NEO for purposes of this disclosure but who now serves as Chief Financial Officer of PCT) on November 15, 2020. For additional details on the terms of Mr. Dee’s employment agreement and awards related to the Business Combination, see “Combined Company Management — Compensation of Directors and Officers — Employment Agreements” above.
2019 Bonus Compensation
None of the NEOs received or were eligible for bonus or cash incentive compensation with respect to fiscal 2019.
Other Cash Compensation Arrangements
Pursuant to a 2019 agreement with Innventure LLC and PCT, Dr. Scott and a certain consultant of Innventure LLC are entitled to share equally in a project fee calculated based on a percentage of certain financing secured with respect to PCT’s business. Pursuant to such agreement, the fee is equal to 1.5% of the total financing, reduced by the amount of retainer fees paid to such consultant. The financing closed in October 2020, and, as a result, Dr. Scott became entitled to a total project fee equal to approximately $1,519,125.
2019 Equity-Based Compensation
PCT has granted Class C Units of PCT (“Incentive Units”) to certain service providers, including the NEOs, pursuant to the PCT Technologies LLC Amended and Restated Equity Incentive Plan (the “LLC Equity Plan”). The Incentive Units are intended to be “profits interests” for U.S. federal income tax purposes, and holders of Incentive Units do not have any voting rights with respect to such Incentive Units. The Incentive Units entitle the holders thereof to participate in distributions of PCT after certain members of PCT have received the return of an amount specified with respect to the Incentive Unit award (the “Distribution Threshold”).
On August 7, 2019, Mr. Otworth was granted 52,500 Incentive Units and Dr. Scott was granted 37,500 Incentive Units. These Incentive Units have a Distribution Threshold of $12 and were 100% vested on the date of grant.
On July 17, 2018, David Brenner was granted 75,327.54 Incentive Units with a Distribution Threshold of $12, of which 40% were automatically vested on the grant date, and 20% were scheduled to vest on each of February 1, 2019, February 1, 2020 and February 1, 2021. In August 2019, David Brenner’s Incentive Units were amended to provide for a modified vesting schedule. As modified, 25% of the Incentive Units were deemed vested as of February 1, 2017, and 1/36 of the remaining Incentive Units were generally scheduled to vest (or deemed to have vested) on the first day of each month thereafter.
90
2021 Equity and Incentive Compensation Plan
Purpose of the Equity Plan
We have adopted the Equity Plan to allow the Combined Company to provide cash awards and equity-based compensation in the form of stock options, stock appreciation rights (“SARs”), restricted stock, restricted stock units (“RSUs”), performance shares, performance units, dividend equivalents, and certain other awards, including those denominated or payable in, or otherwise based on, shares of the Combined Company’s common stock, for the purpose of providing incentives and rewards for service and/or performance to the Combined Company’s non-employee directors, as well as officers, employees and certain consultants of the Combined Company and its subsidiaries. The Equity Plan will afford the Compensation Committee (as defined below) the ability to design compensatory awards that are responsive to the Combined Company’s needs and authorizes a variety of award types designed to advance the interests and long-term success of the Combined Company by encouraging stock ownership among its participants. In addition, the Board believes that the ability to grant cash and equity-based awards will help the Combined Company to attract, retain, and motivate employees, consultants, and directors and encourage them to devote their best efforts to the Combined Company’s business and financial success.
Promotion of Good Corporate Governance Practices
The Board believes the use of stock-based incentive awards promotes best practices in corporate governance by incentivizing the creation of stockholder value. By providing participants in the Equity Plan with a stake in the Combined Company’s success, the interests of the participants are further aligned with those of stockholders. Specific features of the Equity Plan that are consistent with commonly viewed good corporate governance practices include, but are not limited to:
| • | the Equity Plan prohibits the grant of dividend equivalents with respect to options and SARs and subjects all dividends and dividend equivalents paid with respect to other awards to the same vesting conditions as the underlying shares subject to the awards; | |
| • | the Equity Plan does not contain a liberal change in control definition; | |
| • | except in connection with a corporate transaction, options and SARs under the Equity Plan may not be granted with exercise or base prices lower than the fair market value of the underlying shares on the grant date; | |
| • | outside of certain corporate transactions or adjustment events described in the Equity Plan or in connection with a “change in control,” the exercise or base price of stock options and SARs cannot be reduced, and “underwater” stock options or SARs cannot be cancelled in exchange for cash or replaced with other awards with a lower exercise or base price, without stockholder approval under the Equity Plan; and | |
| • | non-employee directors may not be awarded compensation for their service as a director having an aggregate maximum value on the grant date that exceeds $750,000 during any calendar year, and such limit may not be amended without first seeking stockholder approval. |
Summary of the Equity Plan
The following summary of the material terms of the Equity Plan is qualified in its entirety by reference to a copy of the Equity Plan, a copy of which has been filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part.
Administration
The Equity Plan will generally be administered by the compensation committee (or its successor) of the Combined Company’s board of directors (for purposes of this section, the “Compensation Committee”), or any other committee of the Combined Company’s board of directors (the “Combined Company Board”) designated by the Combined Company Board to administer the Equity Plan. However, at the Combined Company Board’s discretion, the Equity Plan may be administered by the Combined Company Board, including with respect to the administration of any responsibilities and duties held by the Compensation Committee under the Equity Plan. References to the “Committee” in this section generally refer to the Compensation Committee or such other committee designated by the Combined Company Board, or the Combined Company Board, as applicable. Among other responsibilities, the Committee will select participants and determine the type of awards to be granted to participants, the number of shares of Common Stock to be covered by awards and the terms and conditions of awards, interpret the Equity Plan and awards granted under it, and make any other determination and take any other action that it deems necessary or desirable to administer the Equity Plan The Committee may from time to time delegate all or any part of its authority under the Equity Plan as permitted by the Equity Plan and applicable law. In addition, the Committee may by resolution, subject to certain restrictions set forth in the Equity Plan, authorize one or more officers of the Combined Company to (1) designate employees to be recipients of awards under the Equity Plan, and (2) determine the size of such awards. The Committee may not, however, delegate such responsibilities to officers for awards granted to non-employee directors or certain officers who are subject to the reporting requirements of Section 16 of the Exchange Act.
91
Eligibility
Any person who is selected by the Committee to receive benefits under the Equity Plan and who is at that time an officer or other employee of the Combined Company or any of its subsidiaries (including a person who has agreed to commence serving in such capacity within 90 days of the date of grant) is eligible to participate in the Equity Plan. In addition, non-employee directors of the Combined Company and certain persons (including consultants) who provide services to the Combined Company or any of its subsidiaries that are equivalent to those typically provided by an employee (provided such persons satisfy the Form S-8 definition of “employee”), may also be selected by the Committee to participate in the Equity Plan.
Shares available for awards under the Equity Plan
Subject to adjustment as described in the Equity Plan and the Equity Plan’s share counting rules, the number of shares of Common Stock available under the Equity Plan for awards of:
| • | stock options or SARs; | |
| • | restricted stock; | |
| • | RSUs; | |
| • | performance shares or performance units; | |
| • | other stock-based awards under the Equity Plan; or | |
| • | dividend equivalents paid with respect to awards under the Equity Plan |
will not exceed, in the aggregate, shares of Common Stock (the “Share Limit”) plus Common Stock that becomes available under the Equity Plan as a result of forfeiture, cancellation, expiration, cash settlement or less-than-maximum earning of Equity Plan awards after the effective date of the Equity Plan. The Share Limit will be automatically increased on the first day of each fiscal year, beginning in 2022 and ending in 2031, by an amount equal to the lesser of (i) 3% of the shares of Common Stock outstanding on the last day of the immediately preceding fiscal year and (ii) such smaller number of shares as determined by the Board.
If any award granted under the Equity Plan expires unexercised, is canceled, forfeited, settled in cash or unearned (in whole or in part), shares of Common Stock subject to such award will again be made available for future grants under the Equity Plan. Use of shares of our common stock to pay the required exercise price or tax obligations, or shares not issued in connection with settlement of an option or stock-settled SAR, or reacquired by the Combined Company on the open market or otherwise using cash proceeds from the exercise of an option will not be available again for other awards under the Equity Plan; provided, however, that shares of our common stock used to satisfy tax obligations for awards other than stock options and SARs will be available for issuance again under the Equity Plan (for up to 10 years from the date of stockholder approval of the Equity Plan if such recycling involves shares that have already been issued). If a participant elects to give up the right to receive compensation in exchange for shares of common stock based on fair market value, such shares of common stock will not count against the aggregate limit of shares authorized under the Equity Plan to the extent permitted by applicable laws and regulations.
92
Subject to adjustment as provided in the Equity Plan, the aggregate number of shares of Common Stock actually issued or transferred upon the exercise of stock options that are intended to qualify as “incentive stock options” under Section 422 of the Code will not exceed shares of Common Stock (the “ISO Limit”), provided that the ISO Limit will increase by shares of Common Stock on the first day of each fiscal year beginning in 2022 and ending in 2031 (subject in all events to the Share Limit).
Types of awards under the Equity Plan
Pursuant to the Equity Plan, the Combined Company may grant cash awards and stock options, SARs, restricted stock, RSUs, performance shares, performance units, and certain other awards based on or related to the Common Stock.
Generally, each grant of an award under the Equity Plan will be evidenced by an award agreement, certificate, resolution or other type or form of writing or other evidence approved by the Committee (an “Evidence of Award”), which will contain such terms and provisions as the Committee may determine, consistent with the Equity Plan. A brief description of the types of awards which may be granted under the Equity Plan is set forth below.
Stock options
A stock option is a right to purchase Common Stock upon exercise of the stock option. Stock options granted to an employee under the Equity Plan may consist of either a stock option intended to be an “incentive stock option” as defined in Section 422 of the Code or a non-qualified stock option, or a combination of both. Incentive stock options may only be granted to employees of the Combined Company or certain of its related corporations. Except with respect to awards issued in substitution for, in conversion of, or in connection with an assumption of stock options held by awardees of an entity engaging in a corporate transaction (including an acquisition or merger) with the Combined Company or any of its subsidiaries, stock options must have an exercise price per share of Common Stock that is not less than the fair market value of a share of Common Stock on the date of grant. The term of a stock option may not extend more than 10 years from the date of grant. The Committee may provide in an Evidence of Award for the automatic exercise of a stock option.
Each grant of a stock option will specify the applicable terms of the stock option, including the number of shares of Common Stock subject to the stock option and the required period or periods of the participant’s continuous service, if any, before any stock option or portion of a stock option will become exercisable. Stock options may provide for continued vesting or the earlier exercise of the stock options, including in the event of retirement, death, disability or termination of employment or service of the participant or in the event of a change in control.
Any grant of stock options may specify management objectives regarding the vesting of the stock options. Each grant will specify whether the consideration to be paid in satisfaction of the exercise price will be payable: (1) in cash, by check acceptable to the Combined Company, or by wire transfer of immediately available funds; (2) by the actual or constructive transfer to the Combined Company of Common Stock owned by the participant with a value at the time of exercise that is equal to the total exercise price; (3) subject to any conditions or limitations established by the Committee, by a net exercise arrangement pursuant to which the Combined Company will withhold Common Stock otherwise issuable upon exercise of a stock option; (4) by a combination of the foregoing methods; or (5) by such other methods as may be approved by the Committee. To the extent permitted by law, any grant may provide for deferred payment of the exercise price from the proceeds of a sale through a bank or broker of some or all of the shares to which the exercise relates. Stock options granted under the Equity Plan may not provide for dividends or dividend equivalents.
SARs
The Committee may, from time to time and upon such terms and conditions as it may determine, authorize the granting of SARs. A SAR is a right to receive from the Combined Company an amount equal to 100%, or such lesser percentage as the Committee may determine, of the spread between the base price and the fair market value of a share of Common Stock on the date of exercise.
93
Each grant of SARs will specify the period or periods of continuous service, if any, by the participant with the Combined Company or any subsidiary that is necessary before the SARs or installments of such SARs will become exercisable. SARs may provide for continued vesting or earlier exercise, including in the case of retirement, death, disability or termination of employment or service of the participant or in the event of a change in control. Any grant of SARs may specify management objectives regarding the vesting of such SARs. A SAR may be paid in cash, Common Stock or any combination of the two.
Except with respect to awards issued in substitution for, in conversion of, or in connection with an assumption of SARs held by awardees of an entity engaging in a corporate transaction (including an acquisition or merger) with the Combined Company or any of its subsidiaries, the base price of a SAR may not be less than the fair market value of a share of Common Stock on the date of grant. The term of a SAR may not extend more than 10 years from the date of grant. SARs granted under the Equity Plan may not provide for dividends or dividend equivalents.
Restricted Stock
Restricted stock constitutes an immediate transfer of the ownership of shares of Common Stock to the participant in consideration of the performance of services, entitling such participant to voting, dividend and other ownership rights, but subject to the substantial risk of forfeiture and restrictions on transfer determined by the Committee for a period of time determined by the Committee or until certain management objectives specified by the Committee are achieved. Each such grant or sale of restricted stock may be made without additional consideration or in consideration of a payment by the participant that is less than the fair market value per share of Common Stock on the date of grant.
Any grant of restricted stock may specify management objectives regarding the vesting of the restricted stock. Any grant of restricted stock may require that any and all dividends or other distributions paid on restricted stock that remains subject to a substantial risk of forfeiture be automatically deferred and/or reinvested in additional restricted stock, which will be subject to the same restrictions as the underlying restricted stock, but any such dividends or other distributions on restricted stock must be deferred until, and paid contingent upon, the vesting of such restricted stock. Restricted stock may provide for continued vesting or the earlier vesting of such restricted stock, including in the event of retirement, death, disability or termination of employment or service of the participant or in the event of a change in control.
RSUs
RSUs awarded under the Equity Plan constitute an agreement by the Combined Company to deliver Common Stock, cash, or a combination of the two, to the participant in the future in consideration of the performance of services, but subject to the fulfillment of such conditions (which may include achievement regarding management objectives) during the restriction period as the Committee may specify. Each grant or sale of RSUs may be made without additional consideration or in consideration of a payment by the participant that is less than the fair market value per share of Common Stock on the date of grant.
RSUs may provide for continued vesting or the earlier lapse or other modification of the restriction period, including in the event of retirement, death, disability or termination of employment or service of the participant or in the event of a change in control. During the restriction period applicable to RSUs, the participant will have no right to transfer any rights under the award and will have no rights of ownership in the Common Stock deliverable upon payment of the RSUs and no right to vote them. Rights to dividend equivalents may be extended to and made part of any RSU award at the discretion of the Committee, on a deferred and contingent basis, either in cash or in additional shares of Common Stock, based upon the vesting of such RSUs. Each grant or sale of RSUs will specify the time and manner of payment of the RSUs that have been earned. An RSU may be paid in cash, Common Stock or any combination of the two.
Performance shares, performance units and cash incentive awards
Performance shares, performance units and cash incentive awards may also be granted to participants under the Equity Plan. A performance share is a bookkeeping entry that records the equivalent of one share of Common Stock, and a performance unit is a bookkeeping entry that records a unit equivalent to $1.00 or such other value as determined by the Committee. Performance shares and performance units each may be payable in cash, Common Stock, or a combination of the two. Each grant will specify the number or amount of performance shares or performance units, or the cash amount payable with respect to a cash incentive award being awarded, which number or amount may be subject to adjustment to reflect changes in compensation or other factors.
94
Each grant of a cash incentive award, performance shares or performance units will specify management objectives regarding the earning of the award. Each grant will specify the time and manner of payment of a cash incentive award, performance shares or performance units that have been earned.
At the discretion of the Committee, any grant of performance shares or performance units may provide for the payment of dividend equivalents in cash or in additional shares of Common Stock, which dividend equivalents will be subject to deferral and payment on a contingent basis based on the participant’s earning and vesting of the performance shares or performance units, as applicable, with respect to which such dividend equivalents are paid.
The performance period with respect to each grant of performance shares or performance units or cash incentive award will be a period of time determined by the Committee and within which the management objectives relating to such award are to be achieved. The performance period may be subject to continued vesting or earlier lapse or modification, including in the event of retirement, death, disability or termination of employment or service of the participant or in the event of a change in control.
Other awards
Subject to applicable law and applicable share limits under the Equity Plan, the Committee may grant to any participant Common Stock or such other awards (“Other Awards”) that may be denominated or payable in, valued in whole or in part by reference to, or otherwise based on, or related to, shares of Common Stock or factors that may influence the value of such Common Stock, including, without limitation, convertible or exchangeable debt securities; other rights convertible or exchangeable into shares of Common Stock; purchase rights for shares of Common Stock; awards with value and payment contingent upon performance of the Combined Company or its specified subsidiaries, affiliates or other business units or any other factors designated by the Committee; and awards valued by reference to the book value of the shares of Common Stock or the value of securities of, or the performance of, the subsidiaries, affiliates or other business units of the Combined Company. The terms and conditions of any such awards will be determined by the Committee. Common Stock delivered under such an award in the nature of a purchase right granted under the Equity Plan will be purchased for such consideration, paid for at such time, by such methods, and in such forms, including, without limitation, Common Stock, other awards, cash, notes or other property, as the Committee determines.
In addition, the Committee may grant cash awards, as an element of or supplement to any other awards granted under the Equity Plan. The Committee may also authorize the grant of shares of Common Stock as a bonus or may authorize the grant of Other Awards in lieu of obligations of the Combined Company or a subsidiary to pay cash or deliver other property under the Equity Plan or under other plans or compensatory arrangements, subject to terms determined by the Committee in a manner that complies with Section 409A of the Code.
Other Awards may provide for the earning or vesting of, or earlier elimination of restrictions applicable to, such award, including in the event of the retirement, death, disability or termination of employment or service of the participant or in the event of a change in control. The Committee may provide for the payment of dividends or dividend equivalents on Other Awards on a deferred and contingent basis, in cash or in additional shares of Common Stock; provided, however, that dividend equivalents or other distributions of Common Stock underlying Other Awards will be deferred until and paid contingent upon the earning and vesting of such awards.
95
Change in control
The Equity Plan includes a definition of “change in control.” In general, except as may be otherwise prescribed by the Committee in an Evidence of Award or as otherwise provided in another plan or agreement applicable to a participant, a change in control shall be deemed to have occurred upon the occurrence of any of the following events occurring after the Business Combination (subject to certain exceptions and limitations and as further described in the Equity Plan): (1) any individual, entity or group is or becomes the beneficial owner of voting securities of the Combined Company where such acquisition causes such person to own more than 50% of the combined voting power of the then outstanding voting shares of the Combined Company (subject to certain exceptions); (2) a majority of the Combined Company Board ceases to be comprised of incumbent directors; (3) stockholder approval of a reorganization, merger or consolidation, or sale or other disposition of all or substantially all of the assets of the Combined Company or the acquisition of assets of another corporation or other transaction, as described in the Equity Plan (subject to certain exceptions); or (4) consummation of a complete liquidation or dissolution of the Combined Company (subject to certain qualifying exceptions).
Management objectives
The Equity Plan generally provides that any of the awards set forth above may be granted subject to the achievement of specified management objectives. Management objectives are defined as performance objective or objectives established pursuant to the Equity Plan for participants who have received grants of performance shares, performance units or cash incentive awards or, when so determined by the Committee, stock options, SARs, restricted stock, RSUs, dividend equivalents or Other Awards. The definition of “Management Objectives” set forth in the Equity Plan includes a list of examples of measures (which is not exhaustive) that may be used as management objectives in awards granted under the Equity Plan.
Additionally, if the Committee determines that a change in the business, operations, corporate structure or capital structure of the Combined Company, or the manner in which it conducts its business, or other events or circumstances render the management objectives unsuitable, the Committee may in its discretion modify such management objectives or the goals or actual levels of achievement, in whole or in part, as the Committee deems appropriate and equitable.
Transferability of awards
Except as otherwise provided by the Committee, and subject to the terms of the Equity Plan with respect to Section 409A of the Code, no stock option, SAR, restricted stock, RSU, performance share, performance unit, cash incentive award, Other Award or dividend equivalents paid with respect to awards made under the Equity Plan will be transferrable by a participant except by will or the laws of descent and distribution. In no event will any such award granted under the Equity Plan be transferred for value. Except as otherwise determined by the Committee, stock options and SARs will be exercisable during the participant’s lifetime only by him or her or, in the event of the participant’s legal incapacity to do so, by his or her guardian or legal representative acting on behalf of the participant in a fiduciary capacity under state law
or court supervision.
Under certain circumstances, the Committee may specify on the grant date that part or all of the shares of Common Stock that are subject to certain awards under the Equity Plan will be subject to further restrictions on transfer.
Adjustments
The Committee will make or provide for such adjustments in: (1) the number and kind of shares of Common Stock covered by outstanding stock options, SARs, restricted stock, RSUs, performance shares and performance units granted under the Equity Plan; (2) if applicable, the number and kind of shares of Common Stock covered by Other Awards; (3) the exercise price or base price provided in outstanding stock options and SARs, respectively; (4) cash incentive awards; and (5) other award terms, as the Committee in its sole discretion, determines, in good faith, is equitably required in order to prevent dilution or enlargement of the rights of participants that otherwise would result from (a) any extraordinary cash dividend, stock dividend, stock split, combination of shares, recapitalization or other change in the capital structure of the Combined Company; (b) any merger, consolidation, spin-off, spin-out, split-off, split-up, reorganization, partial or complete liquidation or other distribution of assets, issuance of rights or warrants to purchase securities; or (c) any other corporate transaction or event having an effect similar to any of the foregoing.
96
In the event of any such transaction or event, or in the event of a change in control of the Combined Company, the Committee may provide in substitution for any or all outstanding awards under the Equity Plan such alternative consideration (including cash), if any, as it may in good faith determine to be equitable under the circumstances and will require in connection therewith the surrender of all awards so replaced in a manner that complies with Section 409A of the Code. In addition, for each stock option or SAR with an exercise price or base price, respectively, greater than the consideration offered in connection with any such transaction or event or change in control of the Combined Company, the Committee may in its discretion elect to cancel such stock option or SAR without any payment to the person holding such stock option or SAR. The Committee will make or provide for such adjustments to the numbers of shares of Common Stock available under the Equity Plan and the share limits of the Equity Plan as the Committee in its sole discretion, determines, in good faith, is appropriate to reflect such transaction or event. Any adjustment to the limit on the number of shares of Common Stock that may be issued upon exercise of incentive stock options, however, will be made only if and to the extent such adjustment would not cause any stock option intended to qualify as an incentive stock option to fail to so qualify.
Prohibition on repricing
Except in connection with certain corporate transactions or changes in the capital structure of the Combined Company or in connection with a change in control, the terms of outstanding awards may not be amended to (1) reduce the exercise price or base price of outstanding stock options or SARs, respectively, or (2) cancel outstanding “underwater” stock options or SARs in exchange for cash, other awards or stock options or SARs with an exercise price or base price, as applicable, that is less than the exercise price or base price of the original stock options or SARs, as applicable, without stockholder approval. These restrictions are intended to prohibit the repricing of “underwater” stock options and SARs and they may not be amended without approval by the Combined Company’s stockholders.
Detrimental activity and recapture
Any Evidence of Award may reference a clawback policy of the Combined Company or provide for the cancellation or forfeiture of an award or forfeiture and repayment to the Combined Company of any gain related to an award, or other provisions intended to have a similar effect, upon such terms and conditions as may be determined by the Committee from time to time, if any participant, either during employment or other service with the Combined Company or its subsidiary or within a specified period after such employment or service, engages in any detrimental activity, as described in the applicable Evidence of Award or such clawback policy. In addition, any Evidence of Award or such clawback policy may provide for cancellation or forfeiture of an award or the forfeiture and repayment of any Common Stock issued under and/or any other benefit related to an award, or other provisions intended to have a similar effect, including upon such terms and conditions as may be required by the Committee or under Section 10D of the Exchange Act and any applicable rules and regulations promulgated by the SEC or any national securities exchange or national securities association on which the Common Stock may be traded.
Non-U.S. participants
In order to facilitate the making of any grant or combination of grants under the Equity Plan, the Committee may provide for such special terms for awards to participants who are foreign nationals or who are employed by the Combined Company or its subsidiary outside of the United States of America or who provide services to the Combined Company or its subsidiary under an agreement with a foreign nation or agency, as the Committee may consider necessary or appropriate to accommodate differences in local law, tax policy or custom. The Committee may approve such supplements to, or amendments, restatements or alternative versions of, the Equity Plan (including sub-plans) as it may consider necessary or appropriate for such purposes, provided that no such special terms, supplements, amendments or restatements will include any provisions that are inconsistent with the terms of the Equity Plan as then in effect unless the Equity Plan could have been amended to eliminate such inconsistency without further approval by the Combined Company’s stockholders.
97
Withholding
To the extent the Combined Company is required to withhold federal, state, local or foreign taxes or other amounts in connection with any payment made or benefit realized by a participant or other person under the Equity Plan, and the amounts available to the Combined Company for such withholding are insufficient, it will be a condition to the receipt of such payment or the realization of such benefit that the participant or such other person make arrangements satisfactory to the Combined Company for payment of the balance of such taxes or other amounts required to be withheld, which arrangements, in the discretion of the Committee, may include relinquishment of a portion of such benefit. When a participant is required to pay the Combined Company an amount required to be withheld under applicable income, employment, tax or other laws, the Committee may require the participant to satisfy the obligation, in whole or in part, by having withheld, from the shares of Common Stock delivered or required to be delivered to the participant, shares of Common Stock having a value equal to the amount required to be withheld or by delivering to the Combined Company other shares of Common Stock held by such participant. The Common Stock used for tax or other withholding will be valued at an amount equal to the fair market value of such Common Stock on the date the benefit is to be included in the participant’s income. In no event will the fair market value of the Common Stock to be withheld and delivered pursuant to the Equity Plan exceed the minimum amount required to be withheld, unless (1) an additional amount can be withheld and not result in adverse accounting consequences, and (2) such additional withholding amount is authorized by the Committee. Participants will also make such arrangements as the Combined Company may require for the payment of any withholding tax or other obligation that may arise in connection with the disposition of Common Stock acquired upon the exercise of stock options.
Amendment and termination of the Equity Plan
The Combined Company Board generally may amend the Equity Plan from time to time in whole or in part. If any amendment, however, for purposes of applicable stock exchange rules (and except as permitted under the adjustment provisions of the Equity Plan) (1) would materially increase the benefits accruing to participants under the Equity Plan, (2) would materially increase the number of securities which may be issued under the Equity Plan, (3) would materially modify the requirements for participation in the Equity Plan or (4) must otherwise be approved by the Combined Company’s stockholders in order to comply with applicable law or the rules of the NASDAQ, or, if the Common Stock is not traded on NASDAQ, the principal national securities exchange upon which the Common Stock is traded or quoted, all as determined by the Combined Company Board, then such amendment will be subject to stockholder approval and will not be effective unless and until such approval has been obtained.
Further, subject to the Equity Plan’s prohibition on repricing, the Committee generally may amend the terms of any award prospectively or retroactively. Except in the case of certain adjustments permitted under the Equity Plan, no such amendment may be made that would materially impair the rights of any participant without his or her consent. If permitted by Section 409A of the Code, but subject to the subject to the preceding sentence, including in the case of termination of employment or service, or in the case of unforeseeable emergency or other circumstances or in the event of a change in control, the Committee may provide for continued vesting or accelerate the timing of vesting or exercisability or the time at which the substantial risk of forfeiture or prohibition or restriction on transfer will lapse or the time when the period of restriction will end, or the time at which cash incentive awards, performance shares or performance units will be deemed to have been earned or the time when such transfer restriction will terminate, in each case as applicable to certain awards granted under the Equity Plan, or waive any other limitation or requirement under any such award.
The Combined Company Board may, in its discretion, terminate the Equity Plan at any time. Termination of the Equity Plan will not affect the rights of participants or their successors under any awards outstanding and not exercised in full on the date of termination. No grant will be made under the Equity Plan on or after the tenth anniversary of the effective date of the Equity Plan, but all grants made prior to such date will continue in effect thereafter subject to their terms and the terms of the Equity Plan.
Allowances for conversion awards and assumed plans
Common Stock (1) subject to awards granted under the Equity Plan in substitution for or conversion of, or in connection with an assumption of, stock options, SARs, restricted stock, RSUs, or other stock or stock-based awards held by awardees of an entity engaging in a corporate transaction (including an acquisition or merger) with the Combined Company or any of its subsidiaries or (2) available for issuance under a previously-approved plan sponsored by a company that is acquired by, or merges with, the Combined Company or any of its subsidiaries, and which then become available for issuance of awards under the Equity Plan, will not count against (or be added to) the aggregate share limit or other Equity Plan limits described above, except as otherwise provided in the Equity Plan.
98
Outstanding Equity Awards at 2019 Fiscal Year-End
The following table and related footnotes set forth information about the outstanding equity awards held by the NEOs as of December 31, 2019, which was the last day of fiscal 2019.
Outstanding Equity Awards at 2019 Fiscal Year-End
| Option Awards | Stock Awards | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options (#) Exercisable | Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options (#) Unexercisable | Option Exercise Price ($) | Option Expiration Date | Number
of | Market Value of Shares or Units of Stock That Have Not Vested ($)(3) | ||||||||||||||||
| Mike Otworth | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Dr. John Scott | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| David Brenner | — | — | — | — | 3,139(1) | $57,130 | ||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Unvested Incentive Units held by David Brenner vested in substantially equal installments on each of January 1, 2020 and February 1, 2020. |
| (2) | For a discussion of the treatment of the NEOs’ vested Incentive Units in the Business Combination, see “Severance and Change in Control of Compensation — Treatment of Incentive Units in Business Combination” below. |
| (3) | The amounts in this column represent the estimated market value of the unvested Incentive Units held by each of the NEOs as of December 31, 2019, as more fully described above under the heading “— 2019 Equity-Based Compensation.” Such value takes into account the Distribution Threshold of $12 and the existing capital structure and distribution provisions related to PCT. |
Retirement Plan
PCT did not offer a defined contribution plan, defined benefit pension plan, nonqualified deferred compensation plan or other retirement plan for its NEOs during 2019.
Severance and Change in Control Compensation
Severance Under Employment Agreements
Pursuant to his New Employment Agreement, if Mr. Otworth’s employment is terminated by PCT without “cause” or by Mr. Otworth for “good reason” (as such terms are defined in his New Employment Agreement) after completion of a SPAC Transaction, Mr. Otworth will be entitled to receive: (1) a lump sum payment equal to his base salary for the unexpired portion of the initial two-year term of his New Employment Agreement; and (2) reimbursement of COBRA continuation coverage premiums for up to 12 months to the extent they exceed the premiums paid by similarly situated active executives of PCT.
Pursuant to David Brenner’s New Employment Agreement, if his employment is terminated by PCT without “cause” or by Mr. Brenner for “good reason” (as such terms are defined in his New Employment Agreement) after completion of a SPAC Transaction, he will be entitled to receive: (1) continued base salary payments for six months; and (2) reimbursement of COBRA continuation coverage premiums for up to six months to the extent they exceed the premiums paid by similarly situated executives of PCT.
Payment of the severance amounts for Messrs. Otworth and Brenner is generally subject to the executive’s compliance with certain restrictive covenants and execution of a customary release of claims in favor of PCT.
99
If Mr. Otworth’s or Mr. Brenner’s employment is terminated due to the executive’s death or disability (as defined in the New Employment Agreements), the executive will be entitled to receive a lump sum cash payment equal to the annual bonus that the executive would have earned for the calendar year of termination based on actual performance achievement for the full performance year, pro-rated based on the executive’s period of service during such year.
Equity Compensation
If an NEO’s employment is terminated, then PCT may (in the discretion of the PCT Board of Directors), redeem such NEO’s vested Incentive Units for fair market value (as defined in the LLC Equity Plan), except that if the termination is by PCT for cause (as defined in the LLC Equity Plan) or PCT would have had the right to terminate the NEO’s employment for cause, such vested Incentive Units may be redeemed for 80% of their fair market value.
In the event that an NEO’s employment is terminated without cause (as defined in the LLC Equity Plan) within 12 months after a change in control (as defined in the LLC Equity Plan), all unvested Incentive Units held by such NEO will become fully vested. The Business Combination will constitute a change in control for purposes of the Incentive Units.
Transaction Bonus
As described above under “— Employment Agreements/Arrangements with Our NEOs,” Mr. Otworth is entitled to a cash bonus equal to $5,000,000 in the event that a SPAC Transaction is successfully completed and Mr. Otworth remains continuously employed with PCT through the completion of the SPAC Transaction.
Other than as described above, the NEOs are not covered by any contracts, agreements or arrangements that provide for severance payments or benefits in connection with a termination of employment or a change in control.
Treatment of Incentive Units in Business Combination
At the time of the Business Combination, unvested Incentive Units held by the NEOs will be exchanged for restricted shares of common stock of the Combined Company that will be subject to the same vesting schedule and forfeiture restrictions as the unvested Incentive Units to which they relate. As of November 16, 2020, the NEOs did not hold any unvested Incentive Units.
As of November 16, 2020, the NEOs held the following vested Incentive Units: Mr. Otworth, 52,500 with a Distribution Threshold of $12, and 60,000 with a Distribution Threshold of $37.20; David Brenner, 75,328 with a Distribution Threshold of $12, and 40,000 with a Distribution Threshold of $37.20; and Dr. Scott, 37,500 with a Distribution Threshold of $12. At the time of the Business Combination, these vested Incentive Units are expected to be exchanged for shares of common stock of the Combined Company. In accordance with the applicable allocation schedule pursuant to the Merger Agreement, the NEOs are expected to receive approximately the following numbers of shares of Combined Company common stock with respect to their vested Incentive Units: Mr. Otworth, 931,393; David Brenner, 996,098; and Dr. Scott, 348,864.
Employment Agreement with Michael Dee
As further described above under “Combined Company Management — Compensation of Directors and Officers — Employment Agreements,” Michael Dee is entitled to certain rights in connection with or following the Business Combination, including severance protection, a transaction bonus, and initial equity compensation awards.
100
PCT Director Compensation
The following table presents the total compensation for services to PCT for each person who served as a member of PCT’s Board of Directors during the year ended December 31, 2019 (other than Mr. Otworth and Dr. Scott). PCT did not have standard compensation arrangements for its directors during 2019, and none of the members of PCT’s Board of Directors received cash, equity or other non-equity compensation specifically for service in their capacity as directors. The amounts reflected in the table below represent compensation for consulting or other services provided to PCT. Mike Otworth and John Scott also served on PCT’s Board of Directors during 2019, but their compensation for services to PCT during 2019 is fully reflected in the 2019 Summary Compensation Table above.
2019 Director Compensation
| Fees Earned | Non-Equity | |||||||||||||||||
| or Paid in | Stock | Incentive Plan | All Other | |||||||||||||||
| Cash | Awards | Option | Compensation | Compensation | Total | |||||||||||||
| Name | ($) | ($)(1) | Awards ($) | ($) | ($)(2) | ($) | ||||||||||||
| Rick Brenner | — | 669,000 | — | — | — | 669,000 | ||||||||||||
| Andy Glockner | — | 8,048 | — | — | — | 8,048 | ||||||||||||
| Jim Donnally | — | 8,028 | — | — | — | 8,028 |
| (1) | Amounts in this column reflect the aggregate grant date fair value of Incentive Units granted in 2019, calculated in accordance with ASC 718. Each of these grants was 100% vested on the grant date. For Mr. Glockner, the amount represents a portion of the grant date fair value of an award granted in 2019 to Assured Solutions Company, Ltd. ($100,350), an entity in which Mr. Glockner holds an 8.02% interest. For Mr. Donnally, the amount represents a portion of the aggregate grant date fair value of awards granted in 2019 to Assured Solutions Company, Ltd. ($100,350), Dam Insurance Management, Ltd. ($100,350), Gleim Insurance Management, Ltd. ($100,350), and Patriot Insurance Management, Ltd. ($100,350); Mr. Glockner holds a 2% interest in each of these entities. For information regarding assumptions underlying the valuation of equity awards, see the discussion under “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations — Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates — Equity-Based Compensation” included elsewhere in this prospectus. None of the directors listed in this table held unvested Incentive Units as of December 31, 2019, but they held the following amounts of vested Incentive Units as of such date: Mr. Brenner, 37,500 Incentive Units; Mr. Glockner, 1,503.75 Incentive Units; and Mr. Donnally, 1,500 Incentive Units. |
101
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
The following is a description of each transaction since January 1, 2017 and each currently proposed transaction in which PCT or ParentCo has been or is to be a participant and:
| • | the amount involved exceeded or exceeds $120,000; and |
| • | any of PCT’s directors, executive officers, or holders of more than 5% of its capital stock, or any immediate family member of, or person sharing the household with, any of these individuals, had or will have a direct or indirect material interest. |
Agreements with Capital Stockholders
Investor Rights Agreement
At the Closing of the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement, ParentCo, certain PCT Unitholders representing at least 70% of PCT’s outstanding membership interests and certain stockholders of ROCH (including certain ROCH officers, directors and sponsors) will also enter into an Investor Rights Agreement, which is a closing condition of the parties to consummate the Business Combination. Pursuant to the Investor Rights Agreement, such PCT Unitholders have agreed to vote in favor of two board designees nominated by a majority of such stockholders of ROCH for a period of two years following the Closing Date (the “IRA Designees”), provided that in the event a majority of the holders of the Pre-PIPE Shares (as defined in the Investor Rights Agreement) choose to select one of the IRA Designees, the majority of such stockholders of ROCH will select one of the IRA Designees and such holders of the Pre- PIPE Shares will select the other. The holders of the Pre-PIPE Shares may continue to select an IRA Designee until they no longer hold 10% or more of the outstanding Combined Company’s Common Stock. Such PCT Unitholders have also agreed, subject to certain limited exceptions, not to transfer ParentCo Common Stock received in the Business Combination except in certain circumstances as described therein. The Investor Rights Agreement also contains registration rights in favor of the PCT Unitholders and ROCH stockholders.
Company Support Agreement
In connection with the execution of the Merger Agreement, PCT Unitholders representing at least 70% of the issued and outstanding Company LLC Interests entered into the Company Support Agreement with ROCH, ParentCo, and PCT, pursuant to which such PCT Unitholders agreed to vote all LLC Interests beneficially owned by them in favor of each of the Proposals, to use their reasonable best efforts to take all actions reasonably necessary to consummate the Business Combination and to not take any action that would reasonably be expected to materially delay or prevent the satisfaction of the conditions to the Business Combination set forth in the Merger Agreement. In addition, such PCT Unitholders also agreed that they would not sell, assign or otherwise transfer any of the Company LLC Interests held by them, with certain limited exceptions, unless the buyer, assignee or transferee executes a joinder agreement to the Company Support Agreement.
Business Combination Private Placement
In connection with the execution of the Merger Agreement, ROCH entered into Subscription Agreements with the Subscribers (as defined in the Subscription Agreements), pursuant to which the Subscribers agreed to purchase, and ROCH agreed to sell the Subscribers, an aggregate of 25,000,000 shares of ROCH Common Stock, for a purchase price of $10.00 per share and an aggregate purchase price of $250.0 million, in the PIPE.
Sylebra Capital (as defined below) agreed to purchase 10,000,000 shares of ROCH Common Stock in the PIPE for an aggregate purchase price of $100.0 million.
The Magnetar Investors, in conjunction with certain other investors, agreed to purchase approximately 3,100,000 shares of ROCH Common Stock in the PIPE for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $31.0 million.
102
Class A Unit Purchase Agreement with Sylebra Capital
On November 12, 2020, pursuant to four Class A Unit Purchase Agreements dated as of the same date, by and between PCT and each of BEMAP Master Fund Ltd., Blackwell Partners LLC — Series A, Sylebra Capital Parc Master Fund and Sylebra Capital Partners Master Fund, Ltd. (each an entity subject to an investment management agreement or sub-management agreement with Sylebra Capital Limited, together, “Sylebra Capital” and the agreements entered into, collectively, the “Sylebra Capital Class A Unit Purchase Agreements”), PCT issued and sold an aggregate of 684,190 Class A Common Units to Sylebra Capital for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $60,000,000 or approximately $87.69 per unit, subject to certain adjustments.
In connection with the Sylebra Capital Class A Unit Purchase Agreements, and as documented in the Investor Rights Agreement, Sylebra Capital will be entitled to select one member of ParentCo’s Board of Directors.
Note Purchase Agreement with Magnetar Capital LLC
On October 6, 2020, pursuant to the Note Purchase Agreement, the Magnetar Investors agreed to purchase from PCT, and PCT agreed to issue to the Magnetar Investors (in one or more transactions), up to $60,000,000 principal amount of Convertible Notes. The Convertible Notes are convertible into PCT Common Stock (as defined in the Magnetar Indenture) on the terms and subject to the limitations set forth in the Magnetar Indenture.
Since the date of the Note Purchase Agreement, the largest aggregate amount of principal outstanding under the Convertible Notes was $48,000,000. Since October 6, 2020, the total principal paid under the Convertible Notes was $0 and total interest paid was $0.
In connection with the Note Purchase Agreement, PCT and the Magnetar Investors entered into the Magnetar Registration Rights Agreement granting the Magnetar Investors certain registration rights for the PCT Common Stock issuable upon conversion of the Convertible Notes.
Right of First Refusal Agreement
On October 7, 2020, and in connection with the Note Purchase Agreement, PCT entered into a right of first refusal agreement (the “ROFR Agreement”) with the Magnetar Investors pursuant to which PCT granted to the Magnetar Investors a right of first refusal with respect to any such Indebtedness (as defined in the Magnetar Indenture) or any other debt, indebtedness or preferred equity of any nature that may be incurred by PCT or any of its respective Subsidiaries (as defined in the Magnetar Indenture) from time to time (collectively, the “Company Group”) on or after October 7, 2020. After October 15, 2022, subject to extension to April 15, 2023 at the election of PCT, PCT may terminate the ROFR Agreement at any time and for any reason. The Magnetar Investors may terminate the ROFR Agreement at any time and for any reason.
Class A Unit Purchase Agreement with Pure Crown LLC
On October 4, 2020, pursuant to the Class A Unit Purchase Agreement dated as of the same date, by and between PCT and Pure Crown LLC (the “Pure Crown Class A Unit Purchase Agreement”), PCT issued and sold an aggregate of 115,428 Class A Common Units to Pure Crown LLC for an aggregate purchase price of $10,000,000 or $86.634 per unit, subject to certain adjustments.
In connection with the Class A Unit Purchase Agreement, PCT entered into a letter agreement, dated October 5, 2020, with Pure Crown LLC (the “Pure Crown Letter Agreement”) whereby, provided certain conditions are met, (1) Pure Crown LLC will be entitled to select one member of ParentCo’s Board of Directors and (2) Pure Crown LLC agreed to purchase an additional 173,142 Class A Common Units from PCT.
103
In October 2020, PCT issued an aggregate of 50,000 Class C Units to Pure Crown LLC, with an approximate aggregate value of $1,560,000, as an inducement to enter into the Pure Crown Class A Unit Purchase Agreement.
Agreements with Innventus Fund I, L.P., Innventure1, LLC, Innventure LLC and Innventure Management Services LLC
Innventus Fund I, L.P. (“Innventus”) is a holder of PCT’s capital stock and is affiliated with Innventure1, LLC (“Innventure1”). Innventure1 is the majority member of Innventure LLC, which is the largest holder of PCT’s capital stock. Wasson Enterprise, LLC, through a subsidiary which is a greater than 5% unit holder in PCT, owns a minority interest in Innventure LLC.
Director and Chief Executive Officer Michael Otworth is the Chief Executive Officer of Innventure LLC and Innventure1, Director and officer John Scott is a co-founder and member of Innventure1. Due to these affiliations with material capital stockholders of PCT, Messrs. Otworth and Scott may be deemed to have a direct or indirect material interest in transactions with Innventus, Innventure1 and Innventure LLC.
Management Services
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 the Company paid $579,620 and $537,606 and $0 respectively, for management services provided by certain personnel of Innventure Management Services LLC (“Management Services”), an affiliate of Innventure LLC, and as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the company owed to Management Services $17,521 and $62,212, respectively. For the nine months ended September 30, 2020, the Company paid $271,386.19 to Management Services, and as of September 30, 2020, the Company owed $10,582.33 to Management Services.
Warrant Agreements
On July 22, 2019, PCT and Innventus entered into a Bridge Note and Warrant Purchase Agreement pursuant to which PCT issued a Unit Purchase Warrant (the “Original July 2019 Warrant”) for 4,787 warrant units at an exercise price of $27.61, allowing Innventus to purchase a variable number of Class B-1 Preferred Units during the exercise period of July 22, 2019 through July 22, 2024. In connection with the Business Combination, the Original July 2019 Warrant will be canceled and PCT will owe no further obligation to Innventus in connection with the Original July 2019 Warrant.
On June 5, 2019, PCT and Innventus entered into a Warrant to Purchase Securities, pursuant to which PCT issued a Unit Purchase Warrant (the “Original June 2019 Warrant”) for 7,978 warrant units at an exercise price of $37.61, allowing Innventus to purchase a variable number of Class B-1 Preferred Units during the exercise period of June 5, 2019 through June 4, 2024. In connection with the Business Combination, the Original June 2019 Warrant will be canceled and PCT will owe no further obligation to Innventus in connection with the Original June 2019 Warrant.
Lease
From May 2018 to September 2020, PCT leased the land for the Project (excluding leased office space described below) from Innventure LLC and paid $28,000 per month over that period for a total of $812,000. Innventure LLC had purchased the land from the Lawrence County Economic Development Corporation (“LCED”) with a term loan from Closed Loop Fund, LP. On October 8, 2020, a PCT subsidiary purchased the land from Innventure LLC by paying in full the remaining Closed Loop Fund, LP term loan of $2,658,010.31, consisting of principal, accrued and unpaid interest and legal fees.
Project Fee
Pursuant to an Amended and Restated Agreement for Services dated February 25, 2019 (the “Agreement for Services”) by and among Innventure LLC, PCT, and a certain consultant of Innventure LLC (the “consultant”), PCT agreed to pay the consultant 1.5% of the proceeds (the “Project Fee”) of the Series 2020A Bonds offered pursuant to the Loan Agreement. The total Project Fee is $3,293,250. Director John Scott is listed as a beneficiary of this agreement and will receive 50% of the Project Fee minus a retainer fee kept by the consultant. Pursuant to the Agreement for Services, Director John Scott is due approximately $1,519,125.
104
Indebtedness
On July 19, 2019, in connection with the Note and Warrant Purchase Agreement between PCT and Innventus, PCT borrowed $600,000 from Innventus pursuant to a Negotiable Promissory Note (the “Innventus Note”) at an annual interest rate of 1-month LIBOR plus 8.00%. Since the date of the Innventus Note, the largest aggregate amount of principal outstanding under the Innventus Note was $600,000. On February 15, 2020, the Innventus Note was paid in full. Until paid in full, the total interest paid on the Innventus Note was $26,266.17.
Since January 1, 2017, PCT has received funding and support services from Innventure LLC. Since January 1, 2017, the largest aggregate amount of principal advanced from Innventure LLC to PCT was $1,950,000. These advances were unsecured, non-interest bearing with no formal terms of repayment. On January 28, 2020 and March 24, 2020, PCT repaid the advances from Innventure LLC of $1,950,000 in full. Since January 1, 2017, the total amount paid to Innventure LLC was $2,086,883 and total interest paid was $0.
Since January 1, 2017, PCT has received funding and support services from Wasson Enterprise, LLC, an affiliate and greater than 5% shareholder of Innventure LLC. Since January 1, 2017, the largest aggregate amount of principal advanced from Wasson Enterprise, LLC to PCT was $746,083, which was the outstanding balance due to Wasson Enterprise as of December 31, 2019. These advances were unsecured, non- interest bearing with no formal terms of repayment. On March 26, 2020, PCT repaid $375,000 of the advances from Wasson Enterprise, LLC. On March 31, 2020 under an Assignment of Indebtedness agreement, Wasson Enterprise, LLC assigned the remaining amount of $371,083 to Innventure, LLC. PCT paid off the balance in full on August 31, 2020.
Agreements with Directors and Executive Officers
Private Placements of PCT’s Securities
Class A Units
In October 2020, PCT issued and sold an aggregate of 173,142 Class A Units at a purchase price of $86.634 per unit, for an aggregate purchase price of $15,000,000.
The table below sets forth the number of Class A Units purchased by PCT’s related parties in the above referenced transaction:
| Stockholder | Class A Units | Purchase Price | ||||||
| Pure Crown LLC* | 115,428 | $ | 10,000,000 | |||||
| * | Pure Crown LLC is a greater than 5% unit holder in PCT pursuant to the Pure Crown Class A Unit Purchase Agreement, as disclosed above. |
Class B-1 Preferred Units
Between September 2018 and January 2020, PCT issued and sold an aggregate of 644,885 Class B-1 Preferred Units, at a purchase price of $37.605 per unit, for an aggregate purchase price of $24,250,891 to the PCT related parties set forth in the table below:
| Stockholder | Class B-1 Preferred Units | Purchase Price | ||||||
| Innventus Fund I, L.P.* | 378,963 | $ | 14,250,891 | |||||
| Pure Crown LLC** | 265,922 | $ | 10,000,000 | |||||
| * | Innventus Fund I, L.P. is a greater than 5% unit holder in PCT. |
| ** | Pure Crown LLC is a greater than 5% unit holder in PCT pursuant to the Pure Crown Class A Unit Purchase Agreement, as disclosed above. |
105
Class B Preferred Units
In January 2017, PCT issued and sold an aggregate of 173,619 Class B Preferred Units, at a purchase price of $1.44 per unit, for an aggregate purchase price of $250,000 to the PCT related parties set forth in the table below:
| Stockholder | Class B Preferred Units | Purchase Price | ||||||
| WE-INN LLC* | 173,619 | $ | 250,000 | |||||
| * | WE-INN LLC is a greater than 5% unit holder in PCT. |
Class C Units
In August 2020, PCT issued an aggregate of 37,500 Class C Units to Pure Crown LLC, with an approximate aggregate value of $1,170,000, as compensation for director Tanya Burnell’s board service.
Glockner Finance, a division of Auto Now Acceptance Co., LLC
On May 5, 2017, PCT entered into a revolving line of credit facility (the “Glockner Line of Credit”) with Glockner Finance, a division of Auto Now Acceptance Co., LLC, which is an entity affiliated with and controlled by director Andy Glockner. Director and former Chief Financial Officer James O. Donnally is the Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of Glockner Finance. Anticipated ParentCo Director Timothy Glockner is the president of Glockner Enterprises, an entity affiliated with Glockner Finance. Since the initiation of the Glockner Line of Credit, the largest aggregate amount of principal outstanding was $14,000,000 and as of September 30, 2020, there was $12,000,000 outstanding. Since the initiation of the Glockner Line of Credit, the total principal paid under the Line of Credit was $2,000,000 and total interest paid was $2,496,510. As of September 30, 2020, the interest payable on the Glockner Line of Credit is 16% per year.
Bird Creek Capital Consulting Services Agreement
On September 29, 2020, PCT entered into a Consulting Services Agreement (the “Bird Creek Agreement”) with Bird Creek Capital, LLC (“Bird Creek”). Chief Financial Officer Michael Dee served as the Managing Member of Bird Creek during this time. Pursuant to the Bird Creek Agreement, Bird Creek provided certain consulting services to PCT, including in connection with the negotiation of PCT’s potential financings and capital structure. The fee payable to Bird Creek pursuant to the Bird Creek Agreement was to be negotiated between the parties in good faith following the date of the Bird Creek Agreement. Certain payments made pursuant to the Dee Employment Agreement (as defined below) are deemed to satisfy, in full, PCT’s obligations under the Bird Creek Agreement. For more details, see the section entitled “Combined Company Management — Employment Agreements.”
Executive Officer and Director Compensation
Incentive Stock Units
PCT has granted management incentive units to its executive officers and certain of its directors. See the sections titled “PCT Executive Compensation — 2019 Equity-Based Compensation — Outstanding Equity Awards at 2019 Fiscal Year End” and “PCT Executive Compensation — Director Compensation” for a description of these incentive units.
Employment Arrangements
Since January 1, 2017, PCT has entered into employment arrangements with Innventure LLC and Wasson Enterprises, LLC, pursuant to which certain employees received allocated compensation from Innventure LLC or Wasson Enterprises, LLC for services rendered to PCT. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, Tayt Rule received compensation from Wasson Enterprises, LLC in the amount of $171,792, $180,574 and $103,097, respectively, for services provided as Chief Operating Officer of PCT.
106
Between January 1, 2020 and April 30, 2020, Mr. Rule received compensation from Wasson Enterprises, LLC in the amount of $80,976 for services provided as Chief Operating Officer of PCT. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, David Brenner received compensation from Innventure LLC in the amounts of $187,751, $173,549 and $162,626, respectively, for services provided as VP, Operations and Chief Integration Officer of PCT. Between January 1, 2020 and October 27, 2020, Mr. Brenner received compensation from Innventure LLC in the amount of $192,675 for services provided as Chief Integration Officer and, as of August 2020, Chief Commercial Officer.
For further information regarding management services provided by certain personnel of Management Services, the Innventure LLC affiliate, please see “— Agreements with Innventus Fund I, L.P., Innventure1, LLC, Innventure LLC and Innventure Management Services LLC — Management Services” above.
Other Compensation
Director John Scott’s wholly-owned entity, Corporate Development Group, receives cash compensation for Director John Scott’s services as an officer and director of PCT at the annual rate of $57,500, payable monthly, beginning on January 1, 2020. Since January 1, 2017, PCT has paid a total of $625,000 to Corporate Development Group.
Limitation of Liability and Indemnification of Directors and Executive Officers
In connection with the merger, PCT plans to enter into indemnification agreements with each of PCT’s directors and executive officers, the form of which is attached as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part. The indemnification agreements will require PCT to indemnify its directors and executive officers to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law.
Policies and Procedures for Related Person Transactions
Although PCT has not had a written policy for the review and approval of transactions with related persons, its board of directors has historically reviewed and approved any transaction where a director or officer had a financial interest, including the transactions described above. Prior to approving such a transaction, the material facts as to a director or officer’s relationship or interest in the agreement or transaction were disclosed to the board of directors.
Following the Business Combination, the Combined Company’s audit committee will have the primary responsibility for reviewing and approving or disapproving “related party transactions,” which are transactions between the Combined Company and related persons in which the aggregate amount involved exceeds or may be expected to exceed $120,000 and in which a related person has or will have a direct or indirect material interest. The written charter of the Combined Company’s audit committee will provide that the Combined Company’s audit committee shall review and approve in advance any related party transaction.
Review and Approval of Review and Approval of Related Person Transactions
In connection with the Business Combination, the Combined Company plans to adopt a formal written policy for the review and approval of transactions with related persons. Such policy will require, among other things, that:
| • | The audit committee shall review the material facts of all related person transactions. |
| • | In reviewing any related person transaction, the committee will take into account, among other factors that it deems appropriate, whether the related person transaction is on terms no less favorable to the Combined Company than terms generally available in a transaction with an unaffiliated third-party under the same or similar circumstances and the extent of the related person’s interest in the transaction. |
| • | In connection with its review of any related person transaction, the Combined Company shall provide the committee with all material information regarding such related person transaction, the interest of the related person and any potential disclosure obligations of the Combined Company in connection with such related person transaction. |
| • | If a related person transaction will be ongoing, the committee may establish guidelines for the Combined Company’s management to follow in its ongoing dealings with the related person. |
107
description of SECURITIES TO BE REGISTERED
As a result of the Business Combination, ROCH stockholders and PCT Unitholders who receive shares of ParentCo Common Stock in the Business Combination will become stockholders of the Combined Company. Your rights as stockholders of the Combined Company will be governed by Delaware law and the Combined Company’s Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation (“Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation”) and Amended and Restated Bylaws (“Amended and Restated Bylaws”), each of which will be effective upon closing of the Business Combination, as described further below. The following description of the material terms of the Combined Company’s capital stock, including the Combined Company’s Common Stock to be issued in the Business Combination, reflects the anticipated state of affairs upon completion of the Business Combination. We urge you to read the applicable provisions of Delaware law and the Combined Company’s forms of Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws carefully and in their entirety because they describe your rights as a holder of shares of the Combined Company’s Common Stock.
The following is a description of the material terms of, and is qualified in its entirety by, the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws, each of which will be effective upon closing of the Business Combination, the forms of which are filed as Exhibits 3.3 and 3.4, respectively, to the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part.
The Combined Company’s purpose is to engage in any lawful act or activity for which corporations may now or hereafter be organized under the DGCL. Upon the consummation of the Business Combination, the Combined Company’s authorized capital stock will consist of shares of the Combined Company’s Common Stock, par value $0.001 per share, and shares of preferred stock, par value $0.001 per share. No shares of preferred stock will be issued or outstanding immediately after the Business Combination.
Common Stock
Holders of the Combined Company’s Common Stock will be entitled to one vote for each share held of record on all matters submitted to a vote of stockholders. The holders of the Combined Company’s Common Stock do not have cumulative voting rights in the election of directors. Upon the Combined Company’s liquidation, dissolution or winding up and after payment in full of all amounts required to be paid to creditors and to the holders of preferred stock having liquidation preferences, if any, the holders of the Combined Company’s Common Stock will be entitled to receive pro rata the Combined Company’s remaining assets available for distribution. Holders of the Combined Company’s Common Stock do not have preemptive, subscription, redemption or conversion rights. The Combined Company’s Common Stock will not be subject to further calls or assessment by the Combined Company. There will be no redemption or sinking fund provisions applicable to the Combined Company’s Common Stock. All shares of the Combined Company’s Common Stock that will be outstanding at the time of the completion of the Business Combination will be fully paid and non-assessable. The rights, powers, preferences and privileges of holders of the Combined Company’s Common Stock will be subject to those of the holders of any shares of the Combined Company’s preferred stock the Combined Company may authorize and issue in the future.
When a quorum is present at any meeting, any matter other than the election of directors to be voted upon by the stockholders at such meeting will be decided by a majority vote of the holders of shares of capital stock present or represented at the meeting and voting affirmatively or negatively on such matter. At all meetings of stockholders for the election of directors at which a quorum is present, a plurality of the votes cast will be sufficient to elect such directors.
As of , 2021, ParentCo had shares of ParentCo Common Stock issued and outstanding and holders of record. After the Business Combination and assuming consummation of the sale of shares pursuant to the Subscription Agreements, there will be approximately 118,324,000 shares of the Combined Company’s Common Stock outstanding, including approximately 60.7 million shares held by certain stockholders of ROCH and PCT that will be subject to certain lock-up or transfer restrictions resulting from the IPO or pursuant to the Investor Rights Agreement.
108
Preferred Stock
The Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will authorize the Combined Company’s board of directors to establish one or more series of preferred stock. Unless required by law or by NASDAQ, the authorized shares of preferred stock will be available for issuance without further action by you. The Combined Company’s board of directors is authorized to fix from time to time before issuance the number of preferred shares to be included in any such series and the designation, powers, preferences and relative participating, optional or other rights, if any, and the qualifications, limitations or restrictions thereof. The authority of the Combined Company’s board of directors with respect to each such series will include, without limiting the generality of the foregoing, the determination of any or all of the following:
| • | the number of shares of any series and the designation to distinguish the shares of such series from the shares of all other series; |
| • | the voting powers, if any, and whether such voting powers are full or limited in such series; |
| • | the redemption provisions, if any, applicable to such series, including the redemption price or prices to be paid; |
| • | whether dividends, if any, will be cumulative or noncumulative, the dividend rate of such series, and the dates and preferences of dividends on such series; |
| • | the rights of such series upon the voluntary or involuntary dissolution of, or upon any distribution of the assets of, the Combined Company; |
| • | the provisions, if any, pursuant to which the shares of such series are convertible into, or exchangeable for, shares of any other class or classes or of any other series of the same or any other class or classes of stock, or any other security, of the Combined Company or any other corporation or other entity, and the rates or other determinants of conversion or exchange applicable thereto; |
| • | the right, if any, to subscribe for or to purchase any securities of the Combined Company or any other corporation or other entity; |
| • | the provisions, if any, of a sinking fund applicable to such series; and |
| • | any other relative, participating, optional, or other special powers, preferences or rights and qualifications, limitations, or restrictions thereof; |
all as may be determined from time to time by the Combined Company’s board of directors and stated or expressed in the resolution or resolutions providing for the issuance of such preferred stock (collectively, a “Preferred Stock Designation”).
The Combined Company could issue a series of preferred stock that could, depending on the terms of the series, impede or discourage an acquisition attempt or other transaction that some, or a majority, of the holders of the Combined Company’s Common Stock might believe to be in their best interests or in which the holders of the Combined Company’s Common Stock might receive a premium for their Combined Company Common Stock over its market price. Additionally, the issuance of preferred stock may adversely affect the rights of holders of the Combined Company’s Common Stock by restricting dividends on the Combined Company’s Common Stock, diluting the voting power of the Combined Company’s Common Stock or subordinating the liquidation rights of the Combined Company’s Common Stock. As a result of these or other factors, the issuance of preferred stock could have an adverse impact on the market price of the Combined Company’s Common Stock. The Combined Company has no current plans to issue any series of preferred stock.
Warrants
The warrants issued in connection with ROCH’s IPO (including in several contemporaneous private placements to insiders, collectively, and for purposes of this section, the “Warrants”) entitle the holder of each whole Warrant to purchase one share of ROCH Common Stock at a price of $11.50 per share, subject to adjustment. There currently are 5,936,625 Warrants issued and outstanding, consisting of 5,737,500 Public Warrants to purchase ROCH Common Stock originally sold as part of ROCH Units in ROCH’s IPO and 199,125 Private Warrants to purchase ROCH Common Stock that were sold as part of the Private Units. Pursuant to the Warrant Agreement (as defined below), a warrantholder may exercise its Warrants only for a whole number of shares of ROCH Common Stock. This means that only a whole Warrant may be exercised at any given time by a warrantholder. No fractional Warrants were issued upon separation of the Units (as defined below) and only whole Warrants trade on NASDAQ. Each Warrant will become exercisable on the later of May 7, 2021 or the consummation of ROCH’s initial business combination (including the Business Combination), and will expire five years after the completion of such initial business combination, or earlier upon redemption.
109
No public Warrants will be exercisable for cash unless there is an effective and current registration statement covering the shares of Common Stock issuable upon exercise of the Warrants and a current prospectus relating to such shares of Common Stock. Notwithstanding the foregoing, if a registration statement covering the shares of Common Stock issuable upon exercise of the public Warrants is not effective within 120 days from the closing of ROCH’s initial business combination (including the Business Combination), Warrant holders may, until such time as there is an effective registration statement and during any period when the ROCH (or the Combined Company, as successor under the Warrant Agreement (as defined below)) shall have failed to maintain an effective registration statement, exercise Warrants on a cashless basis pursuant to an available exemption from registration under the Securities Act. Under the terms of the Warrant Agreement, a current prospectus relating to the shares of Common Stock issuable upon exercise of the Warrants is required to be maintained until the expiration of the Warrants. However, there can be no assurance that this will be case and, if a current prospectus relating to the shares of Common Stock issuable upon exercise of the Warrants is not maintained, holders will be unable to exercise their Warrants for cash and any such warrant exercise is not required to be settled. If the prospectus relating to the shares of Common Stock issuable upon the exercise of the Warrants is not current or if the Common Stock is not qualified or exempt from qualification in the jurisdictions in which the holders of the Warrants reside, there is no requirement to net cash settle or cash settle the Warrant exercise, the Warrants may have no value, the market for the Warrants may be limited and the Warrants may expire worthless.
If (x) ROCH issues additional shares of common stock or equity-linked securities for capital raising purposes in connection with the closing of its initial business combination at an issue price or effective issue price of less than $9.20 per share (with such issue price or effective issue price to be determined in good faith by ROCH’s board of directors), (y) the aggregate gross proceeds from such issuances represent more than 60% of the total equity proceeds, and interest thereon, available for the funding of ROCH’s initial business combination, and (z) the volume weighted average trading price of the ROCH Common Stock during the 20 trading day period starting on the trading day prior to the day on which ROCH consummates its initial business combination (such price, the “Market Price”) is below $9.20 per share, the exercise price of the Warrants will be adjusted (to the nearest cent) to be equal to 115% of the Market Price, and the $18.00 per share redemption trigger price described above will be adjusted (to the nearest cent) to be equal to 180% of the Market Price.
The outstanding Warrants (excluding the Warrants issued to the insiders in the private placements contemporaneous with the IPO) may be called for redemption, in whole and not in part, at a price of $.01 per Warrant:
| • | at any time after the Warrants become exercisable, |
| • | upon not less than 30 days’ prior written notice of redemption to each Warrant holder, |
| • | if, and only if, the reported last sale price of the shares of Common Stock equals or exceeds $18.00 per share, for any 20 trading days within a 30-day trading period commencing after the Warrants become exercisable and ending on the third business day prior to the notice of redemption to Warrant holders, and |
| • | if, and only if, there is a current registration statement in effect with respect to the shares of Common Stock underlying such Warrants at the time of redemption and for the entire 30-day trading period referred to above and continuing each day thereafter until the date of redemption. |
The right to exercise will be forfeited unless the Warrants are exercised prior to the date specified in the notice of redemption. On and after the redemption date, a record holder of a Warrant will have no further rights except to receive the redemption price for such holder’s Warrant upon surrender of such Warrant.
110
The redemption criteria for the Warrants have been established at a price which is intended to provide Warrant holders a reasonable premium to the initial exercise price and provide a sufficient differential between the then-prevailing share price and the Warrant exercise price so that if the share price declines as a result of a redemption call, the redemption will not cause the share price to drop below the exercise price of the Warrants.
If the Warrants are called for redemption as described above, management will have the option to require all holders that wish to exercise Warrants to do so on a “cashless basis.” In such event, each holder would pay the exercise price by surrendering the Warrants for that number of shares of Common Stock equal to the quotient obtained by dividing (x) the product of the number of shares of Common Stock underlying the Warrants, multiplied by the difference between the exercise price of the Warrants and the “fair market value” (defined below) by (y) the fair market value. The “fair market value” for this purpose shall mean the average reported last sale price of the Common Stock for the 10 trading days ending on the third trading day prior to the date on which the notice of redemption is sent to the holders of Warrants. Whether we will exercise our option to require all holders to exercise their Warrants on a “cashless basis” will depend on a variety of factors including the price of the Common Stock at the time the Warrants are called for redemption, ongoing cash needs at such time and concerns regarding dilutive share issuances.
The Warrants have been issued in registered form under a warrant agreement (the “Warrant Agreement”) between Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company, as warrant agent, and ROCH. The Warrant Agreement provides that the terms of the Warrants may be amended without the consent of any holder to cure any ambiguity or correct any defective provision, but requires the approval, by written consent or vote, of the holders of a majority of the then outstanding Warrants in order to make any change that adversely affects the interests of the registered holders.
The exercise price and number of shares of common stock issuable on exercise of the Warrants may be adjusted in certain circumstances including in the event of a share dividend, extraordinary dividend or recapitalization, reorganization, merger or consolidation. However, the Warrants will not be adjusted for issuances of shares of Common Stock at a price below the applicable exercise price.
The Warrants may be exercised upon surrender of the Warrant certificate on or prior to the expiration date at the offices of the warrant agent, with the exercise form on the reverse side of the Warrant certificate completed and executed as indicated, accompanied by full payment of the exercise price, by certified or official bank check, for the number of Warrants being exercised. The Warrant holders do not have the rights or privileges of holders of shares of Common Stock and any voting rights until they exercise their warrants and receive shares of common stock. After the issuance of shares of Common Stock upon exercise of the Warrants, each holder will be entitled to one vote for each share held of record on all matters to be voted on by stockholders.
Warrant holders may elect to be subject to a restriction on the exercise of their Warrants such that an electing Warrant holder would not be able to exercise their Warrants to the extent that, after giving effect to such exercise, such holder would beneficially own in excess of 9.9% of the shares of Common Stock outstanding.
No fractional shares will be issued upon exercise of the Warrants. If, upon exercise of the Warrants, a holder would be entitled to receive a fractional interest in a share, upon exercise, the number of shares of Common Stock to be issued to the Warrant holder will be rounded down to the nearest whole number.
In connection with the RH Merger, the Combined Company will become the successor to ROCH under the warrant agreement and the Warrants will become exercisable for Combined Company Common Stock on the same terms, and subject to the same conditions, as described above. The Warrants and the shares of Combined Company Common Stock issuable upon exercise of the Warrants have been registered pursuant to the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part.
Units
The shares of ROCH Common Stock and Warrants issued in connection with the IPO (including in several contemporaneous private placements to insiders) were sold in the form of units (“Units”), each Unit consisting of one share of ROCH Common Stock and three-quarters of one redeemable Warrant. In connection with the RH Merger, the Combined Company will become the successor to ROCH with respect to the ROCH Common Stock and under the Warrant Agreement and accordingly, any Units outstanding from and after the Business Combination reflect a unit consisting of one share of Combined Company Common Stock and three-quarters of one redeemable Warrant to purchase Combined Company Common Stock.
111
Dividends
The DGCL permits a corporation to declare and pay dividends out of “surplus” or, if there is no “surplus”, out of its net profits for the fiscal year in which the dividend is declared and/or the preceding fiscal year. “Surplus” is defined as the excess of the net assets of the corporation over the amount determined to be the capital of the corporation by the board of directors. The capital of the corporation is typically calculated to be (and cannot be less than) the aggregate par value of all issued shares of capital stock. Net assets equals the fair value of the total assets minus total liabilities. The DGCL also provides that dividends may not be paid out of net profits if, after the payment of the dividend, capital is less than the capital represented by the outstanding stock of all classes having a preference upon the distribution of assets.
Declaration and payment of any dividend will be subject to the discretion of the Combined Company’s board of directors. The time and amount of dividends will be dependent upon the Combined Company’s financial condition, operations, cash requirements and availability, debt repayment obligations, capital expenditure needs and restrictions in the Combined Company’s debt instruments, industry trends, the provisions of Delaware law affecting the payment of distributions to stockholders and any other factors the Combined Company’s board of directors may consider relevant.
Subject to the rights of the holders of any series of preferred stock, holders of the Combined Company’s Common Stock will be entitled to receive such dividends and distributions and other distributions in cash, stock or property of the Combined Company when, as and if declared thereon by the Combined Company’s board of directors from time to time out of assets or funds of the Combined Company legally available therefor.
ParentCo has no current plans to pay dividends on the ParentCo Common Stock and the Combined Company likewise has no plans to pay dividends on the Combined Company’s Common Stock. Any decision to declare and pay dividends in the future will be made at the sole discretion of the Combined Company’s board of directors and will depend on, among other things, the Combined Company’s results of operations, cash requirements, financial condition, contractual restrictions and other factors that the Combined Company’s board of directors may deem relevant. Because the Combined Company will be a holding company with no direct operations, the Combined Company will only be able to pay dividends from funds it receive from its subsidiaries.
Annual Stockholder Meetings
The Amended and Restated Bylaws will provide that annual stockholder meetings will be held wholly or partially by means of remote communication or at such place, within or without the State of Delaware, on such date and at such time as may be determined by the Combined Company’s board of directors, the Chief Executive Officer of the Combined Company (the “Chief Executive Officer”) or the chairman of the board of directors of the Combined Company (the “Chairman”) and as will be designated in the notice of the annual meeting.
Anti-Takeover Effects of the Combined Company’s Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws and Certain Provisions of Delaware Law
The Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws will contain and the DGCL contains provisions, which are summarized in the following paragraphs, that are intended to enhance the likelihood of continuity and stability in the composition of the Combined Company’s board of directors. These provisions are intended to avoid costly takeover battles, reduce the Combined Company’s vulnerability to a hostile change of control and enhance the ability of the Combined Company’s board of directors to maximize stockholder value in connection with any unsolicited offer to acquire the Combined Company. However, these provisions may have an anti-takeover effect and may delay, deter or prevent a merger or acquisition of the Combined Company by means of a tender offer, a proxy contest or other takeover attempt that a stockholder might consider in its best interest, including those attempts that might result in a premium over the prevailing market price for the shares of the Combined Company’s Common Stock held by stockholders.
112
Authorized but Unissued Capital Stock
Delaware law does not require stockholder approval for any issuance of authorized shares. However, the listing requirements of NASDAQ, which would apply if and so long as the Combined Company’s Common Stock remains listed on NASDAQ, require stockholder approval of certain issuances equal to or exceeding 20% of the then outstanding voting power or then outstanding number of shares of common stock. Additional shares that may be used in the future may be issued for a variety of corporate purposes, including future public offerings, to raise additional capital or to facilitate acquisitions.
The Combined Company’s board of directors may generally issue preferred shares on terms calculated to discourage, delay or prevent a change of control of the Combined Company or the removal of the Combined Company’s management. Moreover, the Combined Company’s authorized but unissued shares of preferred stock will be available for future issuances without stockholder approval and could be utilized for a variety of corporate purposes, including future offerings to raise additional capital, to facilitate acquisitions and employee benefit plans.
One of the effects of the existence of unissued and unreserved common stock or preferred stock may be to enable the Combined Company’s board of directors to issue shares to persons friendly to current management, which issuance could render more difficult or discourage an attempt to obtain control of the Combined Company by means of a merger, tender offer, proxy contest or otherwise, and thereby protect the continuity of the Combined Company’s management and possibly deprive the Combined Company’s stockholders of opportunities to sell their shares of the Combined Company’s Common Stock at prices higher than prevailing market prices.
Classified Board of Directors
The Combined Company’s directors, other than those who may be elected by the holders of any future series of preferred stock, will be classified with respect to the time for which they severally hold office into three classes, as nearly equal in number as possible, designated Class I, Class II, and Class III, until the date (the “Sunset Date”) of the first annual meeting of the stockholders that is held after the fifth anniversary of the effectiveness of the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation. At any meeting of stockholders at which directors are to be elected prior to the Sunset Date, the number of directors elected may not exceed the greatest number of directors then in office in any class of directors. The directors first appointed to Class I will hold office for a term expiring at the annual meeting of stockholders to be held in 2021; the directors first appointed to Class II will hold office for a term expiring at the annual meeting of stockholders to be held in 2022; and the directors first appointed to Class III will hold office for a term expiring at the annual meeting of stockholders to be held in 2023, with the members of each class to hold office until their successors are elected and qualified. At each succeeding annual meeting of the stockholders of the Combined Company held prior to the Sunset Date, the successors to the class of directors whose term expires at that meeting will be elected by plurality vote of all votes cast at such meeting to hold office for a term expiring at the annual meeting of stockholders held in the third year following the year of their election and until their successors are elected and qualified. All directors elected at annual meetings of stockholders held on or after the Sunset Date will be elected for terms expiring at the next annual meeting of stockholders and will not be subject to the classification provisions set forth above. Subject to the rights, if any, of the holders of any future series of preferred stock to elect additional directors under circumstances specified in a Preferred Stock Designation, directors may be elected by the stockholders only at an annual meeting of stockholders.
Removal of Directors; Vacancies
Subject to the rights, if any, of the holders of any series of preferred stock to elect additional directors under circumstances specified in a Preferred Stock Designation and other than a ROCH Designated Director (as defined in the Investor Rights Agreement), who may be removed for any reason following the expiration of the Director Designation Period (as defined in the Investor Rights Agreement) with the approval of a majority of the directors of the Combined Company (other than the ROCH Designated Directors), the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will provide that, until the Sunset Date, directors may be removed by the stockholders only for cause and following the Sunset Date, directors may be removed by the stockholders with or without cause, in each case, by the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the voting power of the outstanding voting stock, voting together as a single class, at any annual meeting or special meeting of the stockholders where the notice of which states that the removal of a director or directors is among the purposes of the meeting and identifies the director or directors proposed to be removed.
113
Subject to (a) the rights, if any, of the holders of any future series of preferred stock to elect additional directors under circumstances specified in a Preferred Stock Designation and (b) the Investor Rights Agreement, newly created directorships resulting from any increase in the number of directors and any vacancies on the board of directors resulting from death, resignation, disqualification, removal, or other cause will be filled solely by the affirmative vote of a majority of the remaining directors then in office, even though less than a quorum of the board of directors, or by a sole remaining director. Any director elected in accordance with the preceding sentence will hold office for the remainder of the full term of the class of directors in which the new directorship was created or the vacancy occurred (or, if such directorship was created or vacancy occurred after the Sunset Date, until the next annual meeting of stockholders) and until such director’s successor has been elected and qualified. No decrease in the number of directors constituting the board of directors may shorten the term of any incumbent director.
Special Stockholder Meetings
Subject to the rights of the holders of any future series of preferred stock, special meetings of stockholders may be called only (i) by the Chairman, (ii) by the Chief Executive Officer, or (iii) by the Secretary of the Combined Company (the “Secretary”) acting at the request of the Chairman, the Chief Executive Officer or a majority of the total number of directors that the Combined Company would have if there were no vacancies on its board of directors. At any annual meeting or special meeting of stockholders, only such business will be conducted or considered as has been brought before such meeting in the manner provided in the Amended and Restated Bylaws.
Requirements for Advance Notification of Director Nominations and Stockholder Proposals
The Amended and Restated Bylaws, which are attached as Exhibit 3.4 to the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, will establish advance notice procedures with respect to stockholder proposals and the nomination of candidates for election as directors, other than nominations made by or at the direction of the board of directors or a committee of the board of directors. In order for any matter to be properly brought before a meeting, a stockholder will have to comply with advance notice requirements and provide the Combined Company with certain information. Generally, to be timely, a stockholder’s notice relating to any nomination or other business to be brought before an annual meeting must be delivered to the Secretary at the Combined Company’s principal executive offices not less than 90 days nor more than 120 days prior to the first anniversary date of the immediately preceding annual meeting of stockholders. Notwithstanding the foregoing, in the event that the number of directors to be elected to the board of directors at the annual meeting is increased effective after the time period for which nominations would otherwise be due and there is no public announcement by the Combined Company naming the nominees for the additional directorships at least 100 days prior to the first anniversary of the preceding year’s annual meeting, a stockholder’s notice will also be considered timely, but only with respect to nominees for the additional directorships, if it will be delivered to the Secretary at the principal executive offices of the Combined Company not later than the close of business on the 10th day following the day on which such public announcement is first made by the Combined Company.
To be timely, a stockholder’s notice relating to the nomination of a director to the Combined Company’s board of directors to be brought before a special meeting will be delivered to the Secretary at the principal executive offices of the Combined Company not earlier than the close of business on the 120th day prior to such special meeting and not later than the close of business on the later of the 90th day prior to such special meeting or the 10th day following the day on which public announcement is first made of the date of the special meeting and of the nominees proposed by the board of directors to be elected at such meeting. The Amended and Restated Bylaws also specify requirements as to the form and content of a stockholder’s notice. Notwithstanding the foregoing notice requirements, the notice requirements will not apply to director nominations pursuant the Pure Crown Side Letter (as defined in the Amended and Restated Bylaws).
114
These notice provisions may defer, delay or discourage a potential acquirer from conducting a solicitation of proxies to elect the acquirer’s own slate of directors or otherwise attempting to influence or obtain control of the Combined Company.
Consent of Stockholders in Lieu of Meeting
Subject to the rights of the holders of any series of preferred stock, any action required or permitted to be taken by the stockholders may be taken only at a duly called annual or special meeting of stockholders and may not be taken without a meeting by means of any consent in writing of such stockholder.
Dissenters’ Rights of Appraisal and Payment
Under the DGCL, with certain exceptions, the Combined Company’s stockholders will have appraisal rights in connection with a merger or consolidation of the Combined Company. Pursuant to the DGCL, stockholders who properly request and perfect appraisal rights in connection with such merger or consolidation will have the right to receive payment of the fair value of their shares as determined by the Delaware Court of Chancery.
Stockholders’ Derivative Actions
Under the DGCL, any of the Combined Company’s stockholders may bring an action in the Combined Company’s name to procure a judgment in the Combined Company’s favor, also known as a derivative action, provided that the stockholder bringing the action is a holder of the Combined Company’s shares at the time of the transaction to which the action relates or such stockholder’s stock thereafter devolved by operation of law.
Amendment of the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation
The Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will provide that the Combined Company reserves the right at any time from time to time to amend, alter, change or repeal any provision contained in the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation. Notwithstanding any inconsistent provision of the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation or any provision of law that might otherwise permit a lesser vote or no vote, but in addition to any affirmative vote of the holders of any series of preferred stock required by law, (a) until the Sunset Date, the affirmative vote of the holders of at least 66 2∕3% of the voting power, and (b) following the Sunset Date, the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the voting power, in the case of each of (a) and (b), of the outstanding capital stock entitled to vote, voting together as a single class, will be required to amend, alter, change or repeal, or adopt any provision inconsistent with, certain provisions, as noted in the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, or the definition of any capitalized terms used therein or any successor provision.
Amendment of the Amended and Restated Bylaws
The Amended and Restated Bylaws may be amended in any respect or repealed at any time, either (a) at any meeting of stockholders, provided that any amendment or supplement proposed to be acted upon at any such meeting has been properly described or referred to in the notice of such meeting, or (b) by the Combined Company’s board of directors, provided that no amendment adopted by the board of directors may vary or conflict with any amendment adopted by the stockholders in accordance with the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and the Amended and Restated Bylaws. Notwithstanding the foregoing and anything contained in the Amended and Restated Bylaws, certain provisions of the Amended and Restated Bylaws may not be amended or repealed by the stockholders, and no provision inconsistent therewith may be adopted by the stockholders, without (a) until the Sunset Date, the affirmative vote of the holders of at least 66 2∕3% of the Combined Company’s outstanding capital stock entitled to vote, voting together as a single class and (b) following the Sunset Date, the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the Combined Company’s outstanding capital stock entitled to vote, voting together as a single class.
115
Exclusive Forum Selection
The Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will provide that, unless the Combined Company consents in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, (a) the Court of Chancery (the “Chancery Court”) of the State of Delaware (or, in the event that the Chancery Court does not have jurisdiction, the federal district court for the District of Delaware) will, to the fullest extent permitted by law, be the sole and exclusive forum for (i) any derivative action, suit or proceeding brought on behalf of the Combined Company, (ii) any action, suit or proceeding asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any director, officer, employee or stockholder of the Combined Company to the Combined Company or to the Combined Company’s stockholders, (iii) any action, suit or proceeding arising pursuant to any provision of the DGCL or the Amended and Restated Bylaws or the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation (as either may be amended and/or restated from time to time) or as to which the DGCL confers jurisdiction on the Chancery Court, or (iv) any action, suit or proceeding asserting a claim against the Combined Company governed by the internal affairs doctrine; and (b) subject to the preceding provisions, the federal district courts of the United States will be the exclusive forum for the resolution of any complaint asserting a cause of action arising under the Securities Act. If any action the subject matter of which is within the scope of clause (a) of the immediately preceding sentence is filed in a court other than the courts in the State of Delaware (a “Foreign Action”) in the name of any stockholder, such stockholder will be deemed to have consented to (1) the personal jurisdiction of the state and federal courts in the State of Delaware in connection with any action brought in any such court to enforce the provisions of clause (a) of the immediately preceding sentence and (2) having service of process made upon such stockholder in any such action by service upon such stockholder’s counsel in the Foreign Action as agent for such stockholder. Any person or entity purchasing or otherwise acquiring or holding any interest in any security of the Combined Company will be deemed to have notice of and consented to such provisions of the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the exclusive forum provision will not apply to suits brought to enforce any liability or duty created by the Securities Act, or any other claim for which the federal courts of the United States have exclusive jurisdiction.
Limitations on Liability and Indemnification of Officers and Directors
The DGCL authorizes corporations to limit or eliminate the personal liability of directors to corporations and their stockholders for monetary damages for breaches of directors’ fiduciary duties, subject to certain exceptions. The Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will include a provision that eliminates the personal liability of directors for monetary damages for any breach of fiduciary duty as a director, except to the extent such exemption from liability or limitation thereof is not permitted under the DGCL. The effect of these provisions is to eliminate the rights of the Combined Company and its stockholders, through stockholders’ derivative suits on the Combined Company’s behalf, to recover monetary damages from a director for breach of fiduciary duty as a director, including breaches resulting from grossly negligent behavior. However, exculpation does not apply to any director for any breach of the director’s duty of loyalty to the Combined Company or its stockholders, or if the director has acted in bad faith, knowingly or intentionally violated the law, authorized illegal dividends or redemptions or derived an improper benefit from his or her actions as a director.
The Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will provide that the Combined Company must indemnify and advance expenses to the Combined Company’s directors and officers to the fullest extent authorized by the DGCL. The Combined Company also is expressly authorized maintain insurance, at its expense, to protect itself and any director, officer, employee or agent of the Combined Company or another corporation, partnership, joint venture, trust or other enterprise against any expense, liability or loss, whether or not the Combined Company would have the power to indemnify such person against such expense, liability or loss under the DGCL. The Combined Company believes that these indemnification and advancement provisions and insurance are useful to attract and retain qualified directors and executive officers.
116
The limitation of liability, advancement and indemnification provisions in the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation may discourage stockholders from bringing a lawsuit against directors for breach of their fiduciary duty. These provisions also may have the effect of reducing the likelihood of derivative litigation against directors and officers, even though such an action, if successful, might otherwise benefit the Combined Company and its stockholders. In addition, your investment may be adversely affected to the extent the Combined Company pays the costs of settlement and damage awards against directors and officers pursuant to these indemnification provisions.
There is currently no pending material litigation or proceeding involving any of ROCH’s and PCT’s directors, officers or employees for which indemnification is sought.
117
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT
The following table sets forth pro forma information regarding the beneficial ownership of ParentCo Common Stock immediately after the consummation of the Business Combination by each person who owns or is expected to beneficially own more than 5% of ParentCo’s Common Stock and each officer, each director and all officers and directors as a group of ParentCo. Immediately after the consummation of the Business Combination, ParentCo will have shares of Common Stock issued and outstanding.
Shares which an individual or group has a right to acquire within 60 days pursuant to the exercise or conversion of options, warrants or other similar convertible or derivative securities are deemed to be outstanding for the purpose of computing the percentage ownership of such individual or group, but are not deemed to be outstanding for the purpose of computing the percentage ownership of any other person shown in the table.
Unless otherwise indicated, ParentCo believes that all persons named in the table below have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares of capital stock beneficially owned by them. To ParentCo’s knowledge, no shares of ParentCo Common Stock beneficially owned by any executive officer, director or director nominee have been pledged as security.
| Assuming Maximum | ||||||||||||||||
| Assuming No Redemptions | Redemptions | |||||||||||||||
| Approximate | Approximate | |||||||||||||||
| Amount Beneficial | Percentage of Outstanding | Amount Beneficial | Percentage of Outstanding | |||||||||||||
| Name and Address of Beneficial Owner(1) | Ownership | ParentCo Shares | Ownership | ParentCo Shares | ||||||||||||
| Directors and Executive Officers of ParentCo After Consummation of the Business Combination: | ||||||||||||||||
| Michael Otworth | ||||||||||||||||
| Michael Dee | ||||||||||||||||
| David Brenner | ||||||||||||||||
| Tanya Burnell | ||||||||||||||||
| Richard Brenner | ||||||||||||||||
| Dr. John Scott | ||||||||||||||||
| Jeffrey Fieler | 700,000 | * | 700,000 | * | ||||||||||||
| Timothy Glockner | ||||||||||||||||
| All directors and executive officers of ParentCo as a group (8 individuals) | ||||||||||||||||
| Five Percent or More Holders of ParentCo After Consummation of the Business Combination: | ||||||||||||||||
* less than 1%
118
The shares of ParentCo Common Stock being offered by the Selling Stockholders are those previously issued to the Selling Stockholders in connection with the Business Combination. We are registering the shares of ParentCo Common Stock in order to permit the Selling Stockholders to offer the shares for resale from time to time. Except for the ownership of the shares of ParentCo Common Stock, the Selling Stockholders have not had any material relationship with us within the past three years.
The table below lists the Selling Stockholders and other information regarding the beneficial ownership of the shares of ParentCo Common Stock by each of the Selling Stockholders. The second column lists the number of shares of ParentCo Common Stock expected to be beneficially owned by each Selling Stockholder upon consummation of the Business Combination, based on its ownership of the shares of Common Stock, as of , 2021.
The third column lists the shares of ParentCo Common Stock being offered by this prospectus by the Selling Stockholders.
In accordance with the terms of a registration rights agreement with the Selling Stockholders, this prospectus generally covers the resale of the sum of (i) the number of shares of ParentCo Common Stock issued to the Selling Stockholders in the Business Combination. The fourth column assumes the sale of all of the shares offered by the Selling Stockholders pursuant to this prospectus.
119
The Selling Stockholders may sell all, some or none of their shares in this offering. See "Plan of Distribution."
| Name of Selling Shareholder | Number
of shares of Common Stock Owned Prior to Offering | Maximum Number of shares of Common Stock to be Sold Pursuant to this Prospectus | Number
of shares of Common Stock Owned After Offering | |||||||||
| Peter G. Manganello | 7,500 | 7,500 | -- | |||||||||
| Aaron Mason | 7,500 | 7,500 | -- | |||||||||
| Zachary M. Manganello | 2,500 | 2,500 | -- | |||||||||
| Peter G. Milliken | 30,000 | 30,000 | -- | |||||||||
| Gerrish H. Milliken, III | 200,000 | 200,000 | -- | |||||||||
| Wilmington Trust Co, Stephen G. Milliken & Gerrish H Milliken III SUCC Co-TTEES for the GHM JR 1956 TR 14 FBO PGM Dated 8/20/1956 | 35,000 | 35,000 | -- | |||||||||
Wilmington Trust Co, Stephen G. Milliken & Gerrish H Milliken III SUCC Co-TTEES for the GHM JR 1956 TR 7 FBO JWM Dated 8/20/1956 | 75,000 | 75,000 | -- | |||||||||
| Wilmington Trust Co, John W Milliken & Gerrish H Milliken III SUCC Co-TTEES for the GHM JR 1956 TR 14 FBO SGM Dated 8/20/1956 | 50,000 | 50,000 | -- | |||||||||
| Wilmington Trust Co, John W Milliken & Gerrish H Milliken III SUCC Co-TTEES for the GHM JR 1956 TR 7 FBO SGM Dated 8/20/1956 | 50,000 | 50,000 | -- | |||||||||
| Wilmington Trust Co, John W Milliken & Gerrish H Milliken III SUCC Co-TTEES for the GHM JR 1956 TR 7 FBO JWM Dated 8/20/1956 | 75,000 | 75,000 | -- | |||||||||
| Wilmington Trust Co, John W Milliken & Gerrish H Milliken III SUCC Co-TTEES for the GHM JR 1956 TR 7 FBO PGM Dated 8/20/1956 | 35,000 | 35,000 | -- | |||||||||
| BNP Paribas Asset Management UK Limited as agent on behalf of BNP Paribas Funds Energy Transition | 1,500,000 | 1,500,000 | -- | |||||||||
| Samlyn Net Neutral Master Fund, Ltd. | 877,408 | 877,408 | -- | |||||||||
| Samlyn Long Alpha Master Fund, Ltd. | 22,492 | 22,492 | -- | |||||||||
| Samlyn Offshore Master Fund, Ltd. | 1,107,074 | 1,107,074 | -- | |||||||||
| Samlyn Onshore Fund, LP | 393,026 | 393,026 | -- | |||||||||
| Manatuck Hill Navigator Master Fund, LP | 14,600 | 14,600 | -- | |||||||||
| Manatuck Hill Scout Fund, LP | 77,800 | 77,800 | -- | |||||||||
| Manatuck Hill Mariner Master Fund, LP | 32,600 | 32,600 | -- | |||||||||
| Jefferies Strategic Investments, LLC | 553,729 | 553,729 | -- | |||||||||
| Solanas ESG Sustainability Master Fund LP | 146,271 | 146,271 | -- | |||||||||
| Whitebox Multi-Strategy Partners, LP | 34,833 | 34,833 | -- | |||||||||
| Whitebox Relative Value Partners, LP | 20,167 | 20,167 | -- | |||||||||
| Greenlight Capital, Inc.(1) | 100,000 | 100,000 | -- | |||||||||
| Empery Tax Efficient III, LP(2) | 67,355 | 67,355 | -- | |||||||||
| Empery Tax Efficient, LP(3) | 24,445 | 24,445 | -- | |||||||||
| Empery Asset Master, Ltd(4) | 33,200 | 33,200 | -- | |||||||||
| Joan S. & James G. Blaine 2012 Family Trust UAD 12/27/12 FBO J. Blaine Jr. | 2,500 | 2,500 | -- | |||||||||
| Longhorn Special Opportunities Fund LP | 2,500,000 | 2,500,000 | -- | |||||||||
| Magnetar Capital Master Fund, Ltd. | 7,800 | 7,800 | -- | |||||||||
| Magnetar Constellation Fund II, Ltd. | 59,800 | 59,800 | -- | |||||||||
| Magnetar Constellation Master Fund, Ltd. | 209,700 | 209,700 | -- | |||||||||
| Magnetar Lake Credit Fund LLC | 43,200 | 43,200 | -- | |||||||||
| Magnetar Longhorn Fund LP | 32,600 | 32,600 | -- | |||||||||
| Magnetar SC Fund Ltd. | 55,700 | 55,700 | -- | |||||||||
| Magnetar Structured Credit Fund, LP | 77,000 | 77,000 | -- | |||||||||
| Magnetar Xing He Master Fund Ltd. | 73,400 | 73,400 | -- | |||||||||
| Purpose Alternative Credit Fund - F LLC | 27,200 | 27,200 | -- | |||||||||
| Purpose Alternative Credit Fund - T LLC | 13,600 | 13,600 | -- | |||||||||
120
| MARTIN HALL & JENNIFER S. EWING CO-TTEES U/ART 4TH OF THE WILL OF AMF OVER TRUST DTD 12/9/37 FBO C. STEFANO FRANCHETTI | 50,000 | 50,000 | -- | |||||||||
| MARTIN HALL & JENNIFER S. EWING CO-TTEES U/ART 4TH OF THE WILL OF AMF OVER TRUST DTD 12/9/37 FBO BENJAMIN FRANCHETTI | 10,000 | 10,000 | -- | |||||||||
| MARTIN HALL & JENNIFER S. EWING CO-TTEES U/ART 4TH OF THE WILL OF AMF OVER TRUST DTD 12/9/37 FBO GIORDANO FRANCHETTI | 25,000 | 25,000 | -- | |||||||||
| MARTIN HALL & JENNIFER S. EWING CO-TTEES U/ART 7TH OF THE WILL OF AMF OVER TUW DTD 4/29/47 GHM, SR. FBO GIORDANO FRANCHETTI | 10,000 | 10,000 | -- | |||||||||
| MARTIN HALL & JENNIFER S. EWING TTEES BY POA U/ART 4TH OF THE WILL OF AMF OVER TRUST DTD 12/9/37 FBO BALDASSARRA FRANCHETTI | 10,000 | 10,000 | -- | |||||||||
| MARTIN HALL & JENNIFER S. EWING TTEES BY POA U/ART 4TH OF THE WILL OF AMF OVER TRUST DTD 12/9/37 FBO GREGORIO FRANCHETTI | 10,000 | 10,000 | -- | |||||||||
| MARTIN HALL & JENNIFER S. EWING TTEES BY POA U/ART 4TH OF THE WILL OF AMF OVER TRUST DTD 12/9/37 FBO PRISCA FRANCHETTI | 10,000 | 10,000 | -- | |||||||||
| BEMAP Master Fund Ltd.(5) | 495,766 | 495,766 | -- | |||||||||
| BLACKWELL PARTNERS LLC - SERIES A(5) | 740,215 | 740,215 | -- | |||||||||
| President and Fellows of Harvard College | 2,000,000 | 2,000,000 | -- | |||||||||
| Mousserena, L.P.(6) | 1,500,000 | 1,500,000 | -- | |||||||||
| SYLEBRA CAPITAL PARC MASTER FUND(5) | 1,265,906 | 1,265,906 | -- | |||||||||
| SYLEBRA CAPITAL PARTNERS MASTER FUND, LTD.(5) | 7,498,113 | 7,498,113 | -- | |||||||||
| Jeffrey R. Fieler(7) | 700,000 | 700,000 | -- | |||||||||
| Howard Hughes Medical Institute | 2,000,000 | 2,000,000 | -- |
(1) Greenlight Capital, Inc. (“Greenlight Inc.”) is the investment advisor for Greenlight Capital Qualified, L.P., Greenlight Capital, L.P. and Greenlight Capital Offshore Partners, and as such has voting and dispositive power over 62,020 shares of common stock held by those entities. DME Capital Management, LP (“DME Management”) is the investment manager for Greenlight Capital Investors, LP, and Greenlight Capital Offshore Master, Ltd., and as such has voting and dispositive power over 37,980 shares of common stock held by those entities. DME Advisors GP, LLC (“DME GP”) is the general partner of DME Management, and as such has voting and dispositive power over 37,980 shares of common stock. David Einhorn is the principal of Greenlight Inc., DME Management and DME GP, and as such has voting and dispositive power over 100,000 shares of common stock held by these affiliates of Greenlight, Inc. Each of Mr. Einhorn, Greenlight Inc., DME Management and DME GP disclaims beneficial ownership of these shares of common stock, except to the extent of any pecuniary interest therein.
(2) Empery Asset Management LP, the authorized agent of Empery Tax Efficient III, LP ("ETE III"), has discretionary authority to vote and dispose of the shares held by ETE III and may be deemed to be the beneficial owner of these shares. Martin Hoe and Ryan Lane, in their capacity as investment managers of Empery Asset Management LP, may also be deemed to have investment discretion and voting power over the shares held by ETE III. ETE III, Mr. Hoe and Mr. Lane each disclaim any beneficial ownership of these shares.
(3) Empery Asset Management LP, the authorized agent of Empery Tax Efficient, LP ("ETE"), has discretionary authority to vote and dispose of the shares held by ETE and may be deemed to be the beneficial owner of these shares. Martin Hoe and Ryan Lane, in their capacity as investment managers of Empery Asset Management LP, may also be deemed to have investment discretion and voting power over the shares held by ETE. ETE, Mr. Hoe and Mr. Lane each disclaim any beneficial ownership of these shares.
(4) Empery Asset Management LP, the authorized agent of Empery Asset Master Ltd ("EAM"), has discretionary authority to vote and dispose of the shares held by EAM and may be deemed to be the beneficial owner of these shares. Martin Hoe and Ryan Lane, in their capacity as investment managers of Empery Asset Management LP, may also be deemed to have investment discretion and voting power over the shares held by EAM. EAM, Mr. Hoe and Mr. Lane each disclaim any beneficial ownership of these shares.
(5) On November 12, 2020, pursuant to four Class A Unit Purchase Agreements dated as of the same date, by and between PCT and each of BEMAP Master Fund Ltd., Blackwell Partners LLC — Series A, Sylebra Capital Parc Master Fund and Sylebra Capital Partners Master Fund, Ltd. (each an entity subject to an investment management agreement or sub-management agreement with Sylebra Capital Limited, together, “Sylebra Capital” and the agreements entered into, collectively, the “Sylebra Capital Class A Unit Purchase Agreements”), PCT issued and sold an aggregate of 684,190 Class A Common Units to Sylebra Capital for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $60,000,000 or approximately $87.69 per unit, subject to certain adjustments. In connection with the Sylebra Capital Class A Unit Purchase Agreements, and as documented in the Investor Rights Agreement, Sylebra Capital will be entitled to select one member of ParentCo’s Board of Directors.
(6) Includes 1,500,000 shares of common stock beneficially owned by Mousserena, L.P. Mousserena, L.P. and Charles Heilbronn have shared voting and dispositive power over these shares. The address for Mousserena, L.P. is Ugland House, 135 South Church Street, George Town, Grand Cayman KY1-1104 Cayman Islands. The address for Mr. Heilbronn is c/o Mousse Partners Limited, 9 West 57th Street, New York, NY 10019.
(7) Mr. Fieler has agreed to serve as a member of the Board of Directors of ParentCo following the consummation of the Business Combination.
121
SHARES ELIGIBLE FOR FUTURE SALE
Upon the consummation of the Business Combination, ParentCo will have shares of ParentCo Common Stock authorized and up to shares of ParentCo Common Stock issued and outstanding, assuming no shares of ROCH Common Stock are redeemed in connection with the Business Combination. All of the shares of ParentCo Common Stock issued in connection with the Business Combination will be freely transferable by persons other than by ParentCo’s “affiliates” or ROCH’s “affiliates” without restriction or further registration under the Securities Act. Sales of substantial amounts of the ParentCo Common Stock in the public market could adversely affect prevailing market prices of the ParentCo Common Stock. Prior to the Business Combination, there has been no public market for shares of ParentCo Common Stock. ParentCo has applied for listing of the ParentCo Common Stock, warrants and units on NASDAQ, but ParentCo cannot assure you that a regular trading market will develop in the ParentCo Common Stock.
Lock-up Agreements
Pursuant to the Investor Rights Agreement, almost all of the PCT Unitholders agreed, with certain limited exceptions, to lock up the shares of ParentCo Common Stock they will receive in the Business Combination, to be released in accordance with the following schedule:
| • | From and after the six-month anniversary of the Closing Date, each Founder (as defined in the Investor Rights Agreement) may sell up to 20% of such Founder’s ParentCo Common Shares and each PCT Unitholder that is not a Founder may sell up to 33.34% of such PCT Unitholder’s ParentCo Common Shares. |
| • | From and after the one-year anniversary of the Closing Date, each Founder may sell up to 30% of such Founder’s ParentCo Common Shares and each PCT Unitholder that is not a Founder may sell up to 33.33% of such PCT Unitholder’s ParentCo Common Shares. |
| • | From and after the Phase II Facility becoming operational, as certified by an independent engineering firm, each Founder may sell up to 50% of such Founder’s ParentCo Common Shares and each PCT Unitholder that is not a Founder may sell up to 33.33% of such PCT Unitholder’s shares of ParentCo Common Shares; provided that, in the case of Procter & Gamble, such lock-up will terminate in any event no later than April 15, 2023. |
In addition, ROCH and certain officers, directors and sponsors of ROCH (collectively, the “IPO Insiders”) previously entered into a letter agreement (the “Letter Agreement”) in connection with ROCH’s IPO, pursuant to which the IPO Insiders agreed to certain selling restrictions and hedging restrictions applicable to the Common Stock they hold, which will be converted to ParentCo Common Stock in the Business Combination. Among other things, the IPO Insiders agreed in the Letter Agreement to lock up the shares of ParentCo Common Stock they will receive in the Business Combination for six months following the Business Combination (the “Lock Up Period”), unless the closing price of ParentCo Common stock equals or exceeds $12.50 per share for any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period after the Business Combination, in which case the IPO Insiders may sell up to 50% of their holdings of ParentCo Common Stock. The Letter Agreement also provides that the IPO Insiders will be released from the selling restrictions under the Letter Agreement before the Lock Up Period expires if ParentCo undergoes certain transactions where ParentCo shareholders have the right to exchange their shares of ParentCo Common Stock for cash, securities or other property.
Rule 144
All of ParentCo’s Common Stock that will be outstanding upon the completion of the Business Combination, other than those shares of ParentCo Common Stock registered pursuant to the Registration Statement on Form S-4 of which the Proxy Statement/Prospectus forms a part and those shares of ParentCo Common Stock registered pursuant to the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, will be “restricted securities” as that term is defined in Rule 144 under the Securities Act and may be sold publicly in the United States only if they are subject to an effective registration statement under the Securities Act or pursuant to an exemption from the registration requirement such as those provided by Rule 144 and Rule 701 promulgated under the Securities Act. However, Rule 144 is not available for the resale of securities initially issued by shell companies (other than business combination related shell companies) or issuers that have been at any time previously a shell company. Rule 144 does include an important exception to this prohibition if the following conditions are met:
| • | the issuer of the securities that was formerly a shell company has ceased to be a shell company; |
| • | the issuer of the securities is subject to the reporting requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act; |
| • | the issuer of the securities has filed all Exchange Act reports and material required to be filed, as applicable, during the preceding 12 months (or such shorter period that the issuer was required to file such reports and materials), other than Form 8-K reports; and |
| • | at least one year has elapsed from the time that the issuer filed current Form 10 type information with the SEC reflecting its status as an entity that is not a shell company. |
122
As a result, the initial ROCH holders, purchasers in the PIPE Placement, any of their respective affiliates and other third parties will be able to sell their Founder Shares, Private Shares, Public Shares or PIPE Placement shares, as applicable, pursuant to and in accordance with Rule 144 without registration one year after the completion of the Business Combination. However, if they remain one of our affiliates, they will only be permitted to sell a number of securities that does not exceed the greater of:
| • | 1% of the total number of shares of ParentCo Common Stock then outstanding, including shares held by PCT Unitholders that will be subject to certain lock-up arrangements pursuant to the Investor Rights Agreement, which was shares on , 2021; or |
| • | the average weekly reported trading volume of the Common Stock during the four calendar weeks preceding the filing of a notice on Form 144 with respect to the sale. |
Sales by our affiliates under Rule 144 would also limited be limited by manner of sale provisions and notice requirements and to the availability of current public information about us.
Rule 701
In general, under Rule 701 of the Securities Act as currently in effect, each of PCT’s employees, consultants or advisors who purchases equity shares from ParentCo in connection with a compensatory stock plan or other written agreement executed prior to the completion of the Business Combination is eligible to resell those equity shares in reliance on Rule 144, but without compliance with some of the restrictions, including the holding period, contained in Rule 144. However, the Rule 701 shares would remain subject to lock-up arrangements and would only become eligible for sale when the lock-up period expires.
Registration Rights
In connection with, and as a condition to the consummation of, the Business Combination, the Merger Agreement provides that certain persons and entities holding PCT Units and certain Initial Stockholders will enter into the Investor Rights Agreement. Pursuant to the terms of the Investor Rights Agreement, ParentCo will be obligated to file, after it becomes eligible to use Form S-3 or its successor form, a shelf registration statement to register the resale by the parties of the shares of ParentCo Common Stock issuable in connection with the Business Combination. Approximately shares of ParentCo Common Stock are expected to be covered by the Investor Rights Agreement. The Investor Rights Agreement will also provide the parties with demand, “piggy-back” and Form S-3 registration rights, subject to certain minimum requirements and customary conditions. ParentCo has also granted certain registration rights pursuant to the PIPE Registration Rights Agreement and the Magnetar Registration Rights Agreement, as described elsewhere in this prospectus.
123
Each Selling Stockholder of the securities and any of their pledgees, assignees and successors-in-interest may, from time to time, sell any or all of their securities covered hereby on the principal trading market for such securities or any other stock exchange, market or trading facility on which the securities are traded or in private transactions. These sales may be at fixed or negotiated prices. A Selling Stockholder may use any one or more of the following methods when selling securities:
| · | ordinary brokerage transactions and transactions in which the broker-dealer solicits Subscribers; |
| · | block trades in which the broker-dealer will attempt to sell the securities as agent but may position and resell a portion of the block as principal to facilitate the transaction; |
| · | purchases by a broker-dealer as principal and resale by the broker-dealer for its account; |
| · | an exchange distribution in accordance with the rules of the applicable exchange; |
| · | privately negotiated transactions; |
| · | settlement of short sales; |
| · | in transactions through broker-dealers that agree with the Selling Stockholders to sell a specified number of such securities at a stipulated price per security; |
| · | through the writing or settlement of options or other hedging transactions, whether through an options exchange or otherwise; |
| · | a combination of any such methods of sale; or |
| · | any other method permitted pursuant to applicable law. |
The Selling Stockholders may also sell securities under Rule 144 or any other exemption from registration under the Securities Act, if available, rather than under this prospectus.
Broker-dealers engaged by the Selling Stockholders may arrange for other brokers-dealers to participate in sales. Broker-dealers may receive commissions or discounts from the Selling Stockholders (or, if any broker-dealer acts as agent for the Subscriber of securities, from the Subscriber) in amounts to be negotiated, but, except as set forth in a supplement to this Prospectus, in the case of an agency transaction not in excess of a customary brokerage commission in compliance with FINRA Rule 2440; and in the case of a principal transaction a markup or markdown in compliance with FINRA IM-2440.
In connection with the sale of the securities or interests therein, the Selling Stockholders may enter into hedging transactions with broker-dealers or other financial institutions, which may in turn engage in short sales of the securities in the course of hedging the positions they assume. The Selling Stockholders may also sell securities short and deliver these securities to close out their short positions, or loan or pledge the securities to broker-dealers that in turn may sell these securities. The Selling Stockholders may also enter into option or other transactions with broker-dealers or other financial institutions or create one or more derivative securities which require the delivery to such broker-dealer or other financial institution of securities offered by this prospectus, which securities such broker-dealer or other financial institution may resell pursuant to this prospectus (as supplemented or amended to reflect such transaction).
124
The Selling Stockholders and any broker-dealers or agents that are involved in selling the securities may be deemed to be “underwriters” within the meaning of the Securities Act in connection with such sales. In such event, any commissions received by such broker-dealers or agents and any profit on the resale of the securities purchased by them may be deemed to be underwriting commissions or discounts under the Securities Act. Each Selling Stockholder has informed ParentCo that it does not have any written or oral agreement or understanding, directly or indirectly, with any person to distribute the securities.
The Company is required to pay certain fees and expenses incurred by ParentCo incident to the registration of the securities. The Company has agreed to indemnify the Selling Stockholders against certain losses, claims, damages and liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act.
We agreed to keep this prospectus effective until the earlier of (i) all of the securities have been sold pursuant to this prospectus or Rule 144 under the Securities Act or any other rule of similar effect, (ii) they may be sold pursuant to Rule 144 without volume or manner-of-sale restrictions, as determined by ParentCo; or (iii) it has been two years from the Closing Date. The resale securities will be sold only through registered or licensed brokers or dealers if required under applicable state securities laws. In addition, in certain states, the resale securities covered hereby may not be sold unless they have been registered or qualified for sale in the applicable state or an exemption from the registration or qualification requirement is available and is complied with.
Under applicable rules and regulations under the Exchange Act, any person engaged in the distribution of the resale securities may not simultaneously engage in market making activities with respect to the common stock for the applicable restricted period, as defined in Regulation M, prior to the commencement of the distribution. In addition, the Selling Stockholders will be subject to applicable provisions of the Exchange Act and the rules and regulations thereunder, including Regulation M, which may limit the timing of purchases and sales of the common stock by the Selling Stockholders or any other person. We will make copies of this prospectus available to the Selling Stockholders and have informed them of the need to deliver a copy of this prospectus to each Subscriber at or prior to the time of the sale (including by compliance with Rule 172 under the Securities Act).
125
The audited financial statements of PureCycle Technologies LLC included in this prospectus and elsewhere in the registration statement have been so included in reliance upon the report of Grant Thornton LLP, independent registered public accountants, upon the authority of said firm as experts in accounting and auditing.
The financial statements of Roth CH Acquisition I Co. as of December 31, 2019 and for the period from February 13, 2019 (inception) through December 31, 2019 appearing in this prospectus have been audited by Marcum LLP, independent registered public accounting firm, as set forth in their report, thereon (which contains an explanatory paragraph relating to substantial doubt about the ability of Roth CH Acquisition I Co. to continue as a going concern as described in Note 1 to the financial statements), appearing elsewhere in this prospectus, and are included in reliance on such report given on the authority of such firm as an experts in auditing and accounting.
Loeb & Loeb LLP, New York, New York, will pass upon the validity of the securities offered hereby.
Where You Can Find More Information
We have filed with the SEC a registration statement on Form S-1 under the Securities Act with respect to the shares of our common stock offered by this prospectus. This prospectus, which constitutes a part of the registration statement, does not contain all of the information set forth in the registration statement, some of which is contained in exhibits to the registration statement as permitted by the rules and regulations of the SEC. For further information with respect to us and our common stock, we refer you to the registration statement, including the exhibits filed as a part of the registration statement. Statements contained in this prospectus concerning the contents of any contract or any other document is not necessarily complete. If a contract or document has been filed as an exhibit to the registration statement, please see the copy of the contract or document that has been filed. Each statement is this prospectus relating to a contract or document filed as an exhibit is qualified in all respects by the filed exhibit. The SEC maintains an Internet website that contains reports, proxy statements and other information about issuers, like us, that file electronically with the SEC. The address of that website is www.sec.gov.
126
ROTH CH ACQUISITION I CO. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:
Condensed Financial Statements as of September 30, 2020 and for the periods ended September 30,2020 and 2019
Unaudited Interim Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements as of September 30, 2020 and for the periods ended September 30, 2020 and 2019
Audited Consolidated Financial Statements as of and for the periods ended December 31, 2019 and 2018
F-1
ROTH CH ACQUISITION I CO.
| September
30, 2020 | December
31, 2019 | |||||||
| (Unaudited) | (Audited) | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Current asset | ||||||||
| Cash | $ | 408,543 | $ | 194,970 | ||||
| Prepaid expenses | 146,896 | — | ||||||
| Total Current Assets | 555,439 | 194,970 | ||||||
| Deferred offering costs | — | 85,938 | ||||||
| Deferred tax asset | 196 | — | ||||||
| Marketable securities held in Trust Account | 76,522,615 | — | ||||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 77,078,250 | $ | 280,908 | ||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| Current liabilities | ||||||||
| Accounts payable and Accrued expenses | $ | 124,689 | $ | 1,564 | ||||
| Accrued offering costs | — | 55,938 | ||||||
| Promissory note — Related party | — | 200,000 | ||||||
| Total Current Liabilities | 124,689 | 257,502 | ||||||
| Deferred underwriting fee payable | 2,677,500 | — | ||||||
| Total Liabilities | 2,802,189 | 257,502 | ||||||
| Commitments | ||||||||
| Common stock subject to possible redemption, 6,927,606 shares at redemption value at September 30, 2020 | 69,276,060 | — | ||||||
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||||||||
| Common stock, $0.0001 par value; 50,000,000 shares authorized; 2,900,394 and 2,156,250 shares issued and outstanding (excluding 6,927,606 and no shares subject to possible redemption) as of September 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019(1) | 290 | 216 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 5,225,337 | 24,784 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (225,626 | ) | (1,594 | ) | ||||
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | 5,000,001 | 23,406 | ||||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | $ | 77,078,250 | $ | 280,908 | ||||
(1) Included an aggregate of up to 281,250 shares subject to forfeiture if the over-allotment option was not exercised in full or in part by the underwriters (see Note 5).
F-2
ROTH CH ACQUISITION I CO.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS (Unaudited)
| Nine
Months Ended September 30, 2020 | For
the Period from February 13, 2019 (Inception) Through September 30, 2019 | |||||||
| Formation and operating costs | $ | 246,843 | $ | 1,000 | ||||
| Loss from operations | (246,843 | ) | (1,000 | ) | ||||
| Other income: | ||||||||
| Interest income | 23,547 | |||||||
| Unrealized loss on marketable securities held in Trust Account | (932 | ) | — | |||||
| Other income, net | 22,615 | — | ||||||
| Loss before provision for income taxes | (224,228 | ) | — | |||||
| Benefit from income taxes | 196 | — | ||||||
| Net Loss | $ | (224,032 | ) | $ | (1,000 | ) | ||
| Weighted average shares outstanding, basic and diluted(1) | 2,409,765 | 1,875,000 | ||||||
| Basic and diluted net loss per common share(2) | $ | (0.09 | ) | $ | (0.00 | ) | ||
(1) Excludes an aggregate of up to 6,927,606 shares subject to possible redemption at September 30, 2020 and an aggregate of 281,250 shares subject to forfeiture at September 30, 2019 (see Note 5).
(2) Net loss per common share — basic and diluted excludes income of $12,331 and $0 attributable to common stock subject to possible redemption for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2020, respectively.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the unaudited condensed financial statements.
F-3
ROTH CH ACQUISITION I CO.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (Unaudited)
NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2020
| Additional | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Common Stock(1) | Paid-in | Accumulated | Stockholders’ | |||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Capital | Deficit | Equity | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance – January 1, 2020 | 2,156,250 | $ | 216 | $ | 24,784 | $ | (1,594 | ) | $ | 23,406 | ||||||||||
| Net loss | — | — | — | (470 | ) | (470 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Balance – March 31, 2020 | 2,156,250 | 216 | 24,784 | (2,064 | ) | 22,936 | ||||||||||||||
| Sale of 7,650,000 Units, net of underwriting discounts | 7,650,000 | 765 | 71,820,922 | — | 71,821,687 | |||||||||||||||
| Sale of 265,500 Private Units | 265,500 | 26 | 2,654,974 | — | 2,655,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Forfeiture of Founder Shares | (243,750 | ) | (24 | ) | 24 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Common stock subject to possible redemption | (6,939,626 | ) | (694 | ) | (69,395,566 | ) | — | (69,396,260 | ) | |||||||||||
| Net loss | — | — | — | (103,353 | ) | (103,353 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Balance – June 30, 2020 | 2,888,374 | 289 | 5,105,138 | (105,417 | ) | 5,000,010 | ||||||||||||||
| Common stock subject to possible redemption | 12,020 | 1 | 120,199 | — | 120,200 | |||||||||||||||
| Net loss | — | — | — | (120,209 | ) | (120,209 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Balance – September 30, 2020 | 2,900,394 | $ | 290 | $ | 5,225,337 | $ | (225,626 | ) | $ | 5,000,001 | ||||||||||
FOR THE PERIOD FROM FEBRUARY 13, 2019 (INCEPTION) THROUGH SEPTEMBER 30, 2019
| Additional | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Common Stock(1) | Paid-in | Accumulated | Stockholders’ | |||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Capital | Deficit | Equity | ||||||||||||||||
Balance – February 13, 2019 (inception) | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock to Initial Stockholders(1) | 2,156,250 | 216 | 24,784 | — | 25,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Net loss | — | — | — | (1,000 | ) | (1,000 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Balance – March 31, 2019 | 2,156,250 | 216 | 24,784 | (1,000 | ) | 24,000 | ||||||||||||||
| Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Balance – June 30, 2019 | 2,156,250 | 216 | 24,784 | (1,000 | ) | 24,000 | ||||||||||||||
| Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Balance – September 30, 2019 | 2,156,250 | $ | 216 | $ | 24,784 | $ | (1,000 | ) | $ | 24,000 | ||||||||||
(1) Included an aggregate of up to 281,250 shares subject to forfeiture if the over-allotment option was not exercised in full or in part by the underwriters (see Note 5).
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the unaudited condensed financial statements.
F-4
ROTH CH ACQUISITION I CO.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS (Unaudited)
| Nine
Months Ended September 30, 2020 | For
the Period from February 13, 2019 (Inception) Through September 30, 2019 | |||||||
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities: | ||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (224,032 | ) | $ | (1,000 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | ||||||||
| Interest earned on marketable securities held in Trust Account | (23,547 | ) | — | |||||
| Unrealized loss on marketable securities held in Trust Account | 932 | — | ||||||
| Deferred income tax benefit | (196 | ) | — | |||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||||
| Prepaid expenses | (146,896 | ) | — | |||||
| Accounts payable and Accrued expenses | 123,125 | 1,000 | ||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | (270,614 | ) | — | |||||
| Cash Flows from Investing Activities: | ||||||||
| Investment of cash in Trust Account | (76,500,000 | ) | — | |||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | (76,500,000 | ) | — | |||||
| Cash Flows from Financing Activities: | ||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock to Initial Stockholders | — | 25,000 | ||||||
| Proceeds from sale of Units, net of underwriting discounts paid | 74,970,000 | — | ||||||
| Proceeds from sale of Private Units | 2,655,000 | — | ||||||
| Repayment of promissory note – related party | (200,000 | ) | — | |||||
| Payments of offering costs | (440,813 | ) | — | |||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 76,984,187 | 25,000 | ||||||
| Net Change in Cash | 213,573 | 25,000 | ||||||
| Cash – Beginning | 194,970 | — | ||||||
| Cash – Ending | $ | 408,543 | $ | 25,000 | ||||
| Non-cash investing and financing activities: | ||||||||
| Initial classification of common stock subject to possible redemption | $ | 68,052,060 | $ | — | ||||
| Change in value of common stock subject to possible redemption | $ | 1,224,000 | $ | — | ||||
| Deferred underwriting fee payable | $ | 2,677,500 | $ | — | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the unaudited condensed financial statements.
F-5
ROTH CH ACQUISITION I CO.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS SEPTEMBER 30, 2020
(Unaudited)
NOTE 1. DESCRIPTION OF ORGANIZATION AND BUSINESS OPERATIONS
Roth CH Acquisition I Co. (the “Company”) was incorporated in Delaware on February 13, 2019. The Company is a blank check company formed for the purpose of entering into a merger, share exchange, asset acquisition, stock purchase, recapitalization, reorganization or other similar business combination with one or more businesses or entities (the “Business Combination”).
The Company is an early stage and emerging growth company and, as such, the Company is subject to all of the risks associated with early stage and emerging growth companies.
As of September 30, 2020, the Company had not commenced any operations. All activity for the period from February 13, 2019 (inception) through September 30, 2020 relates to the Company’s formation, the initial public offering (“Initial Public Offering”), which is described below, and activities in connection with the potential acquisition of PureCycle Technologies LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (“PCT”) (see Note 8). The Company will not generate any operating revenues until after the completion of a Business Combination, at the earliest. The Company will generate non-operating income in the form of interest income from the proceeds derived from the Initial Public Offering.
The registration statement for the Company’s Initial Public Offering was declared effective on May 4, 2020. On May 7, 2020, the Company consummated the Initial Public Offering of 7,500,000 units (the “Units” and, with respect to the shares of common stock included in the Units sold, the “Public Shares”), at $10.00 per Unit, generating gross proceeds of $75,000,000, which is described in Note 3.
Simultaneously with the closing of the Initial Public Offering, the Company consummated the sale of 262,500 units (the “Private Units”) at a price of $10.00 per Private Unit in a private placement to our initial stockholders, generating gross proceeds of $2,625,000, which is described in Note 4.
Following the closing of the Initial Public Offering on May 7, 2020, an amount of $75,000,000 ($10.00 per Unit) from the net proceeds of the sale of the Units in the Initial Public Offering and the sale of the Private Units was placed in a trust account (“Trust Account”) which will be invested only in U.S. government securities, within the meaning set forth in Section 2(a)(16) of the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended (the “Investment Company Act”), with a maturity of 180 days or less or in any open- ended investment company that holds itself out as a money market fund selected by the Company meeting the conditions of Rule 2a-7 of the Investment Company Act, as determined by the Company, until the earlier of: (i) the completion of a Business Combination and (ii) the distribution of the Trust Account, as described below.
On May 26, 2020, in connection with the underwriters’ election to partially exercise their over- allotment option, the Company sold an additional 150,000 Units at a purchase price of $10.00 per Unit, generating gross proceeds of $1,500,000. In addition, in connection with the underwriters’ partial exercise of their over-allotment option, the Company also consummated the sale of an additional 3,000 Private Units at a purchase price of $10.00 per Private Unit, generating gross proceeds of $30,000. Following such closing, an additional $1,500,000 was deposited into the Trust Account, resulting in $76,500,000 being held in the Trust Account.
Transaction costs amounted to $4,678,313, consisting of $1,530,000 of underwriting fees, $2,677,500 of deferred underwriting fees and $470,813 of other offering costs. In addition, as of September 30, 2020, cash of $408,543 was held outside of the Trust Account (as defined below) and is available for working capital purposes.
The Company’s management has broad discretion with respect to the specific application of the net proceeds of the Initial Public Offering and the sale of the Private Units, although substantially all of the net proceeds are intended to be applied generally toward consummating a Business Combination. There is no assurance that the Company will be able to complete a Business Combination successfully. The Company must complete a Business Combination having an aggregate fair market value of at least 80% of the assets held in the Trust Account (excluding the deferred underwriting commissions and taxes payable on income earned on the Trust Account) at the time of the agreement to enter into an initial Business Combination. The Company will only complete a Business Combination if the post-transaction company owns or acquires 50% or more of the outstanding voting securities of the target or otherwise acquires a controlling interest in the target sufficient for it not to be required to register as an investment company under the Investment Company Act.
F-6
The Company will provide its holders of the outstanding Public Shares (the “public stockholders”) with the opportunity to redeem all or a portion of their Public Shares upon the completion of a Business Combination either (i) in connection with a stockholder meeting called to approve the Business Combination or (ii) by means of a tender offer. The decision as to whether the Company will seek stockholder approval of a Business Combination or conduct a tender offer will be made by the Company, solely in its discretion. The public stockholders will be entitled to redeem their Public Shares for a pro rata portion of the amount then in the Trust Account ($10.00 per Public Share, plus any pro rata interest earned on the funds held in the Trust Account and not previously released to the Company to pay its tax obligations). There will be no redemption rights upon the completion of a Business Combination with respect to the Company’s warrants.
The Company will proceed with a Business Combination if the Company has net tangible assets of at least $5,000,001 immediately prior to or upon such consummation of a Business Combination and, if the Company seeks stockholder approval, a majority of the shares voted are voted in favor of the Business Combination. If a stockholder vote is not required by law and the Company does not decide to hold a stockholder vote for business or other legal reasons, the Company will, pursuant to its Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation (the “Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation”), conduct the redemptions pursuant to the tender offer rules of the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) and file tender offer documents with the SEC containing substantially the same information as would be included in a proxy statement prior to completing a Business Combination. If, however, stockholder approval of the transaction is required by law, or the Company decides to obtain stockholder approval for business or legal reasons, the Company will offer to redeem shares in conjunction with a proxy solicitation pursuant to the proxy rules and not pursuant to the tender offer rules. If the Company seeks stockholder approval in connection with a Business Combination, the holders of the Company’s shares prior to the Initial Public Offering (the “Initial Stockholders”) have agreed to vote their Founder Shares (as defined in Note 5), Private Shares (as defined in Note 4) and any Public Shares purchased during or after the Initial Public Offering (a) in favor of approving a Business Combination and (b) not to redeem any shares in connection with a stockholder vote to approve a Business Combination or sell any shares to the Company in a tender offer in connection with a Business Combination. Additionally, each public stockholder may elect to redeem their Public Shares irrespective of whether they vote for or against the Initial transaction or don’t vote at all.
The Initial Stockholders have agreed (a) to waive their redemption rights with respect to their Founder Shares, Private Shares and Public Shares held by them in connection with the completion of a Business Combination and (b) not to propose an amendment to the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation that would affect a public stockholders’ ability to convert or sell their shares to the Company in connection with a Business Combination or affect the substance or timing of the Company’s obligation to redeem 100% of its Public Shares if the Company does not complete a Business Combination, unless the Company provides the public stockholders with the opportunity to redeem their Public Shares in conjunction with any such amendment.
The Company will have until November 7, 2021 to complete a Business Combination (the “Combination Period”). If the Company is unable to complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period, the Company will (i) cease all operations except for the purpose of winding up, (ii) as promptly as reasonably possible but not more than five business days thereafter, redeem the Public Shares, at a per-share price, payable in cash, equal to the aggregate amount then on deposit in the Trust Account including interest earned on the funds held in the Trust Account and not previously released to the Company to pay taxes, divided by the number of then outstanding Public Shares, which redemption will completely extinguish public stockholders’ rights as stockholders (including the right to receive further liquidating distributions, if any), subject to applicable law, and (iii) as promptly as reasonably possible following such redemption, subject to the approval of the Company’s remaining stockholders and the Company’s board of directors, dissolve and liquidate, subject in each case to the Company’s obligations under Delaware law to provide for claims of creditors and the requirements of other applicable law.
F-7
The Initial Stockholders have agreed to waive their liquidation rights with respect to the Founder Shares and Private Shares if the Company fails to complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period. However, if the Initial Stockholders acquire Public Shares in or after the Initial Public Offering, such Public Shares will be entitled to liquidating distributions from the Trust Account if the Company fails to complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period. The underwriters have agreed to waive their rights to their deferred underwriting commission (see Note 6) held in the Trust Account in the event the Company does not complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period and, in such event, such amounts will be included with the other funds held in the Trust Account that will be available to fund the redemption of the Public Shares. In the event of such distribution, it is possible that the per share value of the assets remaining available for distribution will be less than the Initial Public Offering price per Unit ($10.00).
In order to protect the amounts held in the Trust Account, the Initial Stockholders have agreed to be liable to the Company if and to the extent any claims by a vendor for services rendered or products sold to the Company, or a prospective target business with which the Company has discussed entering into a transaction agreement, reduce the amount of funds in the Trust Account to below $10.00 per Public Share, except as to any claims by a third party who executed a valid and enforceable agreement with the Company waiving any right, title, interest or claim of any kind they may have in or to any monies held in the Trust Account and except as to any claims under the Company’s indemnity of the underwriters of Initial Public Offering against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”). Moreover, in the event that an executed waiver is deemed to be unenforceable against a third party, the Initial Stockholders will not be responsible to the extent of any liability for such third-party claims. The Company will seek to reduce the possibility that Initial Stockholders will have to indemnify the Trust Account due to claims of creditors by endeavoring to have all vendors, service providers, prospective target businesses or other entities with which the Company does business, execute agreements with the Company waiving any right, title, interest or claim of any kind in or to monies held in the Trust Account.
Liquidity
As of September 30, 2020, the Company had $408,543 in its operating bank accounts, $76,522,615 in marketable securities held in the Trust Account to be used for a Business Combination or to repurchase or redeem stock in connection therewith and working capital of $496,250, which excludes franchise taxes payable of $65,500, of which such amount will be paid from interest earned on the Trust Account. As of September 30, 2020, approximately $23,000 of the amount on deposit in the Trust Account represented interest income, which is available to pay the Company’s tax obligations.
On November 2, 2020, the Sponsor committed to provide the Company an aggregate of $100,000 in loans in order to finance transaction costs in connection with a Business Combination.
The Company may raise additional capital through loans or additional investments from the Sponsor or its stockholders, officers, directors, or third parties. The Company’s officers and directors and the Sponsor may, but are not obligated to (except as described above), loan the Company funds, from time to time, in whatever amount they deem reasonable in their sole discretion, to meet the Company’s working capital needs. Based on the foregoing, the Company believes it will have sufficient cash to meet its needs through the earlier of consummation of a Business Combination or November 7, 2021, the deadline to complete a Business Combination pursuant to the Company’s Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation (unless otherwise amended by stockholders).
Risks and Uncertainties
In March 2020, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak of a novel coronavirus (COVID-19) as a pandemic which continues to spread throughout the United States and the World. As of the date the financial statements were available to be issued, there was considerable uncertainty around the expected duration of this pandemic. We have concluded that while it is reasonably possible that COVID-19 could have a negative effect on identifying a target company for a Business Combination, the specific impact is not readily determinable as of the date of these financial statements. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
F-8
NOTE 2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES Basis of Presentation
The accompanying unaudited condensed financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) for interim financial information and in accordance with the instructions to Form 10-Q and Article 8 of Regulation S-X of the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). Certain information or footnote disclosures normally included in financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP have been condensed or omitted, pursuant to the rules and regulations of the SEC for interim financial reporting. Accordingly, they do not include all the information and footnotes necessary for a complete presentation of financial position, results of operations, or cash flows. In the opinion of management, the accompanying unaudited condensed financial statements include all adjustments, consisting of a normal recurring nature, which are necessary for a fair presentation of the financial position, operating results and cash flows for the periods presented.
The accompanying unaudited condensed financial statements should be read in conjunction with the Company’s prospectus for its Initial Public Offering as filed with the SEC on May 6, 2020, as well as the Company’s Current Reports on Form 8-K, as filed with the SEC on May 7, 2020 and May 13, 2020. The interim results for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for the year ending December 31, 2020 or for any future periods.
Emerging Growth Company
The Company is an “emerging growth company,” as defined in Section 2(a) of the Securities Act, as modified by the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (the “JOBS Act”), and it may take advantage of certain exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies including, but not limited to, not being required to comply with the independent registered public accounting firm attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes- Oxley Act, reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in its periodic reports and proxy statements, and exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved.
Further, Section 102(b)(1) of the JOBS Act exempts emerging growth companies from being required to comply with new or revised financial accounting standards until private companies (that is, those that have not had a Securities Act registration statement declared effective or do not have a class of securities registered under the Exchange Act) are required to comply with the new or revised financial accounting standards. The JOBS Act provides that a company can elect to opt out of the extended transition period and comply with the requirements that apply to non-emerging growth companies but any such election to opt out is irrevocable. The Company has elected not to opt out of such extended transition period which means that when a standard is issued or revised and it has different application dates for public or private companies, the Company, as an emerging growth company, can adopt the new or revised standard at the time private companies adopt the new or revised standard. This may make comparison of the Company’s financial statement with another public company which is neither an emerging growth company nor an emerging growth company which has opted out of using the extended transition period difficult or impossible because of the potential differences in accounting standards used.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of condensed financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires the Company’s management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods. Making estimates requires management to exercise significant judgment. It is at least reasonably possible that the estimate of the effect of a condition, situation or set of circumstances that existed at the date of the financial statements, which management considered in formulating its estimate, could change in the near term due to one or more future confirming events. Accordingly, the actual results could differ significantly from those estimates.
F-9
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all short-term investments with an original maturity of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents. The Company did not have any cash equivalents as of September 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019.
Marketable Securities Held in Trust Account
At September 30, 2020, substantially all of the assets held in the Trust Account were held in money market funds, which primarily invest in U.S. Treasury Bills. During the nine months ended September 30, 2020, the Company did not withdraw any of the interest earned on the Trust Account.
Common Stock Subject to Possible Redemption
The Company accounts for its common stock subject to possible redemption in accordance with the guidance in Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 480 “Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity.” Common stock subject to mandatory redemption is classified as a liability instrument and is measured at fair value. Conditionally redeemable common stock (including common stock that features redemption rights that is either within the control of the holder or subject to redemption upon the occurrence of uncertain events not solely within the Company’s control) is classified as temporary equity. At all other times, common stock is classified as stockholders’ equity. The Company’s common stock features certain redemption rights that are considered to be outside of the Company’s control and subject to occurrence of uncertain future events. Accordingly, common stock subject to possible redemption is presented at redemption value as temporary equity, outside of the stockholders’ equity section of the Company’s condensed balance sheets.
Income Taxes
The Company follows the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes under ASC 740, “Income Taxes.” Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the estimated future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statements carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that included the enactment date. Valuation allowances are established, when necessary, to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized.
ASC 740 prescribes a recognition threshold and a measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. For those benefits to be recognized, a tax position must be more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by taxing authorities. The Company recognizes accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits as income tax expense. There were no unrecognized tax benefits and no amounts accrued for interest and penalties as of September 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019. The Company is currently not aware of any issues under review that could result in significant payments, accruals or material deviation from its position. The Company is subject to income tax examinations by major taxing authorities since inception. The effective tax rate of 0% differs from the statutory tax rate of 21% for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2020 due to the valuation allowance recorded against the Company’s net operating losses.
On March 27, 2020, President Trump signed the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security “CARES” Act into law. The CARES Act includes several significant business tax provisions that, among other things, would eliminate the taxable income limit for certain net operating losses (“NOL) and allow businesses to carry back NOLs arising in 2018, 2019 and 2020 to the five prior years, suspend the excess business loss rules, accelerate refunds of previously generated corporate alternative minimum tax credits, generally loosen the business interest limitation under IRC section 163(j) from 30 percent to 50 percent among other technical corrections included in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act tax provisions.
F-10
Net Loss Per Common Share
Net loss per share is computed by dividing net loss by the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period, excluding shares of common stock subject to forfeiture. At September 30, 2019, weighted average shares were reduced for the effect of an aggregate of 281,250 shares of common stock that were subject to forfeiture if the over-allotment option was not exercised by the underwriters (see Note 7). The Company applies the two-class method in calculating earnings per share. Shares of common stock subject to possible redemption at September 30, 2020, which are not currently redeemable and are not redeemable at fair value, have been excluded from the calculation of basic loss per share since such shares, if redeemed, only participate in their pro rata share of the Trust Account earnings. The Company has not considered the effect of warrants to purchase 5,936,265 shares of common stock that were sold in the Initial Public Offering and the private placement in the calculation of diluted loss per share, since the exercise of the warrants is contingent upon the occurrence of future events. As a result, diluted loss per share is the same as basic loss per share for the period presented.
Reconciliation of Net Loss Per Common Share
The Company’s net loss is adjusted for the portion of income that is attributable to common stock subject to possible redemption, as these shares only participate in the earnings of the Trust Account and not the income and losses of the Company. There were no such adjustments for the three months ended September 30, 2019 and for the period from February 13, 2019 (inception) through September 30, 2019. Accordingly, basic and diluted loss per common share is calculated as follows:
| Nine
Months Ended September 30, 2020 | ||||
| Net loss | $ | (224,032 | ) | |
| Less: Income attributable to shares subject to possible redemption | — | |||
| Adjusted net loss | $ | (224,032 | ) | |
| Weighted average shares outstanding, basic and diluted | 2,409,765 | |||
| Basic and diluted net loss per share | $ | (0.09 | ) | |
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist of a cash account in a financial institution, which, at times, may exceed the Federal Depository Insurance Coverage of $250,000. The Company has not experienced losses on this account and management believes the Company is not exposed to significant risks on such account.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The fair value of the Company’s assets and liabilities, which qualify as financial instruments under ASC 820, “Fair Value Measurement,” approximates the carrying amounts represented in the accompanying condensed balance sheets, primarily due to their short-term nature.
Recent Accounting Standards
Management does not believe that any recently issued, but not yet effective, accounting standards, if currently adopted, would have a material effect on the Company’s condensed financial statements.
NOTE 3. PUBLIC OFFERING
Pursuant to the Initial Public Offering, the Company sold 7,650,000 Units, at a price of $10.00 per Unit, inclusive of 150,000 Units sold to the underwriters on May 26, 2020 upon the underwriters’ election to partially exercise their over-allotment option. Each Unit consists of one share of common stock and three- quarters of one redeemable warrant (“Public Warrant”).
F-11
NOTE 4. PRIVATE PLACEMENT
Simultaneously with the closing of the Initial Public Offering, the Initial Stockholders purchased an aggregate of 262,500 Private Units, at a price of $10.00 per Private Unit, for an aggregate purchase price of $2,625,000. On May 26, 2020, in connection with the underwriters’ election to partially exercise their over- allotment option, the Company sold an additional 3,000 Private Units to the Initial Stockholders, generating gross proceeds of $30,000. Each Private Unit consists of one share of common stock (“Private Share”) and three-quarters of one redeemable warrant (“Private Warrant”). Each whole Private Warrant entitles the holder to purchase one share of common stock at a price of $11.50 per full share (every four units entitles the holder thereof to receive three whole warrants), subject to adjustment (see Note 7). The proceeds from the Private Units were added to the proceeds from the Initial Public Offering held in the Trust Account. If the Company does not complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period, the proceeds from the sale of the Private Units will be used to fund the redemption of the Public Shares (subject to the requirements of applicable law).
NOTE 5. RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Founder Shares
In April 2019, the Initial Stockholders purchased an aggregate of 100 shares of the Company’s common stock for an aggregate price of $25,000. On November 12, 2019, the Company effected a 1 for 21,562.50 dividend in the nature of a stock split that resulted in there being an aggregate of 2,156,250 shares of common stock outstanding and being held by the Initial Stockholders (the “Founder Shares”). All share and per-share amounts have been retroactively restated to reflect the stock dividend. The 2,156,250 Founder Shares included an aggregate of up to 281,250 shares subject to forfeiture by the Initial Stockholders to the extent that the underwriters’ over-allotment was not exercised in full or in part, so that the Initial Stockholders would collectively own 20% of the Company’s issued and outstanding shares after the Initial Public Offering (assuming the Initial Stockholders did not purchase any Public Shares in the Initial Public Offering and excluding the Private Shares). As a result of the underwriters’ election to partially exercise their over-allotment option and forfeit the balance of their option, 243,750 Founder Shares were forfeited and 37,500 Founder Shares are no longer subject to forfeiture. As a result, as of May 26, 2020, there are 1,912,500 Founder Shares issued and outstanding.
The Initial Stockholders have agreed, subject to certain limited exceptions, not to transfer, assign or sell any of the Founder Shares until (1) with respect to 50% of the Founder Shares, the earlier of six months after the completion of a Business Combination and the date on which the closing price of the common stock equals or exceeds $12.50 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, reorganizations, recapitalizations and the like) for any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period commencing after a Business Combination and (2) with respect to the remaining 50% of the Founder Shares, six months after the completion of a Business Combination, or earlier, in either case, if, subsequent to a Business Combination, the Company completes a liquidation, merger, stock exchange or other similar transaction which results in all of the Company’s stockholders having the right to exchange their shares of common stock for cash, securities or other property.
Promissory Note — Related Party
On October 4, 2019, the Company issued an unsecured promissory note to the sponsor (the “Promissory Note”), pursuant to which the Company could borrow up to an aggregate principal amount of $200,000. As of December 31, 2019, there was $200,000 outstanding under the Promissory Note. The Promissory Note was non-interest bearing and payable on the earlier of (i) the consummation of the Initial Public Offering or (ii) the date on which the Company determines not to proceed with the Initial Public Offering. Borrowings outstanding under the Promissory Note of $200,000 were repaid upon the consummation of the Initial Public Offering on May 7, 2020.
F-12
Related Party Loans
In addition, in order to finance transaction costs in connection with a Business Combination, the Initial Stockholders, or certain of the Company’s officers and directors or their affiliates may, but are not obligated to, loan the Company funds as may be required (“Working Capital Loans”). If the Company completes a Business Combination, the Company would repay the Working Capital Loans out of the proceeds of the Trust Account released to the Company. Otherwise, the Working Capital Loans would be repaid only out of funds held outside the Trust Account. In the event that a Business Combination does not close, the Company may use a portion of proceeds held outside the Trust Account to repay the Working Capital Loans, but no proceeds held in the Trust Account would be used to repay the Working Capital Loans. Except for the foregoing, the terms of such Working Capital Loans, if any, have not been determined and no written agreements exist with respect to such loans. The Working Capital Loans would be repaid upon consummation of a Business Combination, without interest.
NOTE 6. COMMITMENTS
Registration Rights
Pursuant to a registration rights agreement entered into on May 4, 2020, the holders of the Founder Shares, as well as the holders of the Private Units (and underlying securities) and any securities issued to the Initial Stockholders, officers, directors or their affiliates in payment of Working Capital Loans made to Company are entitled to registration rights. The holders of a majority of these securities are entitled to make up to two demands that the Company register such securities. The holders of the majority of the Founder Shares can elect to exercise these registration rights at any time commencing three months prior to the date on which these shares of common stock are to be released from escrow. The holders of a majority of the Private Units (and underlying securities) and securities issued in payment of Working Capital Loans (or underlying securities) can elect to exercise these registration rights at any time after the Company consummates a business combination. In addition, the holders have certain “piggy-back” registration rights with respect to registration statements filed subsequent to the consummation of a Business Combination. The Company will bear the expenses incurred in connection with the filing of any such registration statements.
Underwriting Agreement
The Company granted the underwriters a 45-day option from the date of Initial Public Offering to purchase up to 1,125,000 additional Units to cover over-allotments, if any, at the Initial Public Offering price less the underwriting discounts and commissions. On May 26, 2020, the underwriters elected to partially exercise their over-allotment option to purchase an additional 150,000 Units at a purchase price of $10.00
Unit.
The underwriters were paid a cash underwriting discount of 2.00% of the gross proceeds of the Initial Public Offering, or $1,530,000. In addition, the underwriters are entitled to a deferred fee of 3.50% of the gross proceeds of the Initial Offering, or $2,677,500. The deferred fee will be paid in cash upon the closing of a Business Combination from the amounts held in the Trust Account, subject to the terms of the underwriting agreement.
Investor Relations Agreement
On February 27, 2020, the Company entered into an investor relations agreement, pursuant to which, in exchange for investor relations services, the Company will pay the service provider a one-time fee of $10,000. Upon the closing of a Business Combination, the Company will pay the service provider a fee of $50,000 and following the Business Combination, the Company will pay a fee of $10,000 per month for a period of nine months. As of September 30, 2020, the Company has paid $10,000 of such fees.
NOTE 7. STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Common Stock — The Company is authorized to issue 50,000,000 shares of common stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share. At September 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019, there were 2,900,394 and 2,156,250 shares of common stock issued and outstanding, excluding 6,927,606 and no shares of common stock subject to possible redemption, respectively.
F-13
Warrants — The Company will not issue fractional warrants. The Public Warrants will become exercisable on the later of (a) the completion of a Business Combination or (b) 12 months from the closing of the Initial Public Offering. No warrants will be exercisable for cash unless the Company has an effective and current registration statement covering the shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of the warrants and a current prospectus relating to such shares of common stock. Notwithstanding the foregoing, if a registration statement covering the shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of the Public Warrants is not effective within 120 days following the consummation of a Business Combination, warrant holders may, until such time as there is an effective registration statement and during any period when the Company shall have failed to maintain an effective registration statement, exercise warrants on a cashless basis pursuant to the exemption provided by Section 3(a)(9) of the Securities Act, provided that such exemption is available. If that exemption, or another exemption, is not available, holders will not be able to exercise their warrants on a cashless basis. The Public Warrants will expire five years after the completion of a Business Combination or earlier upon redemption or liquidation.
Once the warrants become exercisable, the Company may redeem the Public Warrants:
| • | in whole and not in part; |
| • | at a price of $0.01 per warrant; |
| • | upon not less than 30 days’ prior written notice of redemption; |
| • | if, and only if, the reported last sale price of the shares of common stock equals or exceeds $18.00 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, reorganizations and recapitalizations), for any 20 trading days within a 30 trading day period ending on the third business day prior to the notice of redemption to warrant holders; and |
| • | if, and only if, there is a current registration statement in effect with respect to the shares of common stock underlying the warrants at the time of redemption and for the entire 30-day trading period referred to above and continuing each day thereafter until the date of redemption. |
If the Company calls the Public Warrants for redemption, management will have the option to require all holders that wish to exercise the Public Warrants to do so on a “cashless basis,” as described in the warrant agreement.
In addition, if (x) the Company issues additional shares of common stock or equity-linked securities for capital raising purposes in connection with the closing of a Business Combination at an issue price or effective issue price of less than $9.20 per share of common stock (with such issue price or effective issue price to be determined in good faith by the Company’s board of directors, and in the case of any such issuance to the Initial Stockholders or their affiliates, without taking into account any Founder Shares held by them prior to such issuance), (y) the aggregate gross proceeds from such issuances represent more than 60% of the total equity proceeds, and interest thereon, available for the funding of a Business Combination on the date of the consummation of a Business Combination (net of redemptions), and (z) the volume weighted average trading price of the Company’s common stock during the 20 trading day period starting on the trading day prior to the day on which the Company consummates Business Combination (such price, the “Market Value”) is below $9.20 per share, the exercise price of the warrants will be adjusted (to the nearest cent) to be equal to 115% of the Market Value and the $18.00 per share redemption trigger price described above will be adjusted (to the nearest cent) to be equal to 180% of the Market Price.
The exercise price and number of shares of common stock issuable on exercise of the warrants may be adjusted in certain circumstances including in the event of a stock dividend, extraordinary dividend or our recapitalization, reorganization, merger or consolidation. However, except as described previously, the warrants will not be adjusted for issuances of shares of common stock at a price below their respective exercise prices. Additionally, in no event will the Company be required to net cash settle the warrants. If the Company is unable to complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period and the Company liquidates the funds held in the Trust Account, holders of warrants will not receive any of such funds with respect to their warrants, nor will they receive any distribution from the Company’s assets held outside of the Trust Account with the respect to such warrants. Accordingly, the warrants may expire worthless.
F-14
The Private Warrants are identical to the Public Warrants underlying the Units sold in the Proposed Public Offering, except that the Private Warrants and the shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of the Private Warrants will not be transferable, assignable or saleable until after the completion of a Business Combination, subject to certain limited exceptions. Additionally, the Private Warrants will be exercisable for cash or on a cashless basis, at the holder’s option, and be non-redeemable so long as they are held by the initial purchasers or their permitted transferees. If the Private Warrants are held by someone other than the initial purchasers or their permitted transferees, the Private Warrants will be redeemable by the Company and exercisable by such holders on the same basis as the Public Warrants.
NOTE 8. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
The Company evaluated subsequent events and transactions that occurred after the balance sheet date up to the date that the financial statements were issued. Based upon this review, other than as described below, the Company did not identify any subsequent events that would have required adjustment or disclosure in the condensed financial statements.
On November 16, 2020, the Company, Roth CH Acquisition I Co. Parent Corp., a Delaware corporation (“ParentCo”), Roth CH Merger Sub LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (“Merger Sub LLC”), Roth CH Merger Sub Corp., a Delaware corporation (“Merger Sub Corp”) and PCT, entered into an agreement and plan of merger (the “Merger Agreement”) pursuant to which ParentCo will acquire PCT for consideration of a combination of shares in ParentCo and assumption of indebtedness. Consummation of the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement are subject to customary conditions of the respective parties, including the approval of the Merger Agreement, the Business Combination (as defined in the Merger Agreement) and certain other actions related thereto by the Company’s stockholders, certain regulatory approvals, and the availability of a minimum amount of cash in the Trust Account (and/or from other specified sources, if necessary), after giving effect to redemptions by the Company’s public stockholders, if any.
F-15
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of Roth CH Acquisition I Co.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying balance sheet of Roth CH Acquisition I Co. (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2019 and the related statements of operations, changes in stockholders’ equity and cash flows for the period from February 13, 2019 (inception) through December 31, 2019 and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the period from February 13, 2019 (inception) through December 31, 2019, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Explanatory Paragraph — Going Concern
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As more fully described in Note 1 to the financial statements, the Company’s business plan is dependent on the completion of a financing and the Company’s cash and working capital as of December 31, 2019 are not sufficient to complete its planned activities. These conditions raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans in regard to these matters are also described in Notes 1 and 3. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audit we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audit included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audit also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Marcum LLP
Marcum LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2019.
New York, NY
February 14, 2020
F-16
BALANCE
SHEET
DECEMBER 31, 2019
| ASSETS | ||||
| Current asset – Cash | $ | 194,970 | ||
| Deferred offering costs | 85,938 | |||
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 280,908 | ||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||
| Current liabilities | ||||
| Accrued expenses | $ | 1,564 | ||
| Accrued offering costs | 55,938 | |||
| Promissory note – Related party | 200,000 | |||
| Total Current Liabilities | 257,502 | |||
| Commitments | ||||
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||||
| Common stock, $0.0001 par value; 50,000,000 shares authorized; 2,156,250 shares issued and outstanding(1) | 216 | |||
| Additional paid-in capital | 24,784 | |||
| Accumulated deficit | (1,594 | ) | ||
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | 23,406 | |||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | $ | 280,908 |
(1) Includes up to 281,250 shares subject to forfeiture if the over-allotment option is not exercised in full or in part by the underwriters (see Note 5).
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
F-17
STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS
FOR THE PERIOD FROM FEBRUARY 13, 2019 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2019
| Formation and operating costs | $ | 1,594 | ||
| Net Loss | $ | (1,594 | ) | |
| Weighted average shares outstanding, basic and diluted(1) | 1,875,000 | |||
| Basic and diluted net loss per common share | $ | (0.00 | ) |
(1) Excludes an aggregate of up to 281,250 shares subject to forfeiture if the over-allotment option is not exercised in full or in part by the underwriters (see Note 5).
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
F-18
STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
FOR THE PERIOD FROM FEBRUARY 13, 2019 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2019
| Additional | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Common Stock | Paid in | Accumulated | Stockholders’ | |||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Capital | Deficit | Equity | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance – February 13, 2019 (inception) | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock to Initial Stockholders(1) | 2,156,250 | 216 | 24,784 | — | 25,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Net loss | — | — | — | (1,594 | ) | (1,594 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Balance – December 31, 2019 | 2,156,250 | $ | 216 | $ | 24,784 | $ | (1,594 | ) | $ | 23,406 | ||||||||||
(1) Includes 281,250 shares subject to forfeiture if the over-allotment option is not exercised in full or in part by the underwriters (see Note 5).
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
F-19
STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
FOR THE PERIOD FROM FEBRUARY 13, 2019 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2019
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities: | ||||
| Net loss | $ | (1,594 | ) | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | ||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||
| Accrued expenses | 1,564 | |||
| Net cash used in operating activities | (30 | ) | ||
| Cash Flows from Financing Activities: | ||||
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock to Initial Stockholders | 25,000 | |||
| Proceeds from promissory note – related party | 200,000 | |||
| Payment of offering costs | (30,000 | ) | ||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 195,000 | |||
| Net Change in Cash | 194,970 | |||
| Cash – Beginning | — | |||
| Cash – Ending | $ | 194,970 | ||
| Non-cash investing and financing activities: | ||||
| Deferred offering costs included in accrued offering costs | $ | 55,938 | ||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
F-20
Note 1 — Description of Organization and Business Operations
Roth CH Acquisition I Co. (the “Company”) was incorporated in Delaware on February 13, 2019. The Company is a blank check company formed for the purpose of entering into a merger, share exchange, asset acquisition, stock purchase, recapitalization, reorganization or other similar business combination with one or more businesses or entities (the “Business Combination”).
The Company is an early stage and emerging growth company and, as such, the Company is subject to all of the risks associated with early stage and emerging growth companies.
As of December 31, 2019, the Company had not commenced any operations. All activity for the period from February 13, 2019 (inception) through December 31, 2019 relates to the Company’s formation and the proposed initial public offering (“Proposed Public Offering”), which is described below. The Company will not generate any operating revenues until after the completion of a Business Combination, at the earliest. The Company will generate non-operating income in the form of interest income from the proceeds derived from the Proposed Public Offering. The Company has selected December 31 as its fiscal year end.
The Company’s ability to commence operations is contingent upon obtaining adequate financial resources through a Proposed Public Offering of 7,500,000 units (the “Units” and, with respect to the shares of common stock included in the Units being offered, the “Public Shares”) at $10.00 per Unit (or 8,625,000 units if the underwriters’ over-allotment option is exercised in full), which is discussed in Note 3, and the sale of 262,500 units (or 285,000 units if the underwriters’ over-allotment option is exercised in full) (the “Private Units”) at a price of $10.00 per Private Unit in a private placement to our stockholders prior to the offering that will close simultaneously with the Proposed Public Offering.
The Company’s management has broad discretion with respect to the specific application of the net proceeds of the Proposed Public Offering and the sale of the Private Units, although substantially all of the net proceeds are intended to be applied generally toward consummating a Business Combination. There is no assurance that the Company will be able to complete a Business Combination successfully. The Company must complete a Business Combination having an aggregate fair market value of at least 80% of the assets held in the Trust Account (as defined below) (excluding the deferred underwriting commissions and taxes payable on income earned on the Trust Account) at the time of the agreement to enter into an initial Business Combination. The Company will only complete a Business Combination if the post-transaction company owns or acquires 50% or more of the outstanding voting securities of the target or otherwise acquires a controlling interest in the target sufficient for it not to be required to register as an investment company under the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended (the “Investment Company Act”).
Upon the closing of the Proposed Public Offering, management has agreed that an amount equal to at least $10.00 per Unit sold in the Proposed Public Offering, including the proceeds from the sale of the Private Units, will be held in a trust account (“Trust Account”), located in the United States and invested only in U.S. government securities, within the meaning set forth in Section 2(a)(16) of the Investment Company Act, with a maturity of 180 days or less or in any open-ended investment company that holds itself out as a money market fund selected by the Company meeting the conditions of Rule 2a-7 of the Investment Company Act, as determined by the Company, until the earlier of: (i) the completion of a Business Combination, or (ii) the distribution of the Trust Account, as described below.
The Company will provide its holders of the outstanding Public Shares (the “public stockholders”) with the opportunity to redeem all or a portion of their Public Shares upon the completion of a Business Combination either (i) in connection with a stockholder meeting called to approve the Business Combination or (ii) by means of a tender offer. The decision as to whether the Company will seek stockholder approval of a Business Combination or conduct a tender offer will be made by the Company, solely in its discretion. The public stockholders will be entitled to redeem their Public Shares for a pro rata portion of the amount then in the Trust Account (initially anticipated to be $10.00 per Public Share, plus any pro rata interest earned on the funds held in the Trust Account and not previously released to the Company to pay its tax obligations). There will be no redemption rights upon the completion of a Business Combination with respect to the Company’s warrants. The Public Shares subject to redemption will be recorded at redemption value and classified as temporary equity upon the completion of the Proposed Offering in accordance with the Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 480 “Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity.”
F-21
The Company will proceed with a Business Combination if the Company has net tangible assets of at least $5,000,001 immediately prior to or upon such consummation of a Business Combination and, if the Company seeks stockholder approval, a majority of the shares voted are voted in favor of the Business Combination. If a stockholder vote is not required by law and the Company does not decide to hold a stockholder vote for business or other legal reasons, the Company will, pursuant to its Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation (the “Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation”), conduct the redemptions pursuant to the tender offer rules of the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) and file tender offer documents with the SEC containing substantially the same information as would be included in a proxy statement prior to completing a Business Combination. If, however, stockholder approval of the transaction is required by law, or the Company decides to obtain stockholder approval for business or legal reasons, the Company will offer to redeem shares in conjunction with a proxy solicitation pursuant to the proxy rules and not pursuant to the tender offer rules. If the Company seeks stockholder approval in connection with a Business Combination, the holders of the Company’s shares prior to the Proposed Public Offering (the “Initial Stockholders”) have agreed to vote their Founder Shares (as defined in Note 5), Private Shares (as defined in Note 4) and any Public Shares purchased during or after the Proposed Public Offering (a) in favor of approving a Business Combination and (b) not to redeem any shares in connection with a stockholder vote to approve a Business Combination or sell any shares to the Company in a tender offer in connection with a Business Combination. Additionally, each public stockholder may elect to redeem their Public Shares irrespective of whether they vote for or against the proposed transaction or don’t vote at all.
The Initial Stockholders have agreed (a) to waive their redemption rights with respect to their Founder Shares, Private Shares and Public Shares held by them in connection with the completion of a Business Combination and (b) not to propose an amendment to the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation that would affect a public stockholders’ ability to convert or sell their shares to the Company in connection with a Business Combination or affect the substance or timing of the Company’s obligation to redeem 100% of its Public Shares if the Company does not complete a Business Combination, unless the Company provides the public stockholders with the opportunity to redeem their Public Shares in conjunction with any such amendment.
The Company will have until 18 months from the closing of the Proposed Public Offering to complete a Business Combination (the “Combination Period”).
If the Company is unable to complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period, the Company will (i) cease all operations except for the purpose of winding up, (ii) as promptly as reasonably possible but not more than five business days thereafter, redeem the Public Shares, at a per-share price, payable in cash, equal to the aggregate amount then on deposit in the Trust Account including interest earned on the funds held in the Trust Account and not previously released to the Company to pay taxes, divided by the number of then outstanding Public Shares, which redemption will completely extinguish public stockholders’ rights as stockholders (including the right to receive further liquidating distributions, if any), subject to applicable law, and (iii) as promptly as reasonably possible following such redemption, subject to the approval of the Company’s remaining stockholders and the Company’s board of directors, dissolve and liquidate, subject in each case to the Company’s obligations under Delaware law to provide for claims of creditors and the requirements of other applicable law.
The Initial Stockholders have agreed to waive their liquidation rights with respect to the Founder Shares and Private Shares if the Company fails to complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period. However, if the Initial Stockholders acquire Public Shares in or after the Proposed Public Offering, such Public Shares will be entitled to liquidating distributions from the Trust Account if the Company fails to complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period. The underwriters have agreed to waive their rights to their deferred underwriting commission (see Note 6) held in the Trust Account in the event the Company does not complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period and, in such event, such amounts will be included with the other funds held in the Trust Account that will be available to fund the redemption of the Public Shares. In the event of such distribution, it is possible that the per share value of the assets remaining available for distribution will be less than the Proposed Public Offering price per Unit ($10.00).
F-22
In order to protect the amounts held in the Trust Account, the Initial Stockholders have agreed to be liable to the Company if and to the extent any claims by a vendor for services rendered or products sold to the Company, or a prospective target business with which the Company has discussed entering into a transaction agreement, reduce the amount of funds in the Trust Account to below $10.00 per Public Share, except as to any claims by a third party who executed a valid and enforceable agreement with the Company waiving any right, title, interest or claim of any kind they may have in or to any monies held in the Trust Account and except as to any claims under the Company’s indemnity of the underwriters of Proposed Public Offering against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”). Moreover, in the event that an executed waiver is deemed to be unenforceable against a third party, the Initial Stockholders will not be responsible to the extent of any liability for such third-party claims. The Company will seek to reduce the possibility that Initial Stockholders will have to indemnify the Trust Account due to claims of creditors by endeavoring to have all vendors, service providers, prospective target businesses or other entities with which the Company does business, execute agreements with the Company waiving any right, title, interest or claim of any kind in or to monies held in the Trust Account.
Going Concern Consideration
At December 31, 2019, the Company had cash of $194,970 and working capital deficit of $62,532. The Company has incurred and expects to continue to incur significant costs in pursuit of its financing and acquisition plans. These conditions raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern within one year after the date that the financial statements are issued. Management plans to address this uncertainty through a Proposed Public Offering as discussed in Note 3. There is no assurance that the Company’s plans to raise capital or to consummate a Business Combination will be successful within the Combination Period. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from
the outcome of this uncertainty.
Note 2 — Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements are presented in in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) and pursuant to the rules and regulations of the SEC.
Emerging Growth Company
The Company is an “emerging growth company,” as defined in Section 2(a) of the Securities Act, as modified by the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (the “JOBS Act”), and it may take advantage of certain exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies including, but not limited to, not being required to comply with the independent registered public accounting firm attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in its periodic reports and proxy statements, and exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved.
Further, Section 102(b)(1) of the JOBS Act exempts emerging growth companies from being required to comply with new or revised financial accounting standards until private companies (that is, those that have not had a Securities Act registration statement declared effective or do not have a class of securities registered under the Exchange Act) are required to comply with the new or revised financial accounting standards. The JOBS Act provides that a company can elect to opt out of the extended transition period and comply with the requirements that apply to non-emerging growth companies but any such election to opt out is irrevocable. The Company has elected not to opt out of such extended transition period which means that when a standard is issued or revised and it has different application dates for public or private companies, the Company, as an emerging growth company, can adopt the new or revised standard at the time private companies adopt the new or revised standard. This may make comparison of the Company’s financial statements with another public company which is neither an emerging growth company nor an emerging growth company which has opted out of using the extended transition period difficult or impossible because of the potential differences in accounting standards used.
F-23
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires the Company’s management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period.
Making estimates requires management to exercise significant judgment. It is at least reasonably possible that the estimate of the effect of a condition, situation or set of circumstances that existed at the date of the financial statements, which management considered in formulating its estimate, could change in the near term due to one or more future confirming events. Accordingly, the actual results could differ significantly from those estimates.
Cash and cash equivalents
The Company considers all short-term investments with an original maturity of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents. The Company did not have any cash equivalents as of December 31,
2019.
Deferred Offering Costs
Deferred offering costs consist of legal, accounting, underwriting fees and other costs incurred through the balance sheet date that are directly related to the Proposed Public Offering and that will be charged to stockholders’ equity upon the completion of the Proposed Public Offering. Should the Proposed Public Offering prove to be unsuccessful, these deferred costs, as well as additional expenses to be incurred, will be charged to operations.
Income Taxes
The Company follows the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes under ASC 740, “Income Taxes.” Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the estimated future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statements carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that included the enactment date. Valuation allowances are established, when necessary, to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized.
ASC 740 prescribes a recognition threshold and a measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. For those benefits to be recognized, a tax position must be more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by taxing authorities. The Company recognizes accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits as income tax expense. There were no unrecognized tax benefits and no amounts accrued for interest and penalties as of December 31, 2019. The Company is currently not aware of any issues under review that could result in significant payments, accruals or material deviation from its position. The Company is subject to income tax examinations by major taxing authorities since inception.
The provision for income taxes was deemed to be immaterial for the period from February 13, 2019 (inception) to December 31, 2019.
Net Loss Per Common Share
Net loss per share is computed by dividing net loss by the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period, excluding shares of common stock subject to forfeiture by the Initial Stockholders. Weighted average shares were reduced for the effect of an aggregate of 281,250 shares of common stock that are subject to forfeiture if the over-allotment option is not exercised by the underwriters (see Note 7). At December 31, 2019, the Company did not have any dilutive securities and other contracts that could, potentially, be exercised or converted into shares of common stock and then share in the earnings of the Company. As a result, diluted loss per share is the same as basic loss per share for the period presented.
F-24
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist of a cash account in a financial institution, which, at times, may exceed the Federal Depository Insurance Coverage of $250,000. At December 31, 2019, the Company has not experienced losses on this account and management believes the Company is not exposed to significant risks on such account.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The fair value of the Company’s assets and liabilities, which qualify as financial instruments under ASC 820, “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures,” approximates the carrying amounts represented in the accompanying balance sheet, primarily due to their short-term nature.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Management does not believe that any recently issued, but not yet effective, accounting pronouncements, if currently adopted, would have a material effect on the Company’s financial statements.
Note 3 — Public Offering
Pursuant to the Proposed Public Offering, the Company intends to offer for sale 7,500,000 Units (or 8,625,000 Units if the over-allotment option is exercised in full) at a price of $10.00 per Unit. Each Unit will consist of one share of common stock, and three-quarters of one redeemable warrant (“Public Warrant”).
Note 4 — Private Placement
Our stockholders prior to this offering will enter into an agreement to purchase an aggregate of 262,500 Private Units (or 285,000 Private Units if the over-allotment option is exercised in full) at a price of $10.00 per Private Unit, for an aggregate purchase price of $2,625,000, or $2,850,000 if the over-allotment option is exercised in full, in a private placement that will occur simultaneously with the closing of the Proposed Public Offering. Each Private Unit will consist of one share of common stock (“Private Share”) and three-quarters of one redeemable warrant (“Private Warrant”). Each whole Private Warrant will entitle the holder to purchase one share of common stock at a price of $11.50 per full share (every four units entitles the holder thereof to receive three whole warrants), subject to adjustment (see Note 7). The proceeds from the Private Units will be added to the proceeds from the Proposed Public Offering to be held in the Trust Account. If the Company does not complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period, the proceeds from the sale of the Private Units will be used to fund the redemption of the Public Shares (subject to the requirements of applicable law).
Note 5 — Related Party Transactions
Founder Shares
In April 2019, the Initial Stockholders purchased an aggregate of 100 shares of the Company’s common stock for an aggregate price of $25,000. On November 12, 2019, the Company effected a 1 for 21,562.50 dividend in the nature of a stock split that resulted in there being an aggregate of 2,156,250 shares of common stock outstanding and being held by the Initial Stockholders (the “Founder Shares”). All share and per-share amounts have been retroactively restated to reflect the stock dividend. The 2,156,250 Founder Shares include an aggregate of up to 281,250 shares subject to forfeiture by the Initial Stockholders to the extent that the underwriters’ over-allotment is not exercised in full or in part, so that the Initial Stockholders will collectively own 20% of the Company’s issued and outstanding shares after the Proposed Public Offering (assuming the Initial Stockholders do not purchase any Public Shares in the Proposed Public Offering and excluding the Private Shares).
F-25
The Initial Stockholders have agreed, subject to certain limited exceptions, not to transfer, assign or sell any of the Founder Shares until (1) with respect to 50% of the Founder Shares, the earlier of six months after the completion of a Business Combination and the date on which the closing price of the common stock equals or exceeds $12.50 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, reorganizations, recapitalizations and the like) for any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period commencing after a Business Combination and (2) with respect to the remaining 50% of the Founder Shares, six months after the completion of a Business Combination, or earlier, in either case, if, subsequent to a Business Combination, the Company completes a liquidation, merger, stock exchange or other similar transaction which results in all of the Company’s stockholders having the right to exchange their shares of common stock for cash, securities or other property.
Promissory Note — Related Party
On October 4, 2019, the Company issued an unsecured promissory note to the sponsor (the “Promissory Note”), pursuant to which the Company may borrow up to an aggregate principal amount of $200,000, of which $200,000 was outstanding under the Promissory Note as of December 31, 2019. The Promissory Note is non-interest bearing and payable on the earlier of (i) the consummation of the Proposed Public Offering or (ii) the date on which the Company determines not to proceed with the Proposed Public Offering.
Related Party Loans
In addition, in order to finance transaction costs in connection with a Business Combination, the Initial Stockholders, or certain of the Company’s officers and directors or their affiliates may, but are not obligated to, loan the Company funds as may be required (“Working Capital Loans”). If the Company completes a Business Combination, the Company would repay the Working Capital Loans out of the proceeds of the Trust Account released to the Company. Otherwise, the Working Capital Loans would be repaid only out of funds held outside the Trust Account. In the event that a Business Combination does not close, the Company may use a portion of proceeds held outside the Trust Account to repay the Working Capital Loans, but no proceeds held in the Trust Account would be used to repay the Working Capital Loans. Except for the foregoing, the terms of such Working Capital Loans, if any, have not been determined and no written agreements exist with respect to such loans. The Working Capital Loans would be repaid upon consummation of a Business Combination, without interest.
Note 6 — Commitments
Registration Rights
The holders of the Founder Shares, as well as the holders of the Private Units (and underlying securities) and any securities issued to the Initial Stockholders, officers, directors or their affiliates in payment of Working Capital Loans made to Company, will be entitled to registration rights pursuant to an agreement to be signed prior to or on the effective date of Proposed Public Offering. The holders of a majority of these securities are entitled to make up to two demands that the Company register such securities. The holders of the majority of the Founder Shares can elect to exercise these registration rights at any time commencing three months prior to the date on which these shares of common stock are to be released from escrow. The holders of a majority of the Private Units (and underlying securities) and securities issued in payment of Working Capital Loans (or underlying securities) can elect to exercise these registration rights at any time after the Company consummates a business combination. In addition, the holders have certain “piggy-back” registration rights with respect to registration statements filed subsequent to the consummation of a Business Combination. The Company will bear the expenses incurred in connection with the filing of any such registration statements.
Underwriting Agreement
The Company will grant the underwriters a 45-day option from the date of Proposed Public Offering to purchase up to 1,125,000 additional Units to cover over-allotments, if any, at the Proposed Public Offering price less the underwriting discounts and commissions.
F-26
The underwriters will be entitled to a cash underwriting discount of 2.00% of the gross proceeds of the Proposed Public Offering, or $1,500,000 (or up to $1,725,000 if the underwriters’ over-allotment is exercised in full). In addition, the underwriters will be entitled to a deferred fee of 3.50% of the gross proceeds of the Proposed Offering, or $2,625,000 (or up to $3,018,750 if the underwriters’ over-allotment is exercised in full). The deferred fee will be paid in cash upon the closing of a Business Combination from the amounts held in the Trust Account, subject to the terms of the underwriting agreement.
Note 7 — Stockholders’ Equity
Common Stock — As of December 31, 2019, the Company was authorized to issue 50,000,000 shares of common stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share. At December 31, 2019, there were 2,156,250 shares of common stock issued and outstanding, of which an aggregate of up to 281,250 shares are subject to forfeiture to the extent that the underwriters’ over-allotment option is not exercised in full or in part, so that the Initial Stockholders will collectively own 20% of the Company’s issued and outstanding common stock after the Proposed Public Offering (assuming the Initial Stockholders do not purchase any Public Shares in the Proposed Public Offering and excluding the Private Shares).
Warrants — The Company will not issue fractional warrants. The Public Warrants will become exercisable on the later of (a) the completion of a Business Combination or (b) 12 months from the closing of the Proposed Public Offering. No warrants will be exercisable for cash unless the Company has an effective and current registration statement covering the shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of the warrants and a current prospectus relating to such shares of common stock. Notwithstanding the foregoing, if a registration statement covering the shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of the Public Warrants is not effective within 120 days following the consummation of a Business Combination, warrant holders may, until such time as there is an effective registration statement and during any period when the Company shall have failed to maintain an effective registration statement, exercise warrants on a cashless basis pursuant to the exemption provided by Section 3(a)(9) of the Securities Act, provided that such exemption is available. If that exemption, or another exemption, is not available, holders will not be able to exercise their warrants on a cashless basis. The Public Warrants will expire five years after the completion of a Business Combination or earlier upon redemption or liquidation.
Once the warrants become exercisable, the Company may redeem the Public Warrants:
| • | in whole and not in part; |
| • | at a price of $0.01 per warrant; |
| • | upon not less than 30 days’ prior written notice of redemption; |
| • | if, and only if, the reported last sale price of the shares of common stock equals or exceeds $18.00 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, reorganizations and recapitalizations), for any 20 trading days within a 30 trading day period ending on the third business day prior to the notice of redemption to warrant holders; and |
| • | if, and only if, there is a current registration statement in effect with respect to the shares of common stock underlying the warrants at the time of redemption and for the entire 30-day trading period referred to above and continuing each day thereafter until the date of redemption. |
If the Company calls the Public Warrants for redemption, management will have the option to require all holders that wish to exercise the Public Warrants to do so on a “cashless basis,” as described in the warrant agreement.
In addition, if (x) the Company issues additional shares of common stock or equity-linked securities for capital raising purposes in connection with the closing of a Business Combination at an issue price or effective issue price of less than $9.20 per share of common stock (with such issue price or effective issue price to be determined in good faith by the Company’s board of directors, and in the case of any such issuance to the Initial Stockholders or their affiliates, without taking into account any Founder Shares held by them prior to such issuance), (y) the aggregate gross proceeds from such issuances represent more than 60% of the total equity proceeds, and interest thereon, available for the funding of a Business Combination on the date of the consummation of a Business Combination (net of redemptions), and (z) the volume weighted average trading price of the Company’s common stock during the 20 trading day period starting on the trading day prior to the day on which the Company consummates Business Combination (such price, the “Market Value”) is below $9.20 per share, the exercise price of the warrants will be adjusted (to the nearest cent) to be equal to 115% of the Market Value and the $18.00 per share redemption trigger price described above will be adjusted (to the nearest cent) to be equal to 180% of the Market Price.
F-27
The exercise price and number of shares of common stock issuable on exercise of the warrants may be adjusted in certain circumstances including in the event of a stock dividend, extraordinary dividend or our recapitalization, reorganization, merger or consolidation. However, the warrants will not be adjusted for issuances of shares of common stock at a price below their respective exercise prices. Additionally, in no event will the Company be required to net cash settle the warrants. If the Company is unable to complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period and the Company liquidates the funds held in the Trust Account, holders of warrants will not receive any of such funds with respect to their warrants, nor will they receive any distribution from the Company’s assets held outside of the Trust Account with the respect to such warrants. Accordingly, the warrants may expire worthless.
The Private Warrants will be identical to the Public Warrants underlying the Units being sold in the Proposed Public Offering, except that the Private Warrants and the shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of the Private Warrants will not be transferable, assignable or saleable until after the completion of a Business Combination, subject to certain limited exceptions. Additionally, the Private Warrants will be exercisable for cash or on a cashless basis, at the holder’s option, and be non-redeemable so long as they are held by the initial purchasers or their permitted transferees. If the Private Warrants are held by someone other than the initial purchasers or their permitted transferees, the Private Warrants will be redeemable by the Company and exercisable by such holders on the same basis as the Public Warrants.
Note 8 — Subsequent Events
The Company evaluated subsequent events and transactions that occurred after the balance sheet date up to February 14, 2020, the date that the financial statements were available to be issued. Based upon this review, the Company did not identify any subsequent events that would have required adjustment or disclosure in the financial statements.
F-28
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in United States dollars, except unit amounts)
| (Unaudited) | ||||||||
| September 30, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| CURRENT ASSETS | ||||||||
| Cash | $ | 107,544 | $ | 150,050 | ||||
| Prepaid royalties | 2,100,000 | 2,000,000 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 2,964,795 | 720,578 | ||||||
| Total current assets | 5,172,339 | 2,870,628 | ||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 32,781,523 | 30,410,094 | ||||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 37,953,862 | $ | 33,280,722 | ||||
| LIABILITIES AND MEMBERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| CURRENT LIABILITIES | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 1,864,957 | $ | 2,364,542 | ||||
| Accrued expenses | 2,772,275 | 1,222,692 | ||||||
| Notes payable – current | 4,276,999 | 3,601,246 | ||||||
| Related party notes payable – current | 12,000,000 | 3,303,694 | ||||||
| Total current liabilities | 20,914,231 | 10,492,174 | ||||||
| Deferred research and development obligation . | 1,000,000 | 1,000,000 | ||||||
| Notes payable | 1,021,915 | 1,000,000 | ||||||
| Related party notes payable | — | 12,000,000 | ||||||
| Redeemable warrants | 8,183,146 | 6,408,411 | ||||||
| Commitment and contingencies | ||||||||
| Total liabilities | 31,119,292 | 30,900,585 | ||||||
| MEMBERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| Class A Common units – $0.15 par value; 3,981,282 units authorized; 2,581,282 units issued and outstanding as of September 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019 | 387,192 | 387,192 | ||||||
| Class B Preferred units – $1 par value; 1,938,369 units authorized; 1,727,843 units issued and outstanding as of September 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019 | 1,898,469 | 1,898,469 | ||||||
| Class B-1 Preferred Units – $1 par value; 1,145,584 units authorized, 1,105,287 and 629,727 units issued and outstanding as of September 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019 | 41,162,202 | 23,655,518 | ||||||
| Class C Profits Units – no par value; 1,069,012 units authorized, 754,521 and 513,671 units issued and 656,290 and 435,679 units outstanding as of September 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019 | 6,589,975 | 4,053,833 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 107,178 | 107,178 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (43,310,446 | ) | (27,722,053 | ) | ||||
| Total members’ equity | 6,834,570 | 2,380,137 | ||||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND MEMBERS’ EQUITY | $ | 37,953,862 | $ | 33,280,722 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
F-29
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(Unaudited)
(in United States dollars, except unit amounts)
| Nine months ended September 30, | ||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
| Costs and expenses | ||||||||
| Operating costs | $ | 7,039,530 | $ | 4,901,335 | ||||
| Research and development | 528,142 | 508,951 | ||||||
| Selling, general and administrative | 6,293,437 | 10,082,306 | ||||||
| Total operating costs and expenses | 13,861,109 | 15,492,592 | ||||||
| Interest expense | 1,827,284 | 400,226 | ||||||
| Other (income) expense | (100,000 | ) | 329,944 | |||||
| Total other (income) expense | 1,727,284 | 730,170 | ||||||
| Net loss | (15,588,393 | ) | (16,222,762 | ) | ||||
| Accretion of cumulative earnings to preferred unitholders | 4,833,137 | 1,927,889 | ||||||
| Net loss attributable to common unitholders | $ | (20,421,530 | ) | $ | (18,150,651 | ) | ||
| Loss per unit | ||||||||
| Basic and diluted | $ | (7.91 | ) | $ | (7.03 | ) | ||
| Weighted average common units | ||||||||
| Basic and diluted | 2,581,282 | 2,581,282 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
F-30
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF MEMBERS’ EQUITY
(Unaudited)
(in United States dollars, except unit amounts)
| For the Nine Months Ended September 30, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class A | Class B Preferred | Class B-1 Preferred | Class C | Total
members’ |
Additional
paid-in |
Accumulated | Total
members’ |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Units | Amount | Units | Amount | Units | Amount | Units | Amount | investment | capital | deficit | equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2019 | | 2,581,282 | | $ | 387,192 | | | 1,727,843 | | $ | 1,898,469 | | | 629,727 | | $ | 23,655,518 | | | 435,679 | | $ | 4,053,833 | | $ | 29,995,012 | | $ | 107,178 | | $ | (27,722,053 | ) | $ | 2,380,137 | |
| Issuance of units | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 475,560 | | | 17,506,684 | | | — | | | — | | | 17,506,684 | | | — | | | — | | | 17,506,684 | |
| Redeemable warrants | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Issuance
of units upon vesting of profits interests |
| — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 221,465 | | | 2,552,541 | | | 2,552,541 | | | — | | | — | | | 2,552,541 | |
| Redemption of vested profit units | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (854 | ) | | (16,399 | ) | | (16,399 | ) | | — | | | — | | | (16,399 | ) |
| Net loss | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (15,588,393 | ) | | (15,588,393 | ) |
| Balance, September 30, 2020 | | 2,581,282 | | $ | 387,192 | | | 1,727,843 | | $ | 1,898,469 | | | 1,105,287 | | $ | 41,162,202 | | | 656,290 | | $ | 6,589,975 | | $ | 50,037,838 | | $ | 107,178 | | $ | (43,310,446 | ) | $ | 6,834,570 | |
| For the Nine Months Ended September 30, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class A | Class B Preferred | Class B-1 Preferred | Class C | Total
members’ |
Additional
paid-in |
Accumulated | Total
members’ |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Units | Amount | Units | Amount | Units | Amount | Units | Amount | investment | capital | deficit | equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2018 | | 2,581,282 | | $ | 387,192 | | | 1,727,843 | | $ | 1,898,469 | | | 326,026 | | $ | 12,260,210 | | | 75,830 | | $ | 24,488 | | $ | 14,570,359 | | $ | 32,884 | | $ | (8,409,335 | ) | $ | 6,193,908 | |
| Issuance of units | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 251,048 | | | 9,440,708 | | | — | | | — | | | 9,440,708 | | | — | | | — | | | 9,440,708 | |
| Redeemable warrants | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 74,294 | | | — | | | 74,294 | |
| Issuance
of units upon vesting of profits interests |
| — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 320,111 | | | 3,611,503 | | | 3,611,503 | | | — | | | — | | | 3,611,503 | |
| Redemption of vested profit units | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (753 | ) | | (19,288 | ) | | (19,288 | ) | | — | | | — | | | (19,288 | ) |
| Net loss | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (16,222,762 | ) | | (16,222,762 | ) |
| Balance, September 30, 2019 | | 2,581,282 | | $ | 387,192 | | | 1,727,843 | | $ | 1,898,469 | | | 577,074 | | $ | 21,700,918 | | | 395,188 | | $ | 3,616,703 | | $ | 27,603,282 | | $ | 107,178 | | $ | (24,632,097 | ) | $ | 3,078,363 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
F-31
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Unaudited)
(in United States dollars, except unit amounts)
| Nine months ended September 30, | ||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities | ||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (15,588,393 | ) | $ | (16,222,762 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities | ||||||||
| Employee equity-based compensation | 2,552,541 | 3,611,503 | ||||||
| Non-cash issuance of units | 333,333 | — | ||||||
| Issuance of warrants | — | 6,486,916 | ||||||
| Fair value change of warrants | 1,774,735 | — | ||||||
| Depreciation expense | 1,409,404 | 442,703 | ||||||
| Loss on sale of equipment | — | 255,650 | ||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities | ||||||||
| Prepaid royalties | (100,000 | ) | (2,000,000 | ) | ||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | (128,290 | ) | 147,306 | |||||
| Accounts payable | (626,096 | ) | (2,424,580 | ) | ||||
| Accrued expenses | (411,350 | ) | 282,150 | |||||
| Deferred research and development obligation | — | 1,000,000 | ||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | $ | (10,784,116 | ) | $ | (8,421,114 | ) | ||
| Cash flows from investing activities | ||||||||
| Construction of plant | (2,423,402 | ) | (2,379,442 | ) | ||||
| Proceeds from sale of equipment | — | 110,000 | ||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | $ | (2,423,402 | ) | $ | (2,269,442 | ) | ||
| Cash flows from financing activities | ||||||||
| Proceeds from term loan | 313,500 | 1,000,000 | ||||||
| Proceeds from promissory notes with related party | — | 600,000 | ||||||
| Payments on promissory notes | (863,151 | ) | — | |||||
| Payments on promissory notes with related parties | (600,000 | ) | — | |||||
| Proceeds from advances from related parties | — | 57,902 | ||||||
| Payments on advances from related parties | (2,703,694 | ) | — | |||||
| Bond issuance costs | (154,994 | ) | (294,021 | ) | ||||
| Proceeds from Issuance of units | 17,173,351 | 9,440,708 | ||||||
| Payments on redemption of vested profit units | — | (19,288 | ) | |||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | $ | 13,165,012 | $ | 10,785,301 | ||||
| Net (decrease) increase in cash | (42,506 | ) | 94,745 | |||||
| Cash, beginning of period | 150,050 | 100,814 | ||||||
| Cash, end of period | $ | 107,544 | $ | 195,559 | ||||
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information | ||||||||
| Non-cash operating activities | ||||||||
| Interest paid during the period, net of capitalized interest | $ | 1,581,267 | $ | 255,520 | ||||
| Non-cash investing activities | ||||||||
| Additions to property, plant, and equipment in accounts payable | $ | (1,357,431 | ) | $ | (3,144,405 | ) | ||
| Non-cash financing activities | ||||||||
| Conversion of accounts payable to promissory notes | $ | 1,247,319 | $ | — | ||||
| Bond issuance costs capitalization – additions to accrued expense | $ | 1,960,932 | $ | — | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
F-32
NOTES
TO THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unaudited)
NOTE 1 — ORGANIZATION
Formation and Organization
PureCycle Technologies LLC (“PureCycle”, “PCT”, or the “Company”) was formed as a Delaware limited liability company (“LLC”) on September 15, 2015 (“Date of Formation”), as Advanced Resin Technologies LLC. In November 2016, the Company changed its name to Purecycle Technologies LLC. PureCycle is a majority owned subsidiary of Innventure LLC (formerly WE-Innventure LLC, “Innventure” or the “Parent”).
PureCycle and its wholly owned subsidiary, Purecycle: Ohio LLC, PCT Managed Services LLC and PCO Holdco LLC, are businesses whose planned principal operations are to conduct business as a plastics recycler using PureCycle’s patented recycling process. Developed and licensed by Procter & Gamble (“P&G”), the patented recycling process separates color, odor and other contaminants from plastic waste feedstock to transform it into virgin-like resin. The Company is currently constructing its facility and conducting research and development activities to operationalize the licensed technology.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying unaudited condensed consolidated interim financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”). The unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern; however, the conditions below raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to do so. The consolidated interim financial statements do not include any adjustments to reflect the possible future effects on the recoverability and classification of assets or the amounts and classifications of liabilities that may result should the Company be unable to continue as a going concern.
These unaudited condensed consolidated interim financial statements should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2019. The unaudited consolidated interim financial statements do not include all the information and footnotes required by U.S. GAAP for complete financial statements. The results of operations for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for the entire year ending December 31, 2020. The accompanying unaudited consolidated interim financial statements reflect all adjustments, consisting of normal recurring adjustments, that are, in the opinion of management, necessary to a fair statement of the results for the interim periods presented.
Potential Impact of COVID-19 on the Company’s Business
With the global spread of the COVID-19 pandemic in the first half of 2020 and resulting shelter-in- place orders covering the Company’s corporate headquarters, its Ohio plant operations, and employees, the Company has implemented policies and procedures to continue its operations under minimum business operations guidelines. The extent to which the COVID-19 pandemic impacts the Company’s business, financial condition or results of operations will depend on future developments, which are highly uncertain and cannot be accurately predicted.
Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated interim financial statements include the accounts of the Company, and all significant intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
F-33
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES
TO THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
(Unaudited)
Liquidity and Going Concern
The Company has sustained recurring losses and negative cash flows from operations since its inception. As reflected in the accompanying consolidated financial statements, the Company has not yet begun commercial operations and does not have any sources of revenue. As of September 30, 2020, and December 31, 2019, the Company had a cash balance of $107,544 and $150,050, respectively, a working capital deficit of $15,741,892 and $7,621,546, respectively, and an accumulated deficit of $43,310,446 and $27,722,053, respectively. For nine months ended September 30, 2020, the Company incurred a net loss of $15,588,393. Over the past year, the Company’s growth has been funded through a combination of equity financing, secured term loan, promissory notes, debt financing obtained from a related party, and cash advances obtained from related parties. While the Company believes it is probable it will begin generating revenues in the near future, there is no assurance that the Company will be successful in its business activities or be able to fund its obligations for one year from the date the condensed consolidated financial statements are available to be issued.
Subsequent to September 30, 2020, the Company has raised gross proceeds of $15 million from the sale of Class A Units. The Company expects to raise an additional $15 million from the sale of Class A Units subject to certain conditions including the closing of the Merger. In addition, the Company entered into a Note Purchase Agreement and closed promissory notes to further fund the development of its technologies. Refer to Note 10 for details on subsequent events. There can be no assurance that any future financing will be available or, if available, that it will be on terms that are satisfactory to the Company.
NOTE 2 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the consolidated interim financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates, judgments and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of expenses for the period presented. The Company’s most significant estimates and judgments involve valuation of the Company’s equity, including assumptions made in the fair value of Equity-based compensation and the fair value of warrants it has issued to service providers. Although these estimates are based on management’s best knowledge of current events and actions that the Company may undertake in the future, actual results may be different from these estimates.
Segment Information
Under ASC 280, Segment Reporting, operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise where discrete financial information is available that is evaluated regularly by the chief operating decision maker (“CODM”), in deciding how to allocate resources and in assessing performance. The Company has one component. Therefore, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer, who is also the CODM, makes decisions and manages the Company’s operations as a single operating segment, which is conducting business as a plastic recycler. To date, the Company has not entered into production and measures performance on a consolidated basis.
Bond Issuance Costs
The Company has incurred costs which are directly attributable to the Company’s bond financing. These costs include items such as document preparation costs, underwriting fees, and other external, incremental expenses paid to advisors that directly relate to the financing. During the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and September 30, 2019, the Company incurred $2,115,927 and $294,021, respectively, of bond issuance costs, and as of September 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019, the Company has capitalized bond issuance costs totaling $2,731,822 and $615,896, respectively, which are recorded within Prepaid expenses and other current assets on the consolidated balance sheet. Subsequent to September 30, upon successful completion of the bond offering, these costs have been reclassified to reduce the carrying amount of the bond liability and will be amortized ratably over the term of the bond.
F-34
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO
THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
(Unaudited)
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842), to increase transparency and comparability among organizations by recognizing lease assets and lease liabilities on the balance sheet and disclosing key information about leasing arrangements. In July 2018, ASU 2018-10, Codification Improvements to Topic 842, Leases, was issued to provide more detailed guidance and additional clarification for implementing ASU 2016-02. Furthermore, in July 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-11, Leases (Topic 842): Targeted Improvements, which provides an optional transition method in addition to the existing modified retrospective transition method by allowing a cumulative effect adjustment to the opening balance of retained earnings in the period of adoption. Furthermore, on June 3, 2020, the FASB deferred by one year the effective date of the new leases standard for private companies, private NFPs and public NFPs that have not yet issued (or made available for issuance) financial statements reflecting the new standard. These new leasing standards are effective for the Company beginning after December 15, 2021 and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the effect of the adoption of this guidance on the consolidated financial statements.
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments — Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses of Financial Instruments, which, together with subsequent amendments, amends the requirement on the measurement and recognition of expected credit losses for financial assets held. ASU 2016-13 is effective for the Company beginning December 15, 2022, including interim periods within those fiscal years, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently in the process of evaluating the effects of this pronouncement on the Company’s financial statements and does not expect it to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In June 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-07, “Compensation — Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvements to Nonemployee Share-Based Payment Accounting” (“ASU 2018-07”). ASU 2018-07 extends the scope of Topic 718 to include share-based payment transactions for acquiring goods and services from nonemployees. ASU 2018-07 amendments are effective for the Company beginning January 1, 2020 and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2020. The Company is currently evaluating the effect of the adoption of this guidance on the consolidated financial statements.
NOTE 3 — NOTES PAYABLE AND RELATED PARTY NOTES PAYABLE
Secured Term Loan
Enhanced Capital Ohio Rural Fund, LLC
On February 28, 2019, the Company entered into a subordinated debt agreement with Enhanced Capital Ohio Rural Fund, LLC. The agreement provides for principal of $1,000,000 with an interest rate of the U.S. Federal prime rate per annum.
As of September 30, 2020, the outstanding balance of the loan is $1,000,000. $100,002 is recorded as Notes payable — current and $899,998 recorded as Notes payable in the consolidated balance sheets. As of December 31, 2019, the outstanding balance on the term loan is $1,000,000, recorded within Notes payable in the consolidated balance sheets.
On October 7, 2020, upon the closing of the bond offering, the full outstanding balance was paid off. Refer to Note 10 for details.
F-35
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO
THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
(Unaudited)
Paycheck Protection Program
On May 4, 2020, the Company entered into a Paycheck Protection Program (the “Program”, or “PPP”) Term Note with PNC Bank to obtain principal of $313,500. This Note is issued pursuant to the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act’s (the “CARES Act”) (P.L. 116-136) Paycheck Protection Program. During a period from May 4, 2020 to November 4, 2020 (“Deferral Period”), interests on the outstanding principal balance will accrue at the Fixed Rate of 1% per annum, but neither principal nor interest shall be due during the Deferral Period. At the end of the Deferral Period, the outstanding principal of the loan Facility that is not forgiven under the program shall convert to an amortizing term loan. All or a portion of this Facility may be forgiven in accordance with the program requirements. The amount of forgiveness shall be calculated in accordance with the requirements of the Program, including provisions of Section 1106 of the CARES Act. Not more than 25% of the amount forgiven can be attributable to non- payroll costs. The unforgiven portion of the PPP loan is payable over two years at an interest rate of 1%, with a deferral of payments for the first nine months.
As of September 30, 2020, the outstanding balance on the loan is $313,500. $191,583 is recorded as Notes payable — current and $121,917 is recorded as Notes payable in the consolidated balance sheets.
Promissory Notes
Koch Modular Process Systems Secured Promissory Note
On December 20, 2019, the Company entered into an agreement with Koch Modular Process Systems LLC (“KMPS”) to convert the current balance of Account Payable due to KMPS into a promissory note. The Company issued a Secured Promissory Note for a principal amount of $1,677,489, with a maximum advance of funds up to $3,077,489. The rate of interest on the loan balance is 21% per annum through the month of November 2019 and 24% per annum for December 2019 and thereafter.
As of September 30, 2020, and December 31, 2019, the outstanding balance on the promissory note is $1,993,721 and $1,609,553, recorded within Notes payable — current in the consolidated balance sheets.
On October 1, 2020, the Company was provided an extension to pay off the outstanding balance by October 7, 2020. On October 7, 2020, upon the closing of the bond offering, the full outstanding balance was paid off. Refer to Note 10 for details.
Denham-Blythe Company, Inc. Secured Promissory Note
On December 20, 2019, the Company and Denham-Blythe Company, Inc. (“DB”) entered into an agreement to convert the current balance of Account Payable due to DB into a promissory note. The Company issued a Secured Promissory Note for a principal amount of $2,000,000. The rate of interest on the loan balance is 24% per annum for December 2019 and thereafter with interest on the loan payable monthly.
As of September 30, 2020, and December 31, 2019, the outstanding balance on the promissory note is both $1,991,693, recorded within Notes payable — current in the consolidated balance sheets.
On September 14, 2020, the Company was provided an extension to pay off the outstanding balance by October 7, 2020. On October 7, 2020, upon the closing of the bond offering, the full outstanding balance was paid off. Refer to Note 10 for details.
Promissory Note to Related Party
Innventus Fund I, LP
On July 19, 2019, the Company entered into Note and Warrant Financing agreement with Innventus Fund I, LP to obtain a $600,000 loan and warrant financing. The Negotiable Promissory Note has a maturity date of October 21, 2019, and an interest rate of 1-month LIBOR plus 8.0%. The aggregate unpaid
principal amount of the loan and all accrued and unpaid interest is due on the maturity date.
F-36
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO
THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
(Unaudited)
As of December 31, 2019, the outstanding balance on this Note is $600,000, recorded within Related party notes payable — current in the consolidated balance sheets. The Company repaid the principal and all accrued and unpaid interest on February 5, 2020.
Auto Now Acceptance Company, LLC
On May 5, 2017, the Company entered into a revolving line of credit facility (the “Credit Agreement”) with Auto Now Acceptance Company, LLC, a related party.
On May 3, 2018, the Credit Agreement was amended and restated in its entirety and secured by a Security Agreement dated May 3, 2018. The credit facility was increased to $14,000,000, bearing interest at a rate of LIBOR plus 6.12% per annum, payable monthly. The maturity date was extended to August 15, 2018. On July 31, 2018, the Credit Agreement was amended to extend the maturity date to February 15, 2019. Under the agreement, the Auto Now’s advances of funds to the Company ceased on July 31, 2018.
On May 29, 2020, the Company executed a Second Amended and Restated the Security Agreement and entered into a Third Amended and Restated Promissory Note agreement to extend the financing on the loan from Auto Now Acceptance Company, LLC. The agreement extended the maturity date of the loan to June 31, 2021 and adjusted the interest rate on the third amended loan agreement. The security interests include inventory, equipment, accounts receivables and all the Company’s assets. The interest rate within the amendment increased as follows:
| • | The annual rate of the 1-month LIBOR in U.S. dollars plus 6.12% adjusted daily, from May 3, 2018 through May 18, 2020 |
| • | 12% per annum from May 19, 2020 through August 31, 2020 |
| • | 16% per annum from September 1, 2020 through December 31, 2020 |
| • | 24% per annum from January 1, 2021 through June 30, 2021 |
As of September 30, 2020 the outstanding balance on the credit facility was $12,000,000, recorded within Related party notes payable — current in the consolidated balance sheets. As of December 31, 2019 the outstanding balance was $12,000,000, recorded within Related party notes payable in the consolidated balance sheets.
Advances from Related Parties
During 2019 and 2020, PureCycle received funding and support services from Innventure1 LLC (formerly Innventure LLC) and Wasson Enterprises. The outstanding balance due to Innventure1 LLC as of December 31, 2019 is $1,957,611, recorded within Related party notes payable — current in the consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2019. The balance was repaid in full as of September 30, 2020.
The outstanding balance due to Wasson Enterprise as of December 31, 2019 is $746,083, recorded within Related party notes payable — current in the consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2019. As of June 30, 2020, $375,000 of the outstanding balance was repaid. The remaining balance of $371,083 was assigned from Wasson Enterprise to Innventure LLC (Formerly WE-Innventure LLC) and was paid in full as of September 30, 2020.
NOTE 4 — MEMBERS’ EQUITY
The Company operates subject to the terms and conditions of the amended and restated PureCycle Technologies LLC, Limited Liability Company Agreement (the “LLC Agreement”) dated September 7, 2018. The LLC Agreement was subsequently amended on August 28, 2019.
F-37
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO
THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
(Unaudited)
Class A Units
During the nine months ended September 30, 2020, the Board increased the number of authorized Class A units to 3,981,282. As of September 30, 2020, and September 30, 2019, 2,581,282 units are issued and outstanding. No additional Class A units were issued for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and September 30, 2019. Subsequent to September 30, 2020, the Company issued 115,428 Class A Units to a related party for total consideration of $10 million. The Company expects to raise an additional $15 million from the sale of Class A Units to the related party subject to certain conditions including the closing of the Merger. Please refer to Note 10 for details.
Class B Preferred Units
As of September 30, 2020, and September 30, 2019, 1,727,843 Class B preferred units are issued and outstanding. No additional Class B preferred units were issued for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and September 30, 2019. The Class B P&G warrants were exercised subsequent to September 30, 2020. Refer to Note 10 for details.
Class B-1 Preferred Units
During the nine months ended September 30, 2020, the Board increased the number of authorized Class B-1 preferred units to 1,145,584. During the nine months ended September 30, 2020 the Company issued 8,864 Class B-1 preferred units to a non-employee third party at $37.61 per unit in exchange for services provided. Also during the nine months ended September 30, 2020, the Company issued 265,922 Class B-1 preferred units to a related party at $37.61 per unit. As of September 30, 2020, and September 30, 2019, there are 1,105,287 and 577,074 Class B-1 preferred units issued and outstanding, respectively.
| For the period ended September 30, 2020 | Number of units | Amount | ||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2019 | 629,727 | $ | 23,655,518 | |||||
| Issuance of shares | 475,560 | 17,506,684 | ||||||
| Balance, September 30, 2020 | 1,105,287 | $ | 41,162,202 | |||||
| For the period ended September 30, 2019 | Number of units | Amount | ||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2018 | 326,026 | $ | 12,260,210 | |||||
| Issuance of shares | 251,048 | 9,440,708 | ||||||
| Issuance of shares upon the exercise of warrants | — | — | ||||||
| Balance, September 30, 2019 | 577,074 | $ | 21,700,918 | |||||
Class C Units
During the nine months ended September 30, 2020, the Board increased the number of authorized Class C units to 1,069,012. During the nine months ended September 30, 2020, the Company granted 240,850 Class C incentive units, pursuant to the Company’s equity incentive plan. There were 202,002 granted during the nine months ended September 30, 2019. 37,500 units were issued to a related party. See Note 5 for further information. As of September 30, 2020, and September 30, 2019, 656,290 and 395,188 Class C units are issued and outstanding, respectively. Subsequent to September 30, 2020, the Company issued 50,000 Class C Units to a related party. Please refer to Note 10 for details.
As of September 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019, there were 210,526 warrant units issued and outstanding to P&G to purchase Class B preferred units; 4,787 warrant units issued and outstanding to Innventus Fund I, LP to purchase Class B-1 preferred units; 7,978 warrant units issued and outstanding to
a related party to purchase Class B-1 preferred units; 143,619 warrant units issued and outstanding to RTI to purchase Class C units. The Class B P&G warrants were exercised subsequent to September 30, 2020. Refer to Note 10 for details.
F-38
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO
THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
(Unaudited)
NOTE 5 — EQUITY-BASED COMPENSATION
The Company established an equity incentive plan (the “Plan”) on June 1, 2018 to provide for the grant of Class C incentive units, characterized as profits interests, to certain executives, directors, key employees, and non-employee service providers of the Company. The aggregate number of units that can be granted under the Plan is subject to the authorized amount of Class C Units per the LLC Agreement, which is 1,069,012 total units.
The units issued pursuant to the Plan are time-based and vest over the period defined in each individual grant agreement or upon a change of control event as defined in the Plan. The distribution threshold associated with the units is determined by the Board at the time units are granted. The Company has the option to repurchase all vested units upon a unitholder’s termination of employment or service with the Company.
The Company recognizes compensation expense for the units equal to the fair value of the equity- based compensation awards and is recognized on a straight-line basis over the vesting period of such awards. The fair value of the units is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model using the following assumptions:
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||
| Expected annual dividend yield | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | ||
| Expected volatility | 42.1 – 67.7 | % | 51.1 – 95 | % | ||
| Risk-free rate of return | 0.1 – 1.8 | % | 1.75 – 2.73 | % | ||
| Expected option term (years) | 0.35 – 4.9 | 1.5 – 5 |
The expected term of the units granted is determined based on the period of time the units are expected to be outstanding. The risk-free rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant. The expected volatility was based on the Company’s capital structure and volatility of similar entities referred to as guideline companies. In determining similar entities, the Company considered industry, stage of life cycle, size and financial leverage. The dividend yield on the Company’s units is assumed to be zero since the Company has not historically paid dividends. The fair value of the underlying Company units was determined using the back solve method.
A summary of incentive unit activity for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and September 30, 2019 is as follows:
| Number of units | Weighted average grant date fair value | Weighted average remaining recognition period | ||||||||||
| Non-vested at December 31, 2019 | 72,972 | $ | 2.09 | |||||||||
| Granted | 240,850 | 13.50 | ||||||||||
| Vested | (221,465 | ) | 10.84 | |||||||||
| Forfeited | (1,146 | ) | ||||||||||
| Non-vested at September 30, 2020 | 91,211 | $ | 10.81 | 2.18 | ||||||||
F-39
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO
THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
(Unaudited)
| Number of units | Weighted average grant date fair value | Weighted average remaining recognition period | ||||||||||
| Non-vested at December 31, 2018 | 204,389 | $ | 0.21 | |||||||||
| Granted | 202,002 | 17.84 | ||||||||||
| Vested | (320,111 | ) | 11.33 | |||||||||
| Forfeited | (4,267 | ) | ||||||||||
| Non-vested at September 30, 2019 | 82,013 | $ | 0.32 | 1.72 | ||||||||
Total equity-based compensation cost for nine months ended September 30, 2020 and September 30, 2019 totaled $2,552,541 and $3,611,503, respectively, and is recorded within the selling, general and administrative expenses and operating costs on the consolidated statement of operations.
NOTE 6 — NET LOSS PER SHARE
The Company follows the two-class method when computing net loss per common units when units are issued that meet the definition of participating securities. The two-class method requires income available to common unitholders for the period to be allocated between common and participating securities based upon their respective rights to receive dividends as if all income for the period had been distributed. The two- class method also requires losses for the period to be allocated between common and participating securities based on their respective rights if the participating security contractually participates in losses. As holders of participating securities do not have a contractual obligation to fund losses, undistributed net losses are not allocated to Class C Units for purposes of the loss per unit calculation.
Presented in the table below is a reconciliation of the numerator and denominator for the basic and diluted earnings per unit (“EPU”) calculations for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and September 30, 2019 is as follows:
| September 30, 2020 | September 30, 2019 | ||||||||
| Numerator: | |||||||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to PureCycle Technologies | $ | (15,588,393 | ) | $ | (16,222,762 | ) | |||
| Less cumulative earnings to preferred stockholder | 4,833,137 | 1,927,889 | |||||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders | $ | (20,421,530 | ) | $ | (18,150,651 | ) | |||
| Denominator: | |||||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding, basic and diluted | 2,581,282 | 2,581,282 | |||||||
| Net loss per share attributable to common stockholder, basic and diluted | $ | (7.91 | ) | $ | (7.03 | ) | |||
The weighted-average outstanding common unit equivalents were excluded from the computation of diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders for the periods presented because including them would have been anti-dilutive. These units include vested but not exercised warrants and non-vested profit interest units.
F-40
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO
THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
(Unaudited)
NOTE 7 — PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT
Presented in the table below are the major classes of property, plant and equipment by category as of dates:
| As of September 30, 2020 | ||||||||||||
| Accumulated | ||||||||||||
| Cost | Depreciation | Net Book Value | ||||||||||
| Building | $ | 9,736,424 | $ | 309,577 | $ | 9,426,847 | ||||||
| Machinery and equipment | 15,980,336 | 1,981,606 | 13,998,730 | |||||||||
| Fixtures and Furnishings | 104,484 | 18,658 | 85,826 | |||||||||
| Construction in process | 9,270,120 | — | 9,270,120 | |||||||||
| Total property, plant and equipment | $ | 35,091,364 | $ | 2,309,841 | $ | 32,781,523 | ||||||
| As of December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||
| Accumulated | ||||||||||||
| Cost | Depreciation | Net Book Value | ||||||||||
| Building | $ | 9,703,674 | $ | 122,384 | $ | 9,581,290 | ||||||
| Machinery and equipment | 15,670,237 | 770,590 | 14,899,647 | |||||||||
| Fixtures and Furnishings | 104,484 | 7,463 | 97,021 | |||||||||
| Construction in process | 5,832,136 | — | 5,832,136 | |||||||||
| Total property, plant and equipment | $ | 31,310,531 | $ | 900,437 | $ | 30,410,094 | ||||||
On March 28, 2019, the Company sold machinery and equipment for cash proceeds of $110,000. The net book value of this equipment was $365,650.
Depreciation expense is recorded within the operating expense in the consolidated statements of operations and amounted to $1,409,404 and $442,703 for the nine months ended September 30, 2020 and September 30, 2019.
NOTE 8 — FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
Fair value is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date and sets out a fair value hierarchy. The fair value hierarchy gives the highest priority to quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3). Inputs are broadly defined as assumptions market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability. Assets and liabilities carried at fair value are classified and disclosed in one of the following three categories:
Level 1 — Unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that the reporting entity has the ability to access at the measurement date.
Level 2 — Inputs other than quoted prices within Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, and fair value is determined through the use of models or other valuation methodologies
Level 3 — Inputs are unobservable for the asset or liability and include situations where there is little, if any, market activity for the asset or liability. The inputs into the determination of fair value are based upon the best information in the circumstances and may require significant management judgment or estimation.
F-41
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO
THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
(Unaudited)
Liabilities measured and recorded at Fair Value on a recurring basis
As of September 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019, the Company’s financial liabilities measured and recorded at fair value on a recurring basis were classified within the fair value hierarchy as follow:
| September 30, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P&G warrants | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 8,183,146 | $ | 8,183,146 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 6,408,411 | $ | 6,408,411 | ||||||||||||||||
| $ | — | $ | — | $ | 8,183,146 | $ | 8,183,146 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 6,408,411 | $ | 6,408,411 | |||||||||||||||||
The Company has determined its warrant to be a Level 3 fair value measurement and has remeasured using the Black-Scholes option pricing model to calculate its fair value as of September 30, 2020 using the following assumptions:
| Expected annual dividend yield | 0.0 | % | |
| Expected volatility | 63.8 – 68.34 | % | |
| Risk-free rate of return | 0.2 – 0.23 | % | |
| Expected option term (years) | 0.5 – 3.9 |
Changes in Level 3 liabilities measured at fair value for nine months ended September 30, 2020 are as follows:
| Fair
value (Level 3) | ||||
| Balance at December 31, 2019 | $ | 6,408,411 | ||
| Change in fair value | 1,774,735 | |||
| Balance at September 30, 2020 | $ | 8,183,146 | ||
Assets and liabilities recorded at carrying value
In determining the appropriate levels, the Company performs a detailed analysis of the assets and liabilities that are subject to fair value measurements.
The Company records cash and cash equivalents and accounts payable at cost, which approximates fair value due to their short-term nature or stated rates. The Company records debt at cost. Management believes the fair value of the debt is not materially different than the carrying amount.
NOTE 9 — DEVELOPMENT PARTNER ARRANGEMENTS
Strategic Alliance Agreement
On December 13, 2018, the Company entered into a strategic alliance agreement with Nestec Ltd. (“Nestle”), which expires on December 31, 2023. Upon execution of the agreement, Nestle committed to provide $1.0 million to the Company to fund further research and development efforts. The funding provided by Nestle may be convertible, in whole or in part, into a prepaid product purchase arrangement at Nestle’s option, upon the time of product delivery beginning in 2020. Additionally, in the event that the research and development efforts are not successful by December 31, 2020, up to 50% of the funding may be convertible into a 5-year term loan obligation, payable to Nestle at an interest rate equivalent to the U.S. prime rate.
The Company received the funding from Nestle on January 8, 2019. The Company has recorded $1.0 million as a Deferred research and development obligation as of September 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019. Recognition related to the funding received will be deferred until it is probable that Nestle will not exercise their option. If the prepaid product purchase option is exercised, the obligation will be recognized as an adjustment to the transaction price of future product sales (e.g., net revenue presentation). If the option is not exercised, or in the case of development efforts not being successful, any amounts not converted to a loan obligation will be recognized as a reduction to research and development costs.
F-42
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO
THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
(Unaudited)
NOTE 10 — SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
In connection with the preparation of the unaudited consolidated interim financial statements for the period ended September 30, 2020, management has evaluated events through November 17, 2020, to determine whether any events required recognition or disclosure in the consolidated financial statements. The following subsequent events were identified through the date of these consolidated financial statements:
On October 6, 2020, the Company entered into a Note Purchase Agreement (the “Note Purchase Agreement”) with certain funds managed by Magnetar Capital LLC or its affiliates, providing for the issuance of up to $60.0 million in aggregate principal amount of Convertible Senior Notes due 2022 (the “Convertible Notes”) issuable under an Indenture dated as of October 7, 2020 (the “Magnetar Indenture”) between PCT and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee and collateral agent. On October 7, 2020, PCT issued $48.0 million in aggregate principal amount of Convertible Notes (the “First Tranche Notes”) and expect to issue an additional $12.0 million of aggregate principal amount of Convertible Notes (the “Second Tranche Notes”) to the Convertible Notes Investors within 45 days after the entry into the Merger Agreement, defined below, subject to the satisfaction of customary closing conditions. In the event that the Business Combination is not consummated within 180 days of the entry into the Merger Agreement, the Second Tranche Notes are subject to a special mandatory redemption at a redemption price equal to 100% of their aggregate principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest.
On October 7, 2020, the Southern Ohio Port Authority (“SOPA”) issued certain bonds (“Revenue Bonds”) to be used to (i) acquire, construct and equip the Ohio Plant; (ii) fund a debt service reserve fund for the Series 2020A bonds; (iii) finance capitalized interest; and (iv) pay the costs of issuing the bonds. The bond offering includes ((i) Exempt Facility Revenue Bonds, tax-exempt Series 2020A of approximately $220 million; (ii) Subordinate Exempt Facility Revenue Bonds, tax-exempt Series 2020B of $20.0 million; and (iii) Subordinated Exempt Facility Revenue Bonds, taxable Series 2020C of $10 million. The purchase price of the bonds was payable and immediately available to Southern Ohio Port Authority on the closing date of the bonds, October 7, 2020. PCT is not a direct obligor on the Revenue Bonds and is not a party to the indenture of trust between SOPA and UMB Bank, N.A as trustee. Pursuant to the execution of a loan agreement dated October 1, 2020, PCT executed promissory notes in favor of SOPA and assigned to UMB Bank on October 7, 2020. The amount of each promissory note was the aggregate principal amount of each revenue bond series issued by SOPA. PCT is required to submit a requisition for funds to be disbursed by the UMB Bank outlining the specified purpose.
The proceeds of the Revenue Bonds have been placed in various trust funds and non-interest-bearing accounts established and administered by UMB Bank, N.A., as trustee under the indenture (the “Trustee”). In addition, 100% of revenue attributable to the production of the Phase II Facility must be deposited into a revenue escrow fund. Funds in the trust accounts and revenue escrow account will be disbursed by the Trustee when certain conditions are met, and will be used to pay costs and expenditures related to the development of the Phase II Facility, make required interest and principal payments (including sinking fund redemption amounts) and, in certain circumstances required under the indenture, to redeem the Revenue Bonds.
As conditions for closing the Revenue Bonds, PCT and certain affiliates contributed $60.0 million in equity at closing and has committed to contribute an additional $40.0 million in equity by January 31, 2021. PCT will provide a liquidity reserve for Ohio Plant construction of $50.0 million to be deposited by January 31, 2021. In addition, PCT has to maintain at least $75 million of cash on its balance sheet as of July 31, 2021 and $100.0 million of cash on its balance sheet as of January 31, 2022.
As part of the equity requirement for the bond, on October 4, 2020, the Company raised gross proceeds of $15.0 million through the sale of 173,142 Class A Units, of which 115,428 Class A Units, or $10.0 million, were sold to a related party that has committed to purchase an additional 173,142 Class A Units, or $15.0 million, subject to certain conditions, including the signing of the Merger Agreement. This related party previously purchased Class B-1 Preferred Units from the Company, holds a board seat and was issued 37,500 Class C Units in August 2020 and 50,000 Class C Units subsequent to September 30, 2020.
F-43
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO
THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
(Unaudited)
In conjunction with the bond offering, the company repaid the following:
| • | The note payable with Koch Modular Process Systems for the full outstanding balance of $2,003,025; |
| • | The note payable with Denham-Blythe Company, Inc. for the full outstanding balance of $2,003,693; |
| • | The note payable with Enhanced Capital Ohio Rural Fund, LLC for the full outstanding balance of $1,000,000. |
Pursuant to a 2019 agreement with Innventure LLC and the Company, the Chief Science Officer Dr. John Scott and a certain consultant of Innventure LLC are entitled to share equally in a project fee calculated based on a percentage of the Revenue Bonds. Pursuant to such agreement, the fee is equal to 1.5% of the total financing, reduced by the amount of retainer fees paid to such consultant. The Revenue Bonds closed in October 2020, and, as result, Dr. Scott received a partial payment of $50,000, with the remaining balance of approximately $1,519,125 due to Dr. Scott at the closing of the Merger Agreement described below.
On October 7, 2020, Purecycle: Ohio LLC terminated the lease agreement with Innventure LLC related to land in Lawrence County, Ohio and entered into an agreement to purchase that land from Innventure LLC. On October 7th, 2020 Innventure LLC assigned Purecycle: Ohio LLC the land it had purchased from Lawrence County Economic Development Corporation (“LCED”) with a term loan from Closed Loop Fund, LP. Purecycle: Ohio purchased the land by paying off the outstanding term loan from Closed Loop Fund, LP in the amount of $2,658,010 consisting of principal, accrued and unpaid interest and legal fees.
On October 16, 2020, P&G exercised the P&G warrants and the Company received proceeds of $1 for the exercise of 210,526 outstanding Class B Warrants each exchanged for one Class B Preferred Unit.
On November 11, 2020, JobsOhio, a private non-profit corporation, approved a grant to PCT of $750,000 to be used for construction of the Phase II Facility. In accordance this agreement, after certain condition is met, JobsOhio shall disburse the grant funds for eligible costs incurred after September 24, 2020 and no later than December 31, 2023. If the grant funds are not expended by December 31, 2023, JobsOhio shall have no further obligation to disburse.
On November 12, 2020, the Company raised gross proceeds of $60.0 million through the sale of 684,190 Class A Units.
On November 16, 2020, PCT, Roth CH Acquisition I Co. (“ROCH”), Merger Sub Corp., Merger Sub LLC, and Roth CH Acquisition I Co. Parent Corp (“ParentCo”), entered into the Merger Agreement pursuant to which PCT will be merged with and into Merger Sub LLC, with PCT surviving the merger as a wholly owned subsidiary of ROCH (the “Business Combination”). The transaction estimates $835.0 million pre-money valuation and will include a $250.0 million fully committed private placement of common stock (the “PIPE”). PureCycle was deemed the accounting predecessor and the combined entity will be the successor registrant with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”), meaning that PCT’s consolidated financial statements for previous periods will be disclosed in ParentCo’s future periodic reports filed with the SEC.
While the legal acquirer in the Merger Agreement is ParentCo, for financial accounting and reporting purposes under GAAP, PCT will be the accounting acquirer and the Business Combination will be accounted for as a “reverse recapitalization.” A reverse recapitalization does not result in a new basis of accounting, and the consolidated financial statements of the combined entity represent the continuation of the consolidated financial statements of PCT in many respects. Under this method of accounting, ROCH will be treated as the “acquired” company for financial reporting purposes. For accounting purposes, PCT will be deemed to be the accounting acquirer in the transaction and, consequently, the transaction will be treated as a recapitalization of PCT. Accordingly, the consolidated assets, liabilities and results of operations of PCT will become the historical consolidated financial statements of ParentCo, and ROCH’s assets, liabilities and results of operations will be consolidated with PCT beginning on the acquisition date. Operations prior to the Business Combination will be presented as those of ParentCo in future reports. The net assets of ROCH will be recognized at historical cost (which is expected to be consistent with carrying value), with no goodwill or other intangible assets recorded upon execution of the Business Combination.
F-44
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO
THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
(Unaudited)
As of November 17, 2020, the Company issued 164,100 profit units in accordance with the Plan as described in Note 5.
The Company is not aware of any additional subsequent events, other than those described above, that would require recognition or disclosure in the consolidated financial statements.
F-45
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
Board of Managers
PureCycle Technologies LLC
Opinion on the financial statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of PureCycle Technologies LLC (a Delaware limited liability company) and its subsidiary (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of operations, members’ equity, and cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2019, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Going concern
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company has suffered recurring losses from operations, has a working capital deficit, and has stated that substantial doubt exists about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s evaluation of the events and conditions giving rise to substantial doubt about going concern and management’s plans regarding these matters are also described in Note 1. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the relevant ethical requirements relating to our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB and in accordance with auditing standards generally accepted in the United States of America. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures include examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
| /s/ GRANT THORNTON LLP | |
| We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2019. | |
| Chicago, Illinois | |
| August 25, 2020 |
F-46
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in United States dollars, except unit and per unit amounts)
For the Years ending December 31,
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| CURRENT ASSETS | ||||||||
| Cash | $ | 150,050 | $ | 100,814 | ||||
| Prepaid royalties | 2,000,000 | — | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 720,578 | 577,571 | ||||||
| Total current assets | 2,870,628 | 678,385 | ||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 30,410,094 | 25,059,806 | ||||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 33,280,722 | $ | 25,738,191 | ||||
| LIABILITIES AND MEMBERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| CURRENT LIABILITIES | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 2,364,542 | $ | 4,814,531 | ||||
| Accrued expenses | 1,222,692 | 89,926 | ||||||
| Notes payable-current | 3,601,246 | — | ||||||
| Related party notes payable-current | 3,303,694 | — | ||||||
| Total current liabilities | 10,492,174 | 4,904,457 | ||||||
| Deferred research and development obligation | 1,000,000 | — | ||||||
| Notes payable | 1,000,000 | — | ||||||
| Related party notes payable | 12,000,000 | 14,639,826 | ||||||
| Redeemable warrants | 6,408,411 | — | ||||||
| Commitment and contingencies (Note 8) | ||||||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | 30,900,585 | 19,544,283 | ||||||
| MEMBERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| Class A Common units – $0.15 par value; 2,581,282 units authorized, issued, and outstanding as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 | 387,192 | 387,192 | ||||||
| Class B Preferred units – $1 par value; 1,938,369 units authorized; 1,727,843 units issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019 and 2018 . | 1,898,469 | 1,898,469 | ||||||
| Class B-1 Preferred Units – $1 par value; 1,063,688 units authorized; 629,727 and 326,066 units issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019 and 2018 | 23,655,518 | 12,260,210 | ||||||
| Class C Profits Units – no par value; 719,029 units authorized, 513,671 and 280,219 units issued and 435,679 and 75,830 units outstanding at December 31, 2019 and 2018 | 4,053,833 | 24,488 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 107,178 | 32,884 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (27,722,053 | ) | (8,409,335 | ) | ||||
| Total members’ equity | 2,380,137 | 6,193,908 | ||||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND MEMBERS’ EQUITY | $ | 33,280,722 | $ | 25,738,191 |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-47
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(in United States dollars, except unit and per unit amounts)
For the Years ending December 31,
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Costs and expenses | ||||||||
| Operating costs | $ | 5,965,960 | $ | 1,221,915 | ||||
| Research and development | 526,127 | 786,233 | ||||||
| Selling, general and administrative | 11,478,286 | 2,097,038 | ||||||
| Total operating costs and expenses | 17,970,373 | 4,105,186 | ||||||
| Interest expense | 1,012,402 | — | ||||||
| Other expense | 329,943 | — | ||||||
| Net loss | $ | (19,312,718 | ) | $ | (4,105,186 | ) | ||
| Loss per unit | ||||||||
| Basic and diluted | $ | (8.42 | ) | $ | (1.86 | ) | ||
| Weighted average common units | ||||||||
| Basic and diluted | 2,581,282 | 2,581,282 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-48
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF MEMBERS’ EQUITY
(in United States dollars, except unit and per unit amounts)
For the Years ending December 31,
| Total | Additional | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class A | Class B Preferred | Class B-1 Preferred | Class C | members’ | paid-in | Accumulated | members’ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Units | Amount | Units | Amount | Units | Amount | Units | Amount | investment | capital | deficit | equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2017 (as previously reported) | 2,581,282 | $ | 387,192 | 1,727,843 | $ | 1,898,469 | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | $ | 2,285,661 | $ | 49,296 | $ | (4,353,445 | ) | $ | (2,018,488 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Revisions | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (49,296 | ) | 49,296 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2017 (revised) | 2,581,282 | $ | 387,192 | 1,727,843 | $ | 1,898,469 | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | $ | 2,285,661 | $ | — | $ | (4,304,149 | ) | $ | (2,018,488 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of units | — | — | — | — | 326,026 | 12,260,210 | — | — | 12,260,210 | — | — | 12,260,210 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Redeemable warrants | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 32,884 | — | 32,884 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of units upon vesting of profits units | — | — | — | — | — | — | 75,830 | 15,887 | 15,887 | — | — | 15,887 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (4,073,329 | ) | (4,073,329 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revisions | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 8,601 | 8,601 | (31,857 | ) | (23,256 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2018 | 2,581,282 | $ | 387,192 | 1,727,843 | $ | 1,898,469 | 326,026 | $ | 12,260,210 | 75,830 | $ | 24,488 | $ | 14,570,359 | $ | 32,884 | $ | (8,409,335 | ) | $ | 6,193,908 | |||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of units | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | 303,701 | $ | 11,395,308 | — | $ | — | $ | 11,395,308 | $ | — | $ | — | 11,395,308 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Redeemable warrants | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 74,294 | — | 74,294 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of units upon vesting of profits units | — | — | — | — | — | — | 360,602 | 4,048,633 | 4,048,633 | — | — | 4,048,633 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Redemption of vested profit units | — | — | — | — | — | — | (753 | ) | (19,288 | ) | (19,288 | ) | — | — | (19,288 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (19,312,718 | ) | (19,312,718 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2019 | 2,581,282 | $ | 387,192 | 1,727,843 | $ | 1,898,469 | 629,727 | $ | 23,655,518 | 435,679 | $ | 4,053,833 | $ | 29,995,012 | $ | 107,178 | $ | (27,722,053 | ) | $ | 2,380,137 | |||||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-49
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in United States dollars, except unit and per unit amounts)
For the Years ending December 31,
|
2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities | ||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (19,312,718 | ) | $ | (4,105,186 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities | ||||||||
| Equity-based compensation | 4,048,633 | 24,488 | ||||||
| Issuance of warrants | 6,482,705 | 32,884 | ||||||
| Depreciation expense | 900,437 | — | ||||||
| Loss on sale of equipment | 255,650 | — | ||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities | ||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 151,014 | (122,695 | ) | |||||
| Prepaid royalties | (2,000,000 | ) | — | |||||
| Accounts payable | 1,026,944 | (1,346,198 | ) | |||||
| Accrued expenses | 1,132,766 | 89,926 | ||||||
| Deferred research and development obligation | 1,000,000 | — | ||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | (6,314,569 | ) | (5,426,781 | ) | ||||
| Cash flows from investing activities | ||||||||
| Construction of plant | (5,992,062 | ) | (11,120,983 | ) | ||||
| Proceeds from sale of equipment | 110,000 | — | ||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | (5,882,062 | ) | (11,120,983 | ) | ||||
| Cash flows from financing activities | ||||||||
| Proceeds from secured term loan | 1,000,000 | — | ||||||
| Proceeds from promissory note from related parties | 600,000 | 6,343,239 | ||||||
| Payments on promissory note from related parties | — | (3,143,238 | ) | |||||
| Proceeds from advances from related parties | 63,868 | 1,403,190 | ||||||
| Bond issuance costs | (294,021 | ) | (214,823 | ) | ||||
| Proceeds from issuance of units | 10,895,308 | 12,260,210 | ||||||
| Payments on redemption of vested profit units | (19,288 | ) | — | |||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 12,245,867 | 16,648,578 | ||||||
| Net increase in cash | 49,236 | 100,814 | ||||||
| Cash, beginning of year | 100,814 | — | ||||||
| Cash, end of year | $ | 150,050 | $ | 100,814 | ||||
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information | ||||||||
| Non-cash operating activities | ||||||||
| Interest paid during the year, net of capitalized interest | $ | 1,861 | $ | — | ||||
| Non-cash investing activities | ||||||||
| Additions to property, plant, and equipment in accounts payable | $ | (624,313 | ) | $ | (3,792,835 | ) | ||
| Non-cash financing activities: | ||||||||
| Conversion of accounts payable to promissory notes | $ | 3,601,246 | $ | — | ||||
| Conversion of accounts payable to equity | $ | 500,000 | $ | — | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-50
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2019 and 2018
NOTE 1 — ORGANIZATION
Formation and Organization
PureCycle Technologies LLC (“PureCycle” or the “Company”) was formed as a Delaware limited liability company (“LLC”) on September 15, 2015 (“Date of Formation”), as Advanced Resin Technologies LLC. In November 2016, the Company changed its name to Purecycle Technologies LLC. PureCycle is a majority owned subsidiary of WE-Innventure LLC (“WE-Innventure” or the “Parent”).
PureCycle and its wholly owned subsidiary, Purecycle: Ohio LLC, are businesses whose planned principal operations are to conduct business as a plastics recycler using PureCycle’s patented recycling process. Developed and licensed by Procter & Gamble (“P&G”), the patented recycling process separates color, odor and other contaminants from plastic waste feedstock to transform it into virgin-like resin. The Company is currently constructing its facility and conducting research and development activities to operationalize the licensed technology.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”). The consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern; however, the conditions below raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to do so. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments to reflect the possible future effects on the recoverability and classification of assets or the amounts and classifications of liabilities that may result should the Company be unable to continue as a going concern.
Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company, and all significant intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
Liquidity and going concern
The Company has sustained recurring losses and negative cash flows from operations since its inception. As reflected in the accompanying consolidated financial statements, the Company has not yet begun commercial operations and the Company does not have any sources of revenue. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company had a cash balance of $150,050 and $100,814, respectively, a working capital deficit of $7,621,546 and $4,226,072, respectively, and an accumulated deficit of $27,722,053 and $8,409,335, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company incurred a net loss of $19,312,718 and $4,105,186. Over the past year, the Company’s growth has been funded through a combination equity financing, secured term loan, promissory notes, debt financing obtained from a related party, and cash advances obtained from related parties. While the Company believes it is probable it will begin generating revenues in the near future, there is no assurance that the Company will be successful in its business activities or be able to fund its obligations for one year from the date the consolidated financial statements are available to be issued.
The Company’s promissory note due to a related party (see note 3) matured on February 15, 2019 and has not been repaid. On May 29, 2020, the Company extended the Promissory Note with Auto Now Acceptance Company, LLC to June 30, 2021. The inability of the Company to fund obligations as they become due may result in a material adverse impact on the Company’s financial position and results of operations. These conditions raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
F-51
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
Subsequent to year-end, as of March 31, 2020, the Company repaid advances from Innventure and Wasson Enterprise of $1,950,000 and $375,000 respectively. As of August 24, 2020, the Company has raised net proceeds of $17,068,273 from individual investors from the sale of Class B-1 preferred units. In addition, the Company expects to obtain additional funding through a bond financing to further fund the development of its technologies. There can be no assurance that any future financing will be available or, if available, that it will be on terms that are satisfactory to the Company.
NOTE 2 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Cash
The Company’s cash balance represents cash deposited with financial institutions.
Bond Issuance Costs
The Company has incurred costs which are directly attributable to the Company’s upcoming bond financing. These costs include items such as document preparation costs, underwriting fees, and other external, incremental expenses paid to advisors that directly relate to the financing. Upon successful completion of the bond offering, these costs will be reclassified to reduce the carrying amount of the bond liability and will be amortized ratably over the term of the bond. During the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company incurred $294,021 and $214,823 respectively, of bond issuance costs, and as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company has capitalized bond issuance costs totaling $615,896 and $321,875, respectively, which are recorded within Prepaid expenses and other current assets on the consolidated balance sheet.
Property, Plant and Equipment
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company’s property, plant and equipment consists of building, office equipment and furniture, machinery and equipment, fixtures and furnishings and construction in progress. All property, plant and equipment are located within the United States. Property, plant and equipment are recorded at cost and are amortized over their estimated useful lives, unless the useful life is indefinite, using the straight-line method over the following table:
| Building | 39 years | |||
| Land | Indefinite | |||
| Office equipment and furniture | 7 years | |||
| Machinery and equipment | 5 – 10 years | |||
| Fixtures and Furnishings | 5 years |
Construction in progress relates to costs capitalized in conjunction with major improvements that have not yet been placed in service, and accordingly are not currently being depreciated. The Company capitalizes interest cost incurred on funds used to construct property, plant and equipment. On June 30, 2019 the Feedstock Evaluation Unit (“FEU”) and associated assets were determined to be substantially completed and ready for intended use. In accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 835, Interest, the interest capitalization period covers the duration of the activities required to get the asset ready for its intended use and capitalization continues as long as the activities and incurrence of cost continues. As the FEU unit and associated assets were determined to be ready for intended use on June 30, 2019, the interest capitalization on the Company loans related to those assets ends at that point in time. From July 1, 2019 and going forward, the Company applied a capitalization rate to the average amount of accumulated expenditures related to the current plant being built. The capitalized interest is recorded as part of the asset to which it relates over the asset’s estimated useful life. Interest cost capitalized as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 totaled $1,846,209 and $1,238,135 respectively.
F-52
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
As of December 31, 2019, the Company determined that there were no indicators of impairment and did not recognize any impairment of its property, plant and equipment.
Operating Costs
Operating costs are expensed as incurred. Operating costs consist of facility employee personnel costs, expense for supplies and materials, depreciation, transportation and other operating related expense.
Research and Development Costs
Research and development costs are expensed as incurred. Research and development expenses consist of expenses for services provided by third parties, and payroll and benefits of those employees engaged in research, design and development activities, costs related to design tools, license expenses related to intellectual property, and supplies and services.
Selling, General, and Administrative Costs
Selling, General and Administrative Costs are expensed as incurred. Selling, general, and administrative expense consist of personnel costs, allocated facilities expenses, facility rent, repairs and utilities, office insurance, travel, sales and marketing costs.
Income Taxes
The Company is a limited liability company and has elected to be treated as a partnership for U.S. federal tax purposes. The Company’s taxable income or loss is allocated to its members. The Company is not directly liable for U.S. federal income taxes. The Company is, however, subject to annual state LLC franchise taxes and state LLC fees. During the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, these taxes and fees amounted to $375 and $2,062, respectively, and are included in selling, general and administrative expenses.
Management has evaluated the Company’s tax positions, including their status as a pass-through entity for U.S. federal and state tax purposes, and has determined that the Company has taken no uncertain tax positions that require adjustment to the consolidated financial statements.
Net Loss Per Unit
The Company computes net loss per share in accordance with ASC 260, Earnings per Share. Basic (loss) earnings per unit is computed by dividing (loss) income available to common unitholders by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per unit is computed by dividing income available to common unitholders by the weighted- average number of shares of common units outstanding during the period increased to include the number of additional common units that would have been outstanding if the potentially dilutive securities had been issued, using the treasury stock method.
Equity-Based Compensation
The Company issues grants of incentive units to select employees and service providers. The equity- based compensation cost for the incentive units is measured at the grant date based on the fair value of the award over the requisite service period, which is the vesting period on the straight-line basis. In accordance with ASC 718, Compensation — Stock Compensation (“ASC 718”), in the event of modification, the Company recognizes the remaining compensation cost based on the grant date fair value over the new requisite service period.
The Company applies a zero forfeiture rate for its equity-based awards, as such awards have been granted to a limited number of employees and service providers. A significant forfeiture, or an indication that significant forfeitures may occur, would result in a revised forfeiture rate which would be accounted for prospectively as a change in an estimate.
F-53
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
Warrants
The Company accounts for its warrants issued to nonemployees in accordance with ASC 505, Equity, which requires all nonemployee transactions, in which goods or services are the consideration received in exchange for equity instruments, to be accounted for based on the fair value of the consideration received or the fair value of the equity instruments issued, whichever is more reliably measurable. Accordingly, the Company determines the fair value of the equity instruments issued as of the warrant issuance date, and the fair value is then expensed in accordance with the vesting terms of the warrant agreement. In the event the warrants are issued with other debt instruments, the Company accounts for its warrants in accordance with ASC 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity, for unit of account analysis. In the event the terms of the warrants qualify as a liability under ASC 480, the company accounts for the instrument as a liability recorded at fair value each reporting period.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates, judgments and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of expenses for the period presented. The Company’s most significant estimates and judgments involve valuation of the Company’s equity, including assumptions made in the fair value of Equity- based compensation and the fair value of warrants it has issued to service providers. Although these estimates are based on management’s best knowledge of current events and actions that the Company may undertake in the future, actual results may be different from these estimates.
Segment Information
Under ASC 280, Segment Reporting, operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise where discrete financial information is available that is evaluated regularly by the chief operating decision maker (“CODM”), in deciding how to allocate resources and in assessing performance. The Company has one component. Therefore, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer, who is also the CODM, makes decisions and manages the Company’s operations as a single operating segment, which is conducting business as a plastic recycler. To date, the Company has not entered into production and measures performance on a consolidated basis.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Company applies fair value accounting in accordance with ASC 820, Fair Value Measurements (“ASC 820”) for valuation of financial instruments. ASC 820 defines fair value and establishes a framework for measuring fair value and making disclosures about fair value measurements. This framework applies to all financial assets and liabilities that are being measured and reported at fair value and for disclosures of fair value.
Correction of Immaterial Errors
Management discovered prior period errors that accumulated over prior year 2018. The cumulative adjustment for the errors covering the period from January 1, 2018 to December 31, 2018 was approximately $377,723.
Pursuant to the guidance of Staff Accounting Bulletin (“SAB”) No. 99, Materiality, the Company concluded that the errors were not material to any of its prior period financials. The prior period financial statements were revised, in accordance with SAB No. 108, Considering the Effects of Prior Year Misstatements when Quantifying Misstatements in Current Year Financial Statements.
F-54
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
Reclassifications: Certain amounts in year 2018 have been aggregated or disaggregated to conform to current year presentation. These reclassifications have no effect on previously reported current or total assets, current or total liabilities within the consolidated balance sheets, net loss within the consolidated statements of operation, and the cash provided (used) by operating, investing or financing activities within the consolidated statements of cash flows.
A reconciliation of the effects of the adjustments to the previously reported balance sheet at December 31, 2018 follows:
ASSETS
| As reported | Reclasses | As reclassed | Revision | Revised | ||||||||||||||||
| CURRENT ASSETS | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash | $ | 100,815 | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 100,814 | $ | — | $ | 100,814 | |||||||||
| Prepaid royalties | 1,000,000 | — | 1,000,000 | (1,000,000 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 487,501 | 1 | 487,502 | 90,069 | 577,571 | |||||||||||||||
| Total current assets | 1,588,316 | — | 1,588,316 | (909,931 | ) | 678,385 | ||||||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 24,527,598 | — | 24,527,598 | 532,208 | 25,059,806 | |||||||||||||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 26,115,914 | $ | — | $ | 26,115,914 | $ | (377,723 | ) | $ | 25,738,191 | |||||||||
| LIABILITIES AND MEMBERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CURRENT LIABILITIES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 4,196,704 | $ | (27,706 | ) | $ | 4,168,998 | $ | 645,533 | $ | 4,814,531 | |||||||||
| Accrued expenses | — | 89,926 | 89,926 | — | 89,926 | |||||||||||||||
| Payable to affiliate | 62,220 | (62,220 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Related party notes payable – current | 12,000,000 | (12,000,000 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Total current liabilities | 16,258,924 | (12,000,000 | ) | 4,258,924 | 645,533 | 4,904,457 | ||||||||||||||
| Deferred research and development obligation | 1,000,000 | — | 1,000,000 | (1,000,000 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||
| Notes payable | 2,639,826 | (2,639,826 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Related party notes payable | — | 14,639,826 | 14,639,826 | — | 14,639,826 | |||||||||||||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | 19,898,750 | — | 19,898,750 | (354,467 | ) | 19,544,283 | ||||||||||||||
| MEMBERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Class A Common units | — | 387,192 | 387,192 | — | 387,192 | |||||||||||||||
| Class B Preferred units | — | 1,898,469 | 1,898,469 | — | 1,898,469 | |||||||||||||||
| Class B-1 Preferred Units | — | 12,260,210 | 12,260,210 | — | 12,260,210 | |||||||||||||||
| Class C Profits Units | — | 15,887 | 15,887 | 8,601 | 24,488 | |||||||||||||||
| Members’ Equity | 14,561,758 | (14,561,758 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 82,180 | — | 82,180 | (49,296 | ) | 32,884 | ||||||||||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (8,426,774 | ) | — | (8,426,774 | ) | 17,439 | (8,409,335 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Total members’ equity | 6,217,164 | — | 6,217,164 | (23,256 | ) | 6,193,908 | ||||||||||||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND MEMBERS’ EQUITY | $ | 26,115,914 | $ | — | $ | 26,115,914 | $ | (377,723 | ) | $ | 25,738,191 | |||||||||
F-55
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
A reconciliation of the effects of the adjustments to the previously reported statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2018:
| As reported | Reclasses | As reclassed | Revision | Revised | ||||||||||||||||
| Costs and expenses | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating costs | $ | 1,842,091 | $ | (627,783 | ) | $ | 1,214,308 | $ | 7,607 | $ | 1,221,915 | |||||||||
| Research and development | 786,233 | — | 786,233 | — | 786,233 | |||||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative | 485,741 | 1,587,047 | 2,072,788 | 24,250 | 2,097,038 | |||||||||||||||
| Professional expenses | 959,264 | (959,264 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Total operating costs and expenses | 4,073,329 | — | 4,073,329 | 31,857 | 4,105,186 | |||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Other expense | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (4,073,329 | ) | $ | — | $ | (4,073,329 | ) | $ | (31,857 | ) | $ | (4,105,186 | ) | ||||||
A reconciliation of the effects of the adjustments to the previously reported statement of members’ equity for the year ended December 31, 2018:
| As reported | Reclasses | As reclassed | Revision | Revised | ||||||||||||||||
| Class A | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2017 | $ | 387,192 | $ | — | $ | 387,192 | $ | — | $ | 387,192 | ||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | $ | 387,192 | $ | — | $ | 387,192 | $ | — | $ | 387,192 | ||||||||||
| Class B | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2017 | $ | 1,898,470 | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 1,898,469 | $ | — | $ | 1,898,469 | |||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | $ | 1,898,470 | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 1,898,469 | $ | — | $ | 1,898,469 | |||||||||
| Class B-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2017 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Issuance of units | 12,260,209 | 1 | 12,260,210 | — | 12,260,210 | |||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | $ | 12,260,209 | $ | 1 | $ | 12,260,210 | $ | — | $ | 12,260,210 | ||||||||||
| Class C | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2017 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Issuance of units upon vesting of profit units | 15,887 | — | 15,887 | 8,601 | 24,488 | |||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | $ | 15,887 | $ | — | $ | 15,887 | $ | 8,601 | $ | 24,488 | ||||||||||
| Total members’ investment | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2017 | $ | 2,285,662 | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 2,285,661 | $ | — | $ | 2,285,661 | |||||||||
| Issuance of units | 12,260,209 | 1 | 12,260,210 | — | 12,260,210 | |||||||||||||||
F-56
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
| As reported | Reclasses | As reclassed | Revision | Revised | ||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of units upon vesting of profit units | 15,887 | — | 15,887 | 8,601 | 24,488 | |||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | $ | 14,561,758 | $ | — | $ | 14,561,758 | $ | 8,601 | $ | 14,570,359 | ||||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2017 | $ | 49,296 | $ | — | $ | 49,296 | $ | (49,296 | ) | $ | — | |||||||||
| Redeemable warrants | 32,884 | — | 32,884 | — | 32,884 | |||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | $ | 82,180 | $ | — | $ | 82,180 | $ | (49,296 | ) | $ | 32,884 | |||||||||
| Accumulated deficit | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2017 | $ | (4,353,445 | ) | $ | — | $ | (4,353,445 | ) | $ | 49,296 | $ | (4,304,149 | ) | |||||||
| Net loss | (4,073,329 | ) | — | (4,073,329 | ) | (31,857 | ) | (4,105,186 | ) | |||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | $ | (8,426,774 | ) | $ | — | $ | (8,426,774 | ) | $ | 17,439 | $ | (8,409,335 | ) | |||||||
| Total members’ equity | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2017 | $ | (2,018,487 | ) | $ | (1 | ) | $ | (2,018,488 | ) | $ | — | $ | (2,018,488 | ) | ||||||
| Issuance of units | 12,260,209 | 1 | 12,260,210 | — | 12,260,210 | |||||||||||||||
| Redeemable warrants | 32,884 | — | 32,884 | — | 32,884 | |||||||||||||||
| Issuance of units upon vesting of profit units | 15,887 | — | 15,887 | 8,601 | 24,488 | |||||||||||||||
| Net loss | (4,073,329 | ) | — | (4,073,329 | ) | (31,857 | ) | (4,105,186 | ) | |||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | $ | 6,217,164 | $ | — | $ | 6,217,164 | $ | (23,256 | ) | $ | 6,193,908 | |||||||||
A reconciliation of the effects of the adjustments to the previously reported statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2018:
| As reported | Reclasses | As reclassed | Revision | Revised | ||||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (4,073,329 | ) | $ | — | $ | (4,073,329 | ) | $ | (31,857 | ) | $ | (4,105,186 | ) | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity-based compensation | 15,887 | — | 15,887 | 8,601 | 24,488 | |||||||||||||||
| Issuance of warrants | 32,884 | — | 32,884 | — | 32,884 | |||||||||||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | (32,627 | ) | — | (32,627 | ) | (90,068 | ) | (122,695 | ) | |||||||||||
| Prepaid royalties | (1,000,000 | ) | — | (1,000,000 | ) | 1,000,000 | — | |||||||||||||
| Accounts payable | (1,964,024 | ) | (27,706 | ) | (1,991,730 | ) | 645,532 | (1,346,198 | ) | |||||||||||
| Accrued expenses | — | 89,926 | 89,926 | — | 89,926 | |||||||||||||||
| Payable to affiliate | 62,220 | (62,220 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Deferred research and development obligation | 1,000,000 | — | 1,000,000 | (1,000,000 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | (5,958,989 | ) | — | (5,958,989 | ) | 532,208 | (5,426,781 | ) | ||||||||||||
F-57
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
| As reported | Reclasses | As reclassed | Revision | Revised | ||||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Construction of plant | $ | (10,588,775 | ) | $ | — | $ | (10,588,775 | ) | $ | (532,208 | ) | $ | (11,120,983 | ) | ||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | (10,588,775 | ) | — | (10,588,775 | ) | (532,208 | ) | (11,120,983 | ) | |||||||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from promissory note from related parties | 6,343,239 | — | 6,343,239 | — | 6,343,239 | |||||||||||||||
| Payments on promissory note from related parties | (3,143,239 | ) | 1 | (3,143,238 | ) | — | (3,143,238 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from advances from related parties | 1,403,192 | (2 | ) | 1,403,190 | — | 1,403,190 | ||||||||||||||
| Bond issuance costs | (214,822 | ) | (1 | ) | (214,823 | ) | — | (214,823 | ) | |||||||||||
|
Proceeds from issuance of units | 12,260,209 | 1 | 12,260,210 | — | 12,260,210 | |||||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 16,648,579 | (1 | ) | 16,648,578 | — | 16,648,578 | ||||||||||||||
| Net increase in cash | 100,815 | (1 | ) | 100,814 | — | 100,814 | ||||||||||||||
| Cash, beginning of year | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Cash, end of year | $ | 100,815 | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 100,814 | $ | — | $ | 100,814 | |||||||||
| As reported | Reclasses | As reclassed | Revision | Revised | ||||||||||||||||
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-cash operating activities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest paid during the year, net of capitalized interest | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Non-cash investing activities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Additions to property, plant, and equipment in accounts payable | $ | (3,792,835 | ) | $ | — | $ | (3,792,835 | ) | $ | — | $ | (3,792,835 | ) | |||||||
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
As an emerging growth company (“EGC”), the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act (“JOBS Act”) allows the Company to delay adoption of new or revised accounting pronouncements applicable to public companies until such pronouncements are applicable to private companies. The Company has elected to use this extended transition period under the JOBS Act until such time the Company is no longer considered to be an EGC. The adoption dates discussed below reflect this election.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842), to increase transparency and comparability among organizations by recognizing lease assets and lease liabilities on the balance sheet and disclosing key information about leasing arrangements. In July 2018, ASU 2018-10, Codification Improvements to Topic 842, Leases, was issued to provide more detailed guidance and additional clarification for implementing ASU 2016-02. Furthermore, in July 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-11, Leases (Topic 842): Targeted Improvements, which provides an optional transition method in addition to the existing modified retrospective transition method by allowing a cumulative effect adjustment to the opening balance of retained earnings in the period of adoption. Furthermore, on June 3, 2020, the FASB deferred by one year the effective date of the new leases standard for private companies, private NFPs and public NFPs that have not yet issued (or made available for issuance) financial statements reflecting the new standard. These new leasing standards are effective for the Company beginning after December 15, 2021 and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the effect of the adoption of this guidance on the consolidated financial statements.
F-58
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments — Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses of Financial Instruments, which, together with subsequent amendments, amends the requirement on the measurement and recognition of expected credit losses for financial assets held. ASU 2016-13 is effective for the Company beginning December 15, 2022, including interim periods within those fiscal years, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently in the process of evaluating the effects of this pronouncement on the Company’s financial statements and does not expect it to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In June 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-07, “Compensation — Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvements to Nonemployee Share-Based Payment Accounting” (“ASU 2018-07”). ASU 2018-07 extends the scope of Topic 718 to include share-based payment transactions for acquiring goods and services from nonemployees. ASU 2018-07 amendments are effective for the Company beginning January 1, 2020 and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2020.The Company is currently evaluating the effect of the adoption of this guidance on the consolidated financial statements.
NOTE 3 — NOTES PAYABLE AND DEBT INSTRUMENTS
Secured Term Loan
On February 28, 2019, the Company entered into a subordinated debt agreement with Enhanced Capital Ohio Rural Fund, LLC. The agreement provides for principal of $1,000,000 with an interest of the U.S. Federal prime rate per annum. The interest rate will increase to the U.S. Federal prime rate plus 3% per annum subsequent to the completion of the Company’s upcoming bond financing. As of December 31, 2019, the interest rate was 4.75%. The first 24 months will be an “interest-only period” whereby the Company will only make accrued but unpaid interest payments at the end of each month. At the end of the interest- only period principal payments of $16,667 are payable on the last business day of each month. All unpaid principal and interest are payable on February 27, 2024, the maturity date of the agreement.
Until the closing of the bond indebtedness, the lender shall have first priority lien on all collateral. The term loan is secured by the Company’s receivables, contract rights, general intangibles, equipment, intellectual property, inventory, instruments, investment property, letters of credit and related collateral and proceeds.
The Company may at its option prepay the outstanding principal amount of the Loan. Any voluntary prepayment under the Loan prior to the two-year anniversary of the Closing date is subject to a prepayment penalty of 4.0% on the amount of such payment.
As defined within the agreement, the Company shall use the proceeds of the Term Loan (i) for working capital, (ii) capital spending, (iii) general corporate purposes, (iv) operations and hiring of incremental personnel in a manner consistent with the Ohio Rural Business Growth Act, and (v) to pay the fees, costs and expenses of Lender pursuant to the Loan agreement.
As of December 31, 2019, the outstanding balance on the term loan is $1,000,000, recorded within Notes payable in the consolidated balance sheets. The Company incurred $44,778 of interest cost during 2019. As the secured term loan was used to construct the Company’s property, plant and equipment, the interest costs incurred was capitalized within Property, Plant and Equipment as described in Note 2.
Promissory Notes
Koch Modular Process Systems Secured Promissory Note
On December 20, 2019, the Company entered into an agreement with Koch Modular Process Systems LLC (“KMPS”) to convert the current balance of Account Payable due to KMPS into a promissory note.
F-59
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
The Company issued a Secured Promissory Note for a principal amount of $1,677,489, with a maximum advance of funds up to $3,077,489. This loan provides the Company with the ability to draw additional funds by rolling invoices from KMPS into the balance. The rate of interest on the loan balance is 21% per annum through the month of November 2019 and 24% per annum for December 2019 and thereafter. The aggregate unpaid principal amount of the Loan, all accrued and unpaid interest, and all other amounts payable under this Note are due and payable on the maturity date. The loan maturity date is September 30, 2020 unless PureCycle repays the principal and accrued and unpaid interests from closing of the bond financing earlier.
The promissory note is secured by a first priority of the Company’s fixtures and personal property of every kind and all proceeds and products of each of the foregoing. The Company has the option to prepay the loan in whole or in part at any time or from time to time without penalty or premium by paying the principal amount to be prepaid together with accrued interest thereon to the date of prepayment. Any amount of principal prepaid may not be reborrowed.
As of December 31, 2019, the outstanding balance on the promissory note is $1,609,553 recorded within Notes payable — current in the consolidated balance sheets.
Denham-Blythe Company, Inc. Secured Promissory Note
On December 20, 2019, the Company and Denham-Blythe Company, Inc (“DB”) entered into an agreement to convert the current balance of Account Payable due to DB into a promissory note. The Company issued a Secured Promissory Note for a principal amount of $2,000,000. The rate of interest on the loan balance is 24% per annum for December 2019 and thereafter with interest on the loan payable monthly. The loan maturity date is September 30, 2020 unless PureCycle repays the principal and accrued and unpaid interests from closing of the bond financing.
The promissory note is secured by a first priority lien of the Company’s fixtures and personal property of every kind and all proceeds and products of each of the foregoing. The Company has the option to prepay the loan in whole or in part at any time or from time to time without penalty or premium by paying the principal amount to be prepaid together with accrued interest thereon to the date of prepayment. Any amount of principal prepaid may not be reborrowed.
As of December 31, 2019, the outstanding balance on the promissory note is $1,991,693, recorded within Notes payable — current in the consolidated balance sheets. The Company incurred $12,000 of interest cost during 2019. As the promissory note was used to construct the Company’s property, plant and equipment, the interest costs incurred was capitalized within Property, Plant and Equipment as described in Note 2.
Promissory Note to Related Parties
Innventus Fund I, LP
On July 19, 2019, the Company entered into Note and Warrant Financing agreement with Innventus Fund I, LP to obtain a $600,000 loan and warrant financing. The Negotiable Promissory Note has a maturity date of October 21, 2019, and an interest rate of 1-month LIBOR plus 8.00%. The aggregate unpaid principal amount of the loan and all accrued and unpaid interest is due on the maturity date.
As of December 31, 2019, the outstanding balance on this Note is $600,000, recorded within Related party notes payable — current in the consolidated balance sheets. The Company incurred $21,436 of interest cost during 2019. The effective interest rate is 14.29% as of December 31, 2019. Subsequent to December 31, 2019, the principal and all accrued and unpaid interest was paid on February 15, 2020.
See Note 6 for further information on the issuance of warrants.
F-60
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
Auto Now Acceptance Company, LLC
On May 5, 2017, the Company entered into a revolving line of credit facility (the “Credit Agreement”) with Auto Now Acceptance Company, LLC, a related party. The credit facility provided for a $13,292,000 revolving line of credit. The revolving line of credit was due on demand with interest payable monthly, bearing interest at a rate of 5.0%.
On May 3, 2018, the Credit Agreement was amended and restated in its entirety and secured by a Security Agreement dated May 3, 2018. The credit facility was increased to $14,000,000, bearing interest at a rate of LIBOR plus 6.12% per annum, payable monthly. The maturity date was extended to August 15, 2018. The Credit Agreement was also amended to state that the agreement is collateralized by substantially all assets of the Company.
On July 31, 2018, the Credit Agreement was amended to extend the maturity date to February 15, 2019. Under the agreement, the Auto Now’s advances of funds to the Company will cease on July 31, 2018. Upon execution of the amendment, the agreement was accounted for as a promissory note as the Company was no longer able to draw additional funds on the facility. As the cash flows were not substantially different, the Company accounted for the extension as a debt modification. No additional fees were incurred in connection with the extension, and consequently there was no impact on the carrying value of the debt. As the Company has defaulted the principal payment, the interest is accrued at the annual rate of a month LIBOR plus 10% per annum.
Subsequent to December 31, 2019, on May 29, 2020, the company extended the maturity date to June 30, 2021. See Note 13 for further information.
As of December 31, 2019, and 2018, the outstanding balance on the promissory note is $12,000,000 and $12,000,000, respectively, recorded within Related party notes payable in the consolidated balance sheets. The Company incurred $1,337,857 and $1,081,446 of interest cost during 2019 and 2018, respectively. As the promissory note was used to construct the Company’s property, plant and equipment, the interest cost incurred was capitalized within Property, Plant and Equipment as described in Note 2.
Advances from Related Parties
PureCycle received funding and support services from Innventure and Wasson Enterprise. During the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, PureCycle received $63,868 and $946,963 from Innventure. During the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, PureCycle received $0 and $456,227 from Wasson Enterprise. These advances were unsecured, non-interest bearing with no formal terms of repayment.
The outstanding balance due to Innventure as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 is $1,957,611 and $1,893,743, respectively, recorded within Related party notes payable — current in the consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2019 and recorded within a Related party notes payable in consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2018. The outstanding balance due to Wasson Enterprise is $746,083 as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, recorded within Related party notes payable — current in the consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2019 and recorded within Related party notes payable in consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2018.
The weighted average interest rate on notes payable — current and related party notes payable — current is 12.95% as of December 31, 2019.
F-61
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
Principal repayments due on the Notes payable and Related party notes payable over the next five years are as follows:
| Years ending December, 31 | Amount | |||
| 2020 | $ | 6,904,940 | ||
| 2021 | 12,150,003 | |||
| 2022 | 200,004 | |||
| 2023 | 200,004 | |||
| 2024 | 449,989 | |||
| Thereafter | — | |||
| Total | $ | 19,904,940 | ||
NOTE 4 — MEMBERS’ EQUITY
The Company operates subject to the terms and conditions of the amended and restated PureCycle Technologies LLC, Limited Liability Company Agreement (the “LLC Agreement”) dated September 7, 2018. The LLC Agreement was subsequently amended on August 28, 2019.
The LLC Agreement provides for overall management and control of the Company to be vested in the Board of Managers (the “Board”). The members’ interests are represented by four classes: Class A units, Class B preferred units, Class B-1 preferred units and Class C units. Members owning a majority of the Class A units, Class B preferred units and Class B-1 preferred units are required to elect managers to the Board to serve the Class A unit, Class B preferred unit and Class B-1 preferred unit member interests. Each holder of Class A units, Class B preferred units, and Class B-1 preferred units (“Voting Members”) shall be entitled to one vote per unit held. The holders of Class C units do not have voting rights in respect to their units held. No Member shall be liable for any debts or losses of capital or profits of the Company or be required to guarantee the liabilities of the Company.
Class A Units
The Board authorized up to 2,581,282 Class A units. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, 2,581,282 units are issued and outstanding. No additional Class A units are issuable under the LLC Agreement.
These units were issued to the initial investors of the Company for no cash consideration. Therefore, the Company determined the fair value of the units utilizing the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The fair value of the Class A units granted was determined to be $0.15 per unit.
Class B Preferred Units
The Board authorized up to 1,938,369 Class B preferred units. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, there are 1,727,843 Class B preferred units issued and outstanding. No additional Class B preferred units are issuable under the LLC Agreement. The Class B preferred unit members are entitled to receive a cumulative preferred return at the rate of eight percent (8%) per year on the sum of the unreturned preferred capital and unpaid preferred return through the date of such distribution.
Class B-1 Preferred Units
On August 28, 2019 the Company amended its LLC agreement to increase the number of authorized Class B-1 preferred units to 1,063,688. In 2019 and 2018, the Company issued 303,701 and 326,026 Class B-1 preferred units at a purchase price of $37.61 per B-1 Unit. On October 29, 2019, the Company entered into a Class B-1 Preferred Unit Purchase Agreement with a third party contractors to exchange an outstanding accounts payable balance of $500,000 into 13,296 Class B-1 preferred units at a purchase price of $37.61 per B-1 unit.
F-62
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
As of December 31, 2019, and 2018, there are 629,727 and 326,026 Class B-1 preferred units issued and outstanding, respectively. The Class B-1 preferred unit members are entitled to receive a cumulative preferred return at the rate of eight percent (8%) per year on the sum of the unreturned preferred capital and unpaid preferred return through the date of such distribution.
A summary of the accumulated but unpaid distributions for the Class B and Class B-1 preferred units as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 is as follows:
| Class B | Class B-1 | |||||||
| Accumulated and unpaid, January 1, 2018 | $ | 270,109 | $ | — | ||||
| Accumulated | 148,809 | 279,971 | ||||||
| Distributed | — | — | ||||||
| Accumulated and unpaid, December 31, 2018 | 418,918 | 279,971 | ||||||
| Accumulated | 160,713 | 1,574,354 | ||||||
| Distributed | — | — | ||||||
| Accumulated and unpaid, December 31, 2019 | $ | 579,631 | $ | 1,854,325 | ||||
Class C Units
The Board authorized up to 719,029 Class C units. Class C preferred units are non-voting profits interest incentive units pursuant to individual award agreements determined by the Voting Members at the time of the awards, which set forth such additional terms and conditions, including the vesting and forfeiture terms. Class C Units or any other Units that the Company issued as profits interests are considered as Distribution Threshold Unit and are entitled only to its Sharing Percentage of excess distributions over and above its Distribution Threshold. During 2019 and 2018, the Company granted 233,452 and 280,219 of Class C incentive units, respectively, pursuant to the Company’s equity incentive plan. See note 5 for further information. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, 435,679 and 75,830 Class C units are issued and outstanding, respectively.
Distribution Preferences
Distributions are authorized at the discretion of the Board. Distributions shall be made first to the holders of Class B-1 preferred units and Class B preferred units, ratably among such holders based on the relative aggregate unpaid preferred return with respect to all outstanding preferred units held by each such holder immediately prior to such distribution, until the aggregate unpaid return for the preferred units has been reduced to $0.
Distributions shall be made second to the holders of Class B-1 preferred units and Class B preferred units, ratably among such holders based on the relative aggregate unreturned preferred capital with respect to all outstanding preferred units held by each such holder immediately prior to such distribution, until the aggregate unreturned capital for the preferred units has been reduced to $0.
Distributions will then be made to all members in proportion to their ownership percentages.
Liquidation Preferences
In the event of the dissolution of the Company, the Company’s cash and proceeds obtained from the disposition of the Company’s noncash assets shall be distributed. Distributions shall be made first to the Company’s creditors, including members who are creditors, to satisfy the liabilities of the Company. The remaining cash will then be distributed to the members following the normal distribution preferences described above.
F-63
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
NOTE 5 — EQUITY-BASED COMPENSATION
The Company established an equity incentive plan (the “Plan”) on June 1, 2018 to provide for the grant of Class C incentive units, characterized as profits interests, to certain executives, directors, key employees, and non-employee service providers of the Company. The aggregate number of units that can be granted under the Plan is subject to the authorized amount of Class C Units per the LLC Agreement,
which is 719,029 total units.
On September 7, 2018, the Plan was subsequently amended to shorten the vesting period to 25% vesting immediately upon issuance with the remaining units vesting in equal monthly installments over the next three years. Six employees were impacted by this modification.
The units issued pursuant to the Plan are time-based and vest over the period defined in each individual grant agreement or upon a change of control event as defined in the Plan. The distribution threshold is determined by the Board at the time units are granted. The Company has the option to repurchase all vested units upon a unitholder’s termination of employment or service with the Company.
The Company recognizes compensation expense for the units equal to the fair value of the equity- based compensation awards and is recognized on a straight-line basis over the vesting period of such awards. The fair value of the units is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model using the following assumptions:
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Expected annual dividend yield | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | ||||
| Expected volatility | 42.1 – 67.2 | % | 76.0 | % | ||||
| Risk-free rate of return | 1.55 – 2.0 | % | 1.40 | % | ||||
| Expected option term (years) | 1.0 - 5.0 | 5.0 | ||||||
The expected term of the units granted is determined based on the period of time the units are expected to be outstanding. The risk-free rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant. The expected volatility was based on the Company’s capital structure and volatility of similar entities referred to as guideline companies. In determining similar entities, the Company considered industry, stage of life cycle, size and financial leverage. The dividend yield on the Company’s units is assumed to be zero since the Company has not historically paid dividends. The fair value of the underlying Company units was determined using the backsolve method.
A summary of incentive unit activity for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 is as follows:
| Number of units | Weighted average grant date fair value | Weighted average remaining recognition period (years) | ||||||||||
| Non-vested at January 1, 2018 | — | $ | — | |||||||||
| Granted | 280,219 | 0.21 | ||||||||||
| Vested | (75,830 | ) | 0.21 | |||||||||
| Redeemed | — | — | ||||||||||
| Forfeited | — | — | ||||||||||
| Non-vested at December 31, 2018 | 204,389 | 0.21 | 2.12 | |||||||||
| Granted | 233,452 | 17.87 | ||||||||||
| Vested | (360,602 | ) | 11.26 | |||||||||
| Forfeited | (4,267 | ) | 0.21 | |||||||||
| Non-vested at December 31, 2019 | 72,972 | $ | 2.09 | 1.74 | ||||||||
F-64
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
Total equity-based compensation cost for 2019 and 2018 totaled $4,048,633 and $24,488, respectively, and is recorded within the selling, general and administrative expenses and research and development on the consolidated statement of operations. The total unrecognized compensation cost of non-vested awards not yet recognized for 2019 and 2018 is $157,297 and $34,220, respectively.
NOTE 6 — REDEEMABLE WARRANTS
Warrants issued to purchase Class B Preferred Units
On October 16, 2015, the Company issued a Unit Purchase Warrant to P&G in connection with the patent licensing agreement described in Note 11, for 210,526 warrant units at an exercise price of $1 per unit, allowing P&G to purchase a variable number of Class B preferred units during the exercise period of April 15, 2019 through April 15, 2024. The warrants were determined to vest at the start of the exercise period. The number of units available to P&G to purchase is equal to an amount that initially represents 5% of all outstanding equity of the Company on a fully diluted basis. Additionally, the warrant agreement contains an anti-dilution provision, which states that the number of warrants exercisable upon full exercise of the warrant will be subject to adjustment, such that the ownership percentage is not reduced below 2.5% sharing percentage in the Company, on a fully diluted basis.
The Company determined the warrants issued are liability classified under ASC 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity. Accordingly, the warrant units will be held at their initial fair value and remeasured at fair value at each subsequent reporting date.
The Company has determined its warrant liability to be a Level 3 fair value measurement and has used the Black-Scholes option pricing model to calculate its fair value using the following assumptions:
| Expected annual dividend yield | 0.0 | % | ||
| Expected volatility | 42.7 – 67.2 | % | ||
| Risk-free rate of return | 6 – 2.0 | % | ||
| Expected option term (years) | 1.0 – 5.0 |
The expected term of the units granted are determined based on the period of time the units are expected to be outstanding. The risk-free rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant. The expected volatility was based on the Company’s capital structure and volatility of similar entities referred to as guideline companies. In determining similar entities, the Company considered industry, stage of life cycle, size and financial leverage. The dividend yield on the Company’s units is assumed to be zero since the Company has not historically paid dividends. The fair value of the underlying Company units was determined using the backsolve method.
A summary of the Class B warrant activity for the years ended December 31, 2019 is as follows:
| Number
of warrants | Weighted average exercise price | Weighted average grant date fair value | Weighted average remaining contractual term (years) | |||||||||||||
| Outstanding at January 1, 2019 | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||
| Granted | 210,526 | 1.00 | 30.63 | |||||||||||||
| Exercised | — | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2019 | 210,526 | $ | 1.00 | $ | 30.63 | 4.29 | ||||||||||
| Exercisable | 210,526 | |||||||||||||||
F-65
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
The Company recognized expense of $6,408,411 for 2019, in connection with these warrants, which was recorded within selling, general and administrative on the consolidated statement of operations and within redeemable warrants on the consolidated balance sheets.
* There was no activity during 2018
Warrants issued to purchase Class B-1 Preferred Units
On June 5, 2019, in connection with Class B-1 Preferred Unit Purchase Agreement with a related party, the Company issued a Unit Purchase Warrant for 7,978 warrant units at an exercise price of $37.61, allowing the Company to purchase a variable number of Class B-1 Preferred units during the exercise period of June 5, 2019 through June 4, 2024.
The Company determined the warrants are not a freestanding instrument under ASC 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity. Also, the warrants are determined to be clearly and closely related to the Class B-1 Preferred Units under ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging. Accordingly, they are not recorded in the financial statements until exercised.
On July 22, 2019, in connection with a Bridge Note and Warrant Financing agreement with Innventus Fund I, LP, the Company issued a Unit Purchase Warrant for 4,787 warrant units at an exercise price of $37.61, allowing the Company to purchase a variable number of Class B-1 Preferred units during the exercise period of July 22, 2019 through July 22, 2024.
The Company determined the warrants issued are equity classified under ASC 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity. Accordingly, the warrant units will be held at their initial fair value with no subsequent remeasurement.
The Company has determined its warrant to be a Level 3 fair value measurement and has used the Black- Scholes option pricing model to calculate its fair value using the following assumptions:
| Expected annual dividend yield | 0.0 | % | ||
| Expected volatility | 54.2 – 63.6 | % | ||
| Risk-free rate of return | 1.5 – 1.7 | % | ||
| Expected option term (years) | 4.4 - 4.7 |
A summary of the Class B-1 warrant activity for the years ended December 31, 2019 is as follows:
| Number
of warrants | Weighted average exercise price | Weighted average grant date fair value | Weighted average remaining contractual term (years) | |||||||||||||
| Outstanding at January 1, 2019 | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||
| Granted | 4,787 | 37.61 | 15.52 | |||||||||||||
| Exercised | — | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2019 | 4,787 | $ | 37.61 | $ | 15.52 | 4.56 | ||||||||||
| Exercisable | 4,787 | |||||||||||||||
The Company recognized expense of $74,294 for 2019, in connection with these warrants, which was recorded within selling, general and administrative on the consolidated statement of operations and within additional paid-in capital on the consolidated balance sheets.
* There was no activity during 2018
F-66
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
Warrants issued to purchase Class C Units
On June 29, 2018, the Board approved the issuance of warrants to RTI under the terms of a professional services agreement to purchase an aggregate of 143,619 of the Company’s Class C units at an aggregated exercise price of $37.605 per unit. The warrants vested immediately upon issuance and expire on June 29, 2023 or upon a change in control event, as defined in the warrant agreement. The Company determined the warrants issued are equity classified under ASC 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity. Accordingly, the warrant units will be held at their initial fair value with no subsequent remeasurement.
The Company has determined its warrant to be a Level 3 fair value measurement and used the Black- Scholes option-pricing model using the following assumptions:
| Expected annual dividend yield | 0.0 | % | ||
| Expected volatility | 50.0 | % | ||
| Risk-free rate of return | 2.82 | % | ||
| Expected option term (years) | 5.0 |
The expected term of the units granted are determined based on the period of time the units are expected to be outstanding. The risk-free rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant. The expected volatility was based on the Company’s capital structure and volatility of similar entities referred to as guideline companies. In determining similar entities, the Company considered industry, stage of life cycle, size and financial leverage. The dividend yield on the Company’s units is assumed to be zero since the Company has not historically paid dividends. The fair value of the underlying Company units was determined using the backsolve method.
A summary of the Class C warrant activity for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 is as follows:
| Number
of warrants | Weighted average exercise price | Weighted average grant date fair value | Weighted
average remaining contractual term (years) | |||||||||||||
| Outstanding at January 1, 2018 | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||
| Granted | 143,619 | 37.61 | 0.23 | |||||||||||||
| Exercised | — | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2018 | 143,619 | $ | 37.61 | $ | 0.23 | 4.5 | ||||||||||
| Granted | — | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Exercised | — | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2019 | 143,619 | $ | 37.61 | $ | 0.23 | 3.5 | ||||||||||
| Exercisable | 143,619 | |||||||||||||||
The Company recognized expense of $32,884 for 2018, in connection with these warrants, which was recorded within selling, general and administrative on the consolidated statement of operations and within additional paid-in capital on the consolidated balance sheets.
NOTE 7 — RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
The Company is majority owned by WE-Innventure. WE-Innventure, in turn, is majority owned by Innventure LLC (“Innventure”) and WE-INN LLC (“WE-INN”). WE-INN holds a minority interest in Innventure, and WE-INN is majority owned by Wasson Enterprises.
F-67
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
WE-Innventure holds majority interests in the following legal entities: Innventure Management Services LLC, Innventure GP LLC, and Aeroflexx LLC. WE-Innventure has a controlling financial interest over each of the legal entities within the group and has decision-making ability over the group whereby significant managerial and operational support is provided by WE-Innventure personnel. This includes certain executive management and officers of PureCycle and other legal entities that are employees or officers of WE-Innventure. The legal entities, including PureCycle, are deemed to be under common control by WE Innventure. There were no transactions between PureCycle and its affiliates, Innventure GP LLC and Aeroflexx LLC, during the years ended December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018.
Innventure Management Services LLC, Innventure, and Wasson Enterprises provide significant managerial support to the other legal entities below WE-Innventure, including PureCycle.
Management services
During the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, PureCycle reimbursed Innventure Management Services LLC for certain expenses related to certain expenses incurred on its behalf. For the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company paid $579,620 and $537,606, respectively, to Innventure Management Services LLC related to this arrangement, which was included in selling, general and administrative expenses in the consolidated statement of operations. As of December 31, 2019, and 2018, the Company owed Innventure Management Services LLC $17,521 and $62,220, respectively, related to this arrangement, which is classified as a current liability on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
Notes payable and debt instruments
On May 5, 2017, the Company entered into a revolving line of credit facility with Auto Now Acceptance Company.
On July 19, 2019, the Company entered into Note and Warrant Financing agreement with Innventus Fund I, LP to obtain a $600,000 loan and warrant financing.
Since the inception of the company, PureCycle has been receiving advances from Innventure, LLC and Wasson Enterprises.
Refer to Note 3 for notes payable and debt instruments to related parties.
Leases
The Company leases its office and production facilities from Innventure, as described in Note 8.
NOTE 8 — COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Operating leases
The Company leases its offices under non-cancelable operating leases which terminate July 31, 2043. Certain leases contain escalation clauses and renewal options. In 2018, the Company entered into a 25-year operating lease with Innventure, a related party, for the Company’s primary office space in Lawrence County, Ohio. The initial term of the lease in Lawrence County, Ohio, terminates on July 31, 2043. Upon the completion of the initial term the Lessor, Innventure LLC, grants the option to extend the term for five successive periods of five years each.
F-68
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
Future minimum lease payments under non-cancellable operating leases for the years ending December 31 are as follows:
| 2020 | $ | 336,000 | ||
| 2021 | 336,000 | |||
| 2022 | 336,000 | |||
| 2023 | 336,000 | |||
| 2024 | 336,000 | |||
| Thereafter | 6,244,000 | |||
| Total future minimum lease payments | $ | 7,924,000 |
Rent expense totaled $421,700 and $290,809 for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018.
NOTE 9 — NET LOSS PER UNIT
The Company follows the two-class method when computing net loss per common units when units are issued that meet the definition of participating securities. The two-class method requires income available to common unitholders for the period to be allocated between common and participating securities based upon their respective rights to receive dividends as if all income for the period had been distributed. The two- class method also requires losses for the period to be allocated between common and participating securities based on their respective rights if the participating security contractually participates in losses. As holders of participating securities do not have a contractual obligation to fund losses, undistributed net losses are not allocated to Class B, Class B-1 and Class C Units for purposes of the loss per unit calculation.
Presented in the table below is a reconciliation of the numerator and denominator for the basic and diluted earnings per unit (“EPU”) calculations for the year ended:
| Numerator: | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to PureCycle Technologies | $ | (19,312,718 | ) | $ | (4,105,186 | ) | ||
| Less cumulative earnings to preferred shareholder | 2,433,956 | 698,889 | ||||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders | $ | (21,746,674 | ) | $ | (4,804,075 | ) | ||
| Denominator: | ||||||||
| Weighted average common units outstanding, basic and diluted | 2,581,282 | 2,581,282 | ||||||
| Net loss per unit attributable to common stockholder, basic and diluted | $ | (8.42 | ) | $ | (1.86 | ) | ||
The weighted-average outstanding common unit equivalents were excluded from the computation of diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders for the periods presented because including them would have been anti-dilutive. These units include vested but not-exercised warrants and non-vested profits interest units.
F-69
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
NOTE 10 — PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT
Presented in the table below are the major classes of property, plant and equipment by category as of dates:
| As of December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||
| Cost | Accumulated Depreciation | Net Book Value | ||||||||||
| Building | $ | 9,703,674 | $ | 122,384 | $ | 9,581,290 | ||||||
| Machinery and equipment | 15,670,238 | 770,590 | 14,899,648 | |||||||||
| Fixtures and Furnishings | 104,484 | 7,463 | 97,021 | |||||||||
| Construction in process | 5,832,135 | — | 5,832,135 | |||||||||
| Total property, plant and equipment | $ | 31,310,531 | $ | 900,437 | $ | 30,410,094 | ||||||
| As of December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||
| Cost | Accumulated Depreciation | Net Book Value | ||||||||||
| Building | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
| Machinery and equipment | — | — | — | |||||||||
| Fixtures and Furnishings | — | — | — | |||||||||
| Construction in process | 25,059,806 | — | 25,059,806 | |||||||||
| Total property, plant and equipment | $ | 25,059,806 | $ | — | $ | 25,059,806 | ||||||
On March 28, 2019, the Company sold equipment for cash proceeds of $110,000. The net book value of this equipment was $365,650.
Depreciation expense is recorded within the operating costs in the consolidated statements of operations and amounted to $900,437 for the year ended December 31, 2019. There is no depreciation expense as of December 31, 2018.
NOTE 11 — DEVELOPMENT PARTNER ARRANGEMENTS
License Agreement
On October 16, 2015, the Company entered into a patent license agreement with P&G. The agreement outlines three phases with specific deliverables for each phase. During Phase 1 of the agreement, P&G provides the Company with up to one full-time employee to assist in the execution of the Company’s research and development activities. During Phase 2, P&G provides up to two full-time employees to assist in the execution of the Company’s research and development activities. During Phases 1 and 2 of the agreement, the Company is required to make payments to P&G in the amount of $100,000 and $200,000, respectively, every six months. These payments are amortized ratably to research and development expense over each six-month period. In April 2019, the Company elected to enter into Phase 3 of the agreement and prepaid a royalty payment in the amount of $2,000,000, which will be reduced against future royalties payable as sales occur. Phase 3 of the agreement relates to the commercial manufacture period for the manufacture of the licensed product. This phase includes the construction of the first commercial plant for the manufacture of the licensed product, details on the commercial sales capacity and the pricing of the product to P&G and third parties. Where the Company has made royalty payments to its product development partners, the Company expenses such payments as incurred unless it has determined that is it probable that the such prepaid royalties have future economic benefit to the Company. In such cases prepaid royalties will be reduced as royalties would otherwise be due to the partners.
F-70
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
As of December 31, 2019, the Company is in Phase 3 of the agreement and has recorded $2,000,000 within Prepaid royalties on the consolidated balance sheets. As of December 31, 2018, the Company was in Phase 2 of the agreement and had $133,000 prepaid license costs recorded within Prepaid expenses and other current assets on the consolidated balance sheets. For the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company recorded $333,000 and $400,000, respectively, of research and development expenses in connection with this agreement.
Strategic Alliance Agreement
On December 13, 2018, the Company entered into a strategic alliance agreement with Nestec Ltd. (“Nestle”), which expires on December 31, 2023. Upon execution of the agreement, Nestle committed to provide $1,000,000 to the Company to fund further research and development efforts. The funding provided by Nestle may be convertible, in whole or in part, into a prepaid product purchase arrangement at Nestle’s option, upon the time of product delivery beginning in 2020. Additionally, in the event that the research and development efforts are not successful by December 31, 2020, up to 50% of the funding may be convertible into a 5-year term loan obligation, payable to Nestle at an interest rate equivalent to the U.S. prime rate.
The Company received the funding from Nestle on January 8, 2019. As of December 31, 2019, the Company has recorded $1,000,000 in Deferred research and development obligation. Recognition related to the funding received will be deferred until it is probable that Nestle will not exercise their option. If the prepaid product purchase option is exercised, the obligation will be recognized as an adjustment to the transaction price of future product sales (e.g., net revenue presentation). If the option is not exercised, or in the case of development efforts not being successful, any amounts not converted to a loan obligation, the residual balance will be recognized as a reduction to research and development costs.
NOTE 12 — FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
Fair value is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date and sets out a fair value hierarchy. The fair value hierarchy gives the highest priority to quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3). Inputs are broadly defined as assumptions market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability. Assets and liabilities carried at fair value are classified and disclosed in one of the following three categories:
Level 1— Unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that the reporting entity has the ability to access at the measurement date. The type of investments included in Level 1 includes listed equities.
Level 2 — Inputs other than quoted prices within Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, and fair value is determined through the use of models or other valuation methodologies. Investments that are generally included in this category include corporate bonds and loans, less liquid and restricted equity securities, and certain over-the-counter derivatives. A significant adjustment to a Level 2 input could result in the Level 2 measurement becoming a Level 3 measurement.
Level 3 — Inputs are unobservable for the asset or liability and include situations where there is little, if any, market activity for the asset or liability. The inputs into the determination of fair value are based upon the best information in the circumstances and may require significant management judgment or estimation. Investments that are included in this category generally include equity and debt positions in private companies.
Liabilities measured and recorded at Fair Value on a recurring basis
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company’s financial liabilities measured and recorded at fair value on a recurring basis were classified within the fair value hierarchy as follows:
F-71
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P&G warrants | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 6,408,411 | $ | 6,408,411 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| $ | — | $ | — | $ | 6,408,411 | $ | 6,408,411 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||||||||
Changes in Level 3 liabilities measured at fair value for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 are as follows:
| Fair
value (Level 3) | ||||
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | $ | — | ||
| Fair value of P&G warrants at inception | 6,448,411 | |||
| Change in fair value | (40,000 | ) | ||
| Balance at December 31, 2019 | $ | 6,408,411 | ||
There were no transfers between the levels during 2019 or 2018.
The fair value of the warrants described in Note 6 was determined using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, which is an income approach.
Assets and liabilities recorded at carrying value
In determining the appropriate levels, the Company performs a detailed analysis of the assets and liabilities that are subject to fair value measurements.
NOTE 13 — SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
In connection with the preparation of the consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2019, management has evaluated events through August 25 2020, to determine whether any events required recognition or disclosure in the consolidated financial statements. The following subsequent events were identified through the date of these consolidated financial statements:
On February 15, 2020, the Company repaid the promissory note to Innventus Fund I, LP for principal of $600,000 and all accrued unpaid interests.
On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization declared the coronavirus outbreak of 2019 (“COVID-19”) a pandemic. With the global spread of the COVID-19 pandemic and resulting shelter-in- place orders covering the Company’s corporate headquarters, primary our Ohio plant operations, and employees, the Company has implemented policies and procedures to continue its operations under minimum business operations guidelines. The extent to which the COVID-19 pandemic impacts the Company’s business, financial condition or results of operations will depend on future developments, which are highly uncertain and cannot be accurately predicted.
On January 28, 2020 and March 24, 2020, the Company repaid advances from Innventure of $1,950,000 in full.
On March 26, 2020, the Company repaid advances from Wasson Enterprise of $375,000 and assigned the remaining outstanding balance from Wasson Enterprise to WE-Innventure LLC.
On May 4, 2020, the Company entered into Paycheck Protection Program (the “Program”) Term Note with PNC Bank to obtain $313,500. This Note is issued pursuant to the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act’s (the “CARES Act”) (P.L. 116-136) Paycheck Protection Program. During a period from May 4, 2020 to November 4, 2020 (“Deferral Period”), interests on the outstanding principal balance will accrue at the Fixed Rate of 1% per annum, but neither principal nor interest shall be due during the Deferral Period. At the end of the Deferral Period, the outstanding principal of the loan Facility that is not forgiven under the program shall convert to an amortizing term loan. All or a portion of this Facility may be forgiven in accordance with the program requirement. The unforgiven portion of the PPP loan is payable over two years at an interest rate of 1%, with a deferral of payments for the first six months.
F-72
PureCycle Technologies LLC
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
December 31, 2019 and 2018
On May 29, 2020, the Company executed a Second Amended and Restated the Security Agreement and entered into a Third Amended and Restated Promissory Note agreement to extend the financing on the loan from Auto Now Acceptance Company, LLC. The agreement extended the maturity date of the loan to June 30, 2021 and adjusted the interest rate on the third amended loan agreement. The security interests include inventory, equipment, accounts receivables and all the Company’s assets. The interest rate within the amendment increased as follows:
| • | The annual rate of the 1-month LIBOR in U.S. dollars plus 6.12% adjusted daily, from May 3, 2018 through May 18, 2020 |
| • | 12% per annum from May 19, 2020 through August 31, 2020 |
| • | 16% per annum from September 1, 2020 through December 31, 2020 |
| • | 24% per annum from January 1, 2021 through June 30, 2021 |
As of August 25 2020, the Company issued 56,450 profit units in accordance with The Plan as described in Note 5. As of August 25 2020, the Company has raised net proceeds of $17,068,273 from individual investors from the sale of Class B-1 preferred units.
The Company was awarded a $200,000 grant on May 21, 2018 by the Southern Ohio Agricultural & Community Development Foundation (“SOACDF”). The grant was to be dispersed at two points in time, 1) fifty percent (50%) of the funds awarded to be dispersed upon execution of the agreement and once contingencies were met, and 2) the remaining fifty percent (50%) was be paid after the Ohio project was initially complete. The Ohio project was considered initially complete once it met certain requirements outlined in the agreement, which includes; a) physical completion of the FEU, b) a required number of jobs were created and retained for a minimum of six months, c) project completion and request form was received by SOACDF, and d) site monitoring demonstrates compliance. The first portion of the grant was received on May 18, 2018 in the amount of $100,000. In June 2020, the Company received the second $100,000 portion of the total grant amount of $200,000. The funds were to be allocated solely for the purchase of the FEU.
The Company expects to obtain additional funding through a bond financing and is actively seeking to raise additional equity financing to be used in connection with the construction and equipping certain solid waste disposal facilities. The Company is working with the investment bank Piper Sandler and issuing three series of bonds of approximately, (i) $280 million of senior tax exempt bonds (ii) $20 million of subordinate tax exempt bonds, and (iii) $10 million of subordinate taxable bonds.
The Company is not aware of any additional subsequent events, other than those described above, that would require recognition or disclosure in the consolidated financial statements.
F-73
PART II – INFORMATION NOT REQUIRED IN PROSPECTUS
Item 13. Other Expenses of Issuance and Distribution
The following table sets forth the expenses in connection with this registration statement. All of such expenses are estimates, other than the filing fees payable to the Securities and Exchange Commission.
| Amount to be paid |
||||
| SEC registration fee | $ | 28,502.38 | ||
| Accounting fees and expenses | $ | * | ||
| Legal fees and expenses | $ | * | ||
| Printing and miscellaneous expenses | $ | * | ||
| Total | $ | * | ||
| * | To be completed by amendment |
Item 14. Indemnification of Directors and Officers
Section 145(a) of the DGCL provides, in general, that a corporation may indemnify any person who was or is a party or is threatened to be made a party to any threatened, pending or completed action, suit or proceeding, whether civil, criminal, administrative or investigative (other than an action by or in the right of the corporation), because he or she is or was a director, officer, employee or agent of the corporation, or is or was serving at the request of the corporation as a director, officer, employee or agent of another corporation, partnership, joint venture, trust or other enterprise, against expenses (including attorneys’ fees), judgments, fines and amounts paid in settlement actually and reasonably incurred by the person in connection with such action, suit or proceeding, if he or she acted in good faith and in a manner he or she reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the best interests of the corporation and, with respect to any criminal action or proceeding, had no reasonable cause to believe his or her conduct was unlawful.
Section 145(b) of the DGCL provides, in general, that a corporation may indemnify any person who was or is a party or is threatened to be made a party to any threatened, pending or completed action or suit by or in the right of the corporation to procure a judgment in its favor because the person is or was a director, officer, employee or agent of the corporation, or is or was serving at the request of the corporation as a director, officer, employee or agent of another corporation, partnership, joint venture, trust or other enterprise, against expenses (including attorneys’ fees) actually and reasonably incurred by the person in connection with the defense or settlement of such action or suit if he or she acted in good faith and in a manner he or she reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the best interests of the corporation, except that no indemnification shall be made with respect to any claim, issue or matter as to which he or she shall have been adjudged to be liable to the corporation unless and only to the extent that the Court of Chancery or other adjudicating court determines that, despite the adjudication of liability but in view of all of the circumstances of the case, he or she is fairly and reasonably entitled to indemnity for such expenses that the Court of Chancery or other adjudicating court shall deem proper.
Section 145(g) of the DGCL provides, in general, that a corporation may purchase and maintain insurance on behalf of any person who is or was a director, officer, employee or agent of the corporation, or is or was serving at the request of the corporation as a director, officer, employee or agent of another
corporation, partnership, joint venture, trust or other enterprise against any liability asserted against such person and incurred by such person in any such capacity, or arising out of his or her status as such, whether or not the corporation would have the power to indemnify the person against such liability under
Section 145 of the DGCL.
The Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, which will become effective upon consummation of the Business Combination, will provide that no Director of the Combined Company will be personally liable to the Combined Company or its stockholders for or with respect to any breach of fiduciary duty or other act or omission as a director of the Combined Company. In addition, the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will provide that if the DGCL is amended to authorize the further elimination or limitation of the liability of directors, then the liability of a director of the Combined Company shall be eliminated or limited to the fullest extent permitted by the DGCL, as so amended.
127
The Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will further provide that any repeal or modification of such article by its stockholders or amendment to the DGCL will not adversely affect any right or protection existing at the time of such repeal or modification with respect to any acts or omissions occurring before such repeal or modification of a director serving at the time of such repeal or modification.
The Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will provide that it will indemnify each person who was or is a party or threatened to be made a party to any threatened, pending or completed action, suit or proceeding whether civil, criminal, administrative or investigative (other than an action by or in the right of the Combined Company) by reason of the fact that he or she is or was, or has agreed to become, the Combined Company’s director or officer, or is or was serving, or has agreed to serve, at the Combined Company’s request as a director, officer, partner, employee or trustee of, or in a similar capacity with, another corporation, partnership, joint venture or other enterprise (all such persons being referred to as an Indemnitee), or by reason of any action alleged to have been taken or omitted in such capacity, against all Indemnifiable Losses if such Indemnitee acted in good faith and in a manner he or she reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the Combined Company’s best interests, and, with respect to any criminal action or proceeding, he or she had no reasonable cause to believe his or her conduct was unlawful, subject to limited exceptions. The Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will also provide that it will advance expenses to Indemnitees in connection with a legal proceeding, subject to limited exceptions.
In connection with the Business Combination, the Combined Company will enter into indemnification agreements with each of its directors and executive officers. These agreements will provide that the Combined Company will indemnify each of its directors and such officers to the fullest extent permitted by law and its charter and its bylaws.
The Combined Company will also maintain a general liability insurance policy, which will cover certain liabilities of directors and officers of the Combined Company arising out of claims based on acts or omissions in their capacities as directors or officers.
Item 15. Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
Private Placements in Connection with ROCH IPO
In May 2019, CR Financial Holdings, Inc., an entity affiliated with ROCH, purchased an aggregate of 100 shares of Common Stock for an aggregate purchase price of $25,000. On May 2, 2019, CR Financial Holdings, Inc. transferred all of its shares to Roth, Craig-Hallum and officers and directors of Roth and Craig-Hallum for the same price per share that it originally paid for such shares.
Such initial stockholders purchased an aggregate of 265,000 ROCH Units in connection with the IPO in exchange for $2,650,000 in the aggregate.
The sales of the above securities were exempt from the registration requirements of the Securities Act in reliance on the exemptions afforded by Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act. Other than the IPO, no sales involved underwriters, underwriting discounts or commissions or public offerings of securities of the registrant.
PIPE Placement
In connection with entering into the Merger Agreement, ROCH entered into the Subscription Agreements, each dated as of November 16, 2020, with the PIPE Investors, pursuant to which, among other things, ROCH agreed to the PIPE Placement.
The PIPE Placement closed immediately prior to the Business Combination on the Closing Date. The shares of Common Stock issued to the PIPE Investors, were exchanged for shares of ParentCo Common Stock upon consummation of the Business Combination.
The shares issued to the Investors in the PIPE Placement on the Closing Date were issued pursuant to and in accordance with the exemption from registration under the Securities Act, under Section 4(a)(2) and/or Regulation D promulgated under the Securities Act.
Item 16. Exhibits
The following is a list of exhibits filed as a part of this registration statement:
128
(a) Exhibits
129
130
(1) Previously filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-4, as amended (File No. 333-250847)
(2) Previously filed as an exhibit to Roth CH Acquisition I Co.’s Registration Statement on Form S-1, as amended (File No. 333- 236852)
(3) Previously filed as an exhibit to Roth CH Acquisition I Co.’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 16, 2020
+ Refiled with modifications.
* To be filed by amendment.
** Certain portions of the exhibit have been omitted pursuant to Rule 601(b)(10) of Regulation S-K. The omitted information is (i) not material and (ii) would likely cause competitive harm to the registrant if publicly disclosed.
† Schedules have been omitted pursuant to Item 601(a)(5) of Regulation S-K. The registrant hereby undertakes to furnish copies of any of the omitted schedules upon request by the Securities and Exchange Commission.
(b) Financial Statement Schedules
None.
131
Undertakings
The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes:
(1) To file, during any period in which offers or sales are being made, a post effective amendment to this registration statement:
(i) To include any prospectus required by Section 10(a)(3) of the Securities Act of 1933;
(ii) To reflect in the prospectus any facts or events arising after the effective date of the registration statement (or the most recent post-effective amendment thereof) which, individually or in the aggregate, represent a fundamental change in the information set forth in the registration statement. Notwithstanding the foregoing, any increase or decrease in volume of securities offered (if the total dollar value of securities offered would not exceed that which was registered) and any deviation from the low or high end of the estimated maximum offering range may be reflected in the form of prospectus filed with the Commission pursuant to Rule 424(b) if, in the aggregate, the changes in volume and price represent no more than 20 percent change in the maximum aggregate offering price set forth in the ‘‘Calculation of Registration Fee’’ table in the effective registration statement.
(iii) To include any material information with respect to the plan of distribution not previously disclosed in the registration statement or any material change to such information in the registration statement.
(2) That, for the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each such post effective amendment shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof.
(3) To remove from registration by means of a post effective amendment any of the securities being registered which remain unsold at the termination of the offering.
(4) That, for the purpose of determining liability under the Securities Act to any purchaser, each prospectus filed pursuant to Rule 424(b) as part of a registration statement relating to an offering, other than registration statements relying on Rule 430B or other than prospectuses filed in reliance on Rule 430A, shall be deemed to be part of and included in the registration statement as of the date it is first used after effectiveness. Provided, however, that no statement made in a registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement or made in a document incorporated or deemed incorporated by reference into the registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement will, as to a purchaser with a time of contract of sale prior to such first use, supersede or modify any statement that was made in the registration statement or prospectus that was part of the registration statement or made in any such document immediately prior to such date of first use.
(5) That, for the purpose of determining liability of the registrant under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser in the initial distribution of the securities:
The undersigned registrant undertakes that in a primary offering of securities of the undersigned registrant pursuant to this registration statement, regardless of the underwriting method used to sell the securities to the purchaser, if the securities are offered or sold to such purchaser by means of any of the following communications, the undersigned registrant will be a seller to the purchaser and will be considered to offer or sell such securities to such purchaser:
(i) Any preliminary prospectus or prospectus of the undersigned registrant relating to the offering required to be filed pursuant to Rule 424;
(ii) Any free writing prospectus relating to the offering prepared by or on behalf of the undersigned registrant or used or referred to by the undersigned registrant;
(iii) The portion of any other free writing prospectus relating to the offering containing material information about the undersigned registrant or its securities provided by or on behalf of the undersigned registrant; and
(iv) Any other communication that is an offer in the offering made by the undersigned registrant to the purchaser.
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the registrant pursuant to the foregoing provisions, or otherwise, the registrant has been advised that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the registrant in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the registrant will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue.
132
Signatures
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act, the registrant has duly caused this registration statement to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the City of Newport Beach, State of California on November 30, 2020.
| ROTH CH ACQUISITION I CO. PARENT CORP. | |||
| By: | /s/ Byron Roth | ||
| Name: | Byron Roth | ||
| Title: | CEO & Chairman | ||
KNOW ALL PERSONS BY THESE PRESENTS, that each person whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints Byron Roth and Aaron Gurewitz, and each of them, his or her true and lawful attorneys-in-fact and agents, each with full power of substitution and resubstitution, for him or her and in his or her name, place and stead, in any and all capacities, to sign any or all amendments (including post-effective amendments) to this registration statement and any and all related registration statements pursuant to Rule 462(b) of the Securities Act, and to file the same, with all exhibits thereto, and other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorneys-in-fact and agents, or any of them, or their substitute or substitutes, may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act, this registration statement has been signed below by the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
| /s/ Byron Roth | Chairman and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) |
November 30, 2020 | ||
| Byron Roth | ||||
| /s/ Gordon Roth | Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
November 30, 2020 | ||
| Gordon Roth | ||||
| /s/ John Lipman | Chief Operating Officer and Director | November 30, 2020 | ||
| John Lipman | ||||
| /s/ Molly Hemmeter | Director | November 30, 2020 | ||
| Molly Hemmeter | ||||
| /s/ Adam Rothstein | Director | November 30, 2020 | ||
| Adam Rothstein | ||||
| /s/ Daniel M. Friedberg | Director | November 30, 2020 | ||
| Daniel M. Friedberg |
133